Month: May 2022
SECURITY RESEARCHER FINDS NEW WAY TO EXPLOIT CVE-2022-22005, RECENTLY PATCHED DESERIALIZATION BUG IN MICROSOFT SHARPOINT
In early 2022, Microsoft addressed CVE-2022-22005, a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability that used website creation features in SharePoint, releasing a security patch. Even though the flaw had already been fixed, a security researcher found a new way to exploit the deserialization bug by uploading malicious files to the server.
Many languages use serialization and deserialization to pass complex objects to servers and between processes. If the deserialization process is not secure, attackers will be able to exploit it to send malicious objects and execute them on the server. Nguyễn Tiến Giang, a security researcher at StarLabs, found that when servers are configured in a certain way, they are prone to deserialization attacks, which would eventually lead to code execution.
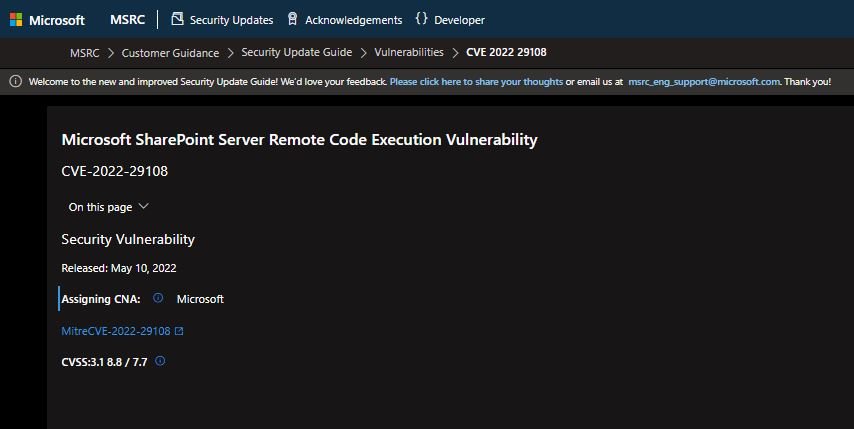
In his blog, the expert explains that hackers can exploit the bug by creating a SharePoint List on the server and loading a string of malicious devices with the deserialization payload as a PNG attachment. By sending a processing request for the uploaded file, the attacker will trigger the error and execute the payload on the affected deployment.
The good news is that the flaw can only be exploited by authenticated threat actors, plus a default disabled setting is required. This variant of the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-29108, was addressed in Microsoft’s May patch.
The expert found the flaw while analyzing CVE-2022-22005, finding that there was another way to trigger the attack: “Actually, this error is very easy to detect. There was a publication about it March; you just have to follow the instructions in that post and people can easily detect the new variant of CVE-2022-22005. It’s like drinking an old wine from a new bottle,” the expert joked.
Finally, the researcher known as hir0ot, who had published a detailed analysis on CVE-2022-22005, mentions that there are two main ways to correct deserialization failures: by limiting the endpoints that deserialize untrusted data, or by using a folder of a type based on a whitelist.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
4 THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE STARTING A TRANSLATION BUSINESS
Are you skilled with languages, and looking to start your own translation business? Globalization means that translators are in greater demand than they have ever been before, and clients are looking for professional translators for a variety of fields and languages. However, language skills on their own aren’t enough if you want to make your new translation business a success, and there’s a lot more you need to know.
If you’re a newcomer to running a business, getting hold of this information may prove a challenge. If that sounds like you, don’t worry – you’re in the right place. Here are 4 things you need to know before starting a translation business.
- Start with Specialization
One of the biggest challenges that translation businesses make when they’re just getting off the ground is that they feel the need to offer services translating every language possible for themselves and their employees. However, rather than creating a sense of confidence, this wide range of services can actually dissuade clients from hiring your business.
The wider your menu of translation options, the greater the chance that you’ll make a mistake. This is especially true for a new business – remember, you’re just getting your feet wet, and your clients will likely take a bit of time to trust you fully. If they feel like you’re overextending yourself, they’ll be less likely to hire your business.
Instead, choose a single language to build your reputation with – preferably one that you, personally, are very familiar with. There are a number of benefits to choosing a specialization, including gaining a mastery of the language you choose to focus on. Expertise in a single language will encourage people to hire your business, allowing you to build up to a point where you can add additional languages to your repertoire.
Furthermore, it’s essential to remember that you will make mistakes, especially as a new business. These mistakes will be most easily rectified when you’re working with a language you’re completely familiar with. You can then use the lessons learned from those mistakes and implement them when expanding your business to additional languages. This will help make further translations more effective and efficient and allow you to have confidence in your team members when they’re working on translations in languages you may not be personally familiar with.
- Make Sure You’re Organised
As a new business owner, you need to meet all the legal requirements of forming a business before you start to advertise yourself. This includes formally setting up a company, with the help of a company formation service or business.
If you haven’t yet gone through this integral process, then you need to make sure you get that squared away immediately so as to avoid any possible legal trouble. Decide on your business’s name, then choose a locally based business that can handle company formation; simply go to website to further understand how you can get your legal documentation completed as soon as possible. Be thoughtful while choosing a name for your business – it should be one that defines and sets aside your brand from others, and should help inspire faith and confidence in your services as well.
When registering your startup, make sure you’re aware of how you’ll be handling taxes for it going forward. Paying taxes for a business is very different from doing so as an employee at someone else’s company or as a freelancer. Knowing what you’re facing can help reduce the risk of you getting in trouble with the authorities.
- Choose Your Marketing Niche
Aside from choosing a language to focus on, you should also choose a marketing niche to concentrate your marketing efforts on.
In the world of language translations, there are three key ways of distinguishing your business from others – quality, speed, and cost. Focusing on each requires different capabilities from a translation business – those that focus on cost often use machine translation and post-editing, while those focusing on quality have a rigorous screening process when choosing translators to hire. Businesses focusing on speed may offer 24/7 support and automation to help guarantee fast turnaround times.
No approach is better than the other. Each has its own pros and cons – and you need to choose which your business will focus on.
Make sure you don’t try to specialize in all three options. This can end in your business being good at translating fast, accurately, and affordably – but you’ll be unable to distinguish yourself in one aspect and truly stand out from the crowd. On the other hand, if you choose one to focus on, you can truly build a stand-out brand. For example, if you choose to focus on speed and emphasize industry-leading turnaround times, clients that need work done quickly will choose your business over competitors that work fast but not fast enough, as they’re also trying to ensure top-notch speed and affordable prices at the same time.
- Hire Linguists with Cultural Knowledge
Excellent translation requires more than just language skills – it also needs cultural knowledge. Translators with cultural knowledge will not only be able to translate certain words and phrases to culture-specific equivalents, but they’ll also be able to advise a client if their work contains a cultural misstep.
People with cultural knowledge are generally people who have grown up in a country or have spent several years there. It’s essential to keep in mind that your translators’ cultural knowledge will not be foolproof, as customs vary from area to area with the same state or country. However, a broad understanding of the target country/group of people will help your business distinguish itself.
This is also why you should start by focusing on a single business. It is easier to look for cultural experts in a single language rather than multiple languages and countries all at once.
Just like any other new business, starting a new translation business can be a demanding challenge. However, with confidence and a well-thought-out plan, you’ll soon find that your translation company is doing better than you have ever imagined – and the tips above will help make your business a roaring success.
RESEARCHERS FIND NEW WAY TO HACK ANY IPHONE EVEN WHEN IT’S TURNED OFF
Cybersecurity experts published a research detailing how Bluetooth, Near Field Communication (NFC) and Ultra-wideband (UWB) wireless features on iPhone devices would allow some variants of cyberattacks to be deployed, as they remain active even when the affected devices are turned off.
These features have access to Secure Element, which stores sensitive device information and remains active on the latest iPhone models even with the phone turned off. According to specialists at the Technical University of Darmstadt, Germany, this would allow malware to be loaded onto a Bluetooth chip running on an inactive device.
The compromise of these features would allow threat actors to access protected information, including payment card details, banking information and other sensitive data. While this risk is considered real and active, the researchers acknowledge that exploiting these flaws is complex, as hackers would require loading malware onto a target iPhone when it’s turned on, which mandatory requires a remote code execution (RCE) tool.

According to the report, the bug exists because of the way Low Power Mode (LPM) is implemented on Apple’s wireless chips: “The LPM setting is triggered when the user turns off their phone or when the iOS system automatically shuts down due to lack of battery.”
Experts believe that, in addition to its obvious advantages, the current implementation of LPM created new attack vectors. LPM support is based on iPhone hardware, so bugs like this can’t be fixed with software updates.
One attack scenario, tested by the researchers, describes how the smartphone’s firmware would allow attackers to have system-level access for remote code execution using a known Bluetooth vulnerability, such as the popular Braktooth flaw. The research was shared with Apple before its publication. Although the company did not comment on it, experts proposed that Apple add a hardware-based switch to disconnect the battery, preventing functions related to the error from receiving power with the device turned off.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
MORE THAN 200 APPS ON PLAY STORE WITH MILLIONS OF DOWNLOADS ARE STEALING USERS’ PASSWORDS AND SENSITIVE INFORMATION
Researchers at Trend Micro identified a set of mobile apps available on the Google Play Store performing malicious tasks in the background, including stealing user credentials and banking details from Android users. Some of these apps have nearly 100,000 downloads, so the scope of the problem is considerable.
In total, the analysis revealed the detection of 200 malicious applications that hide code from dangerous malware variants, capable of putting users of the affected devices in serious trouble.
SIMPLE TOOLS, COMPLEX ISSUES
One of the main threats identified is Facestealer, a spyware variant capable of stealing Facebook access credentials, allowing subsequent phishing campaigns, social engineering, and invasive advertising. Facestealer is constantly updated and there are multiple versions, making it easy for them to get into the Play Store.
Daily Fitness OL is described as a fitness tool, offering exercise routines and demonstration videos. Although there doesn’t seem to be anything wrong with this app, an in-depth analysis shows that the app’s code hides a load of The Facestealer spyware.

When a user opens this app, a request is sent to hxxps://sufen168.space/config to download their encrypted settings. This setting sends the user a message requesting to log in to Facebook, after which the app launches a WebView to load a malicious URL. Subsequently, a snippet of JavaScript code is injected into the loaded website, allowing the theft of the user’s credentials.
Once the user logs into their Facebook account, the app collects the cookies and the spyware encrypts the collected information to send it to a remote server.
Other malicious apps, such as Enjoy Photo Editor or Panorama Camera, also hide Facestealer loads and have a very similar attack process, although they may vary in some stages or methods.
RISK FOR CRYPTO INVESTORS
Experts have also identified more than 40 fraudulent cryptocurrency apps disguised as legitimate tools, even taking their image or using similar names. The developers of these tools seek to get affected users to buy supposed Premium versions at high costs with fake ads.
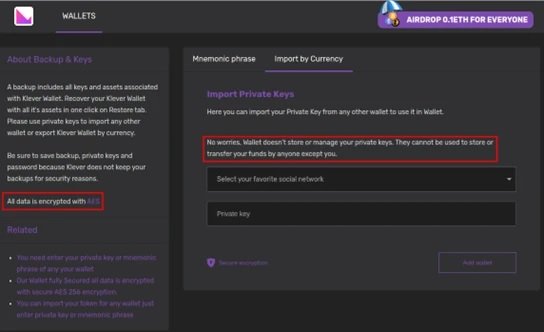
Tools like “Cryptomining Farm Your Own Coin” do not demonstrate invasive behaviors even in test environments, so they effectively evade security mechanisms in the Play Store. However, when trying to connect a Bitcoin wallet to this application, a message appears asking the user to enter their private keys, a clear red flag alerting that something’s wrong.
A sample of the code was developed using Kodular, a free online suite for mobile app development. Trend Micro notes that most fake cryptocurrency apps use the same framework.
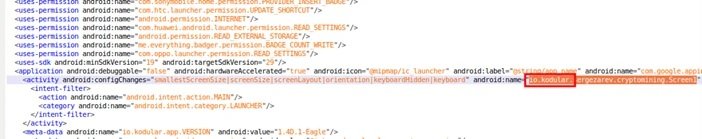
The analyzed app only loads a website and does not even have capabilities to simulate mining processes or cryptocurrency transactions.
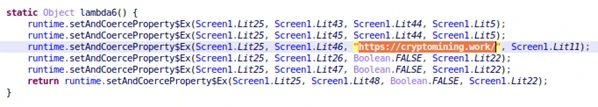
The uploaded website mentions users who can participate in a cloud mining project in order to lure them to the true start of the attack. Next, threat actors ask users to link a digital wallet to this website, in an attempt to collect private keys, which are further processed with no encryption at all.
Although the malicious applications were reported to Google and have already been removed from the official store, the researchers believe that the company must considerably improve security measures in the Play Store, as many developers of malicious applications continue to find methods to evade the security of the app repository, putting millions of users at risk.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CRITICAL VULNERABILITY IN BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY (BLE) ALLOWS EASILY HACKING TESLA CARS, SMART LOCKS AND MILLIONS OF DEVICES THAT USE THIS BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY
Specialists from the security firm NCC Group developed a tool capable of deploying relay attacks against Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), which would allow bypassing any existing protection in the target system, authenticating without any problem. This technology is used in all kinds of products, including smartphones, laptops, access control systems, and even in Tesla Model 3 and Model Y cars.
In relay attacks, threat actors begin by intercepting and manipulating communications between two parties, such as a keyless car and the device that opens its doors. Attackers must place themselves in the middle of both ends of communication, transmitting a malicious signal to impersonate the legitimate user.
Technology devices that use BLE for authentication have security measures against relay attacks by default, most based on latency and link-layer encryption. The tool developed by the researchers operates at the link layer and has a latency of 8ms, within the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) response range.
Thanks to its features, the tool can forward encrypted link layer PDUs, in addition to detecting encrypted changes in connection parameters to continue relaying connections through parameter changes. That is why BLE protections do not work against this attack.
Experts at NCC Group mention that it takes around 10 seconds to complete an attack on any of the affected systems, including Tesla Model 3 and Model Y cars, as they use a BLE-based input system.
While the technical details behind this new attack have not been released, researchers reported testing this tool on a 2020 Tesla Model 3, via an iPhone 13 mini with version 4.6.1-891 of the Tesla app. The attack was also successfully replicated in a Tesla Model Y 2021 model, as they employ similar technologies.
The researchers mention that it is complicated to implement solutions for this security problem due to the features of BLE. In addition, even if industry members responded immediately and in a coordinated manner, updates could take months to arrive for all affected users.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
HACKERS REMOTELY TAKE CONTROL OF WHEELED SURVEILLANCE ROBOTS AT RUSSIAN AIRPORT
A cybercriminal group claims to have compromised the systems of a robotics company specializing in surveillance solutions around the world. Identified as CaucasNet, the group shared via Twitter some screenshots of an allegedly compromised web portal, used as a control panel for surveillance robot vehicles at Sheremetyevo International Airport in Russia.
These Tral Patrol 4.0 devices, unmanned vehicles for ground surveillance, are designed for outdoor patrol due to their intelligent video surveillance system, which automatically scans the areas predetermined by their administrators. Affected devices are developed by SPM Robotics.
An alleged member of CaucasNet was interviewed by Daily Dot, claiming that hackers detected a critical vulnerability in the online administration panel to control these devices, which allowed them to take control of this technology.
The post includes a video that appears to prove the hackers’ claims. In this footage, you could see how the Tral Patrol devices were controlled by an unknown actor while the Ukrainian national anthem was played in the background.
The footage suggests that the attackers used one of the robots to communicate with an unknown English-speaking actor. Due to the appearance of the Ukrainian anthem, and the location of the incident, investigators believe that this could be a type of protest against the Russian military invasion into Ukrainian territory.
Representatives at Sheremetyevo International Airport declined to confirm or deny whether any of its robots had been compromised. SMP Robotics has also not issued any statements on the matter.
Cyberattacks against critical infrastructure in Russia have been a constant in the context of the invasion of Ukraine; A few weeks ago, a hacking group allegedly linked to Anonymous gained access to dozens of CCTV systems, sharing a message against the Russian president: “Putin is killing children,” the compromised monitors read.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CRITICAL VULNERABILITY IN FLUX2, A KUBERNETES CONTINUOUS DELIVERY TOOL, ENABLES HACKING BETWEEN NEIGHBORING DEPLOYMENTS
A recently detected vulnerability affecting Flux, a popular continuous delivery (CD) tool for Kubernetes, would reportedly allow tenants to sabotage the activities of “neighbors” who use the same infrastructure outside of their own facilities.
Flux is an open and extensible CD solution to keep Kubernetes clusters in sync with configuration sources, and is used by firms across all industries, including Maersk, SAP, Volvo, and Grafana Labs, among many others. In its most recent version (Flux2), multi-tenant support was introduced, among other features.
The vulnerability was described as a remote code execution (RCE) error that exists due to improper validation of kubeconfig files, which define commands that will be executed to generate on-demand authentication tokens: “Flux2 can reconcile the state of a remote cluster when a kubeconfig file exists with the correct access rights,” points a report posted on GitHub.
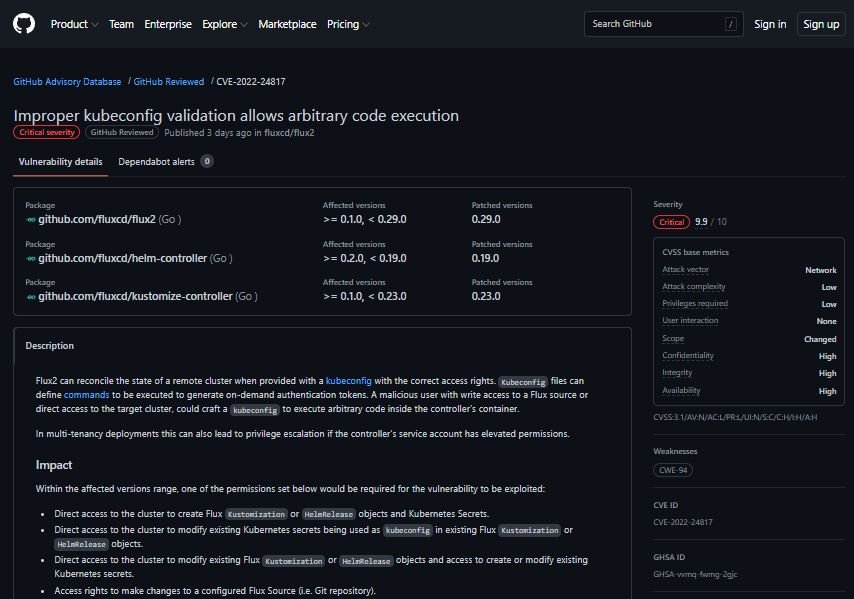
Paulo Gomes, a software engineer who collaborates at the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), which originated GitOps and provides support for Flux and Kubernetes, mentions: “The tool can synchronize the declared state defined in a Git repository with the cluster in which it is installed, which is the most commonly used approach, or it can target a remote group.”
Gomes adds that the access required to target remote clusters depends largely on the intended scope. This is completely flexible and is based on the fact that Kubernetes RBAC has a wide range of granularity. This behavior allows a malicious user with write access to a Flux source or direct access to the target cluster to create a specially crafted kubeconfig file to execute arbitrary code in the controller container.
When analyzed according to version 2 of the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), this vulnerability was considered of medium severity and received a score of 6.8/10, because in single-tenant deployments, the error is less dangerous and the attackers obtain almost the same privileges required for exploitation.
However, the flaw receives a score of 9.9/10 according to CVSS v3.1, as this release includes a metric around ‘scope’ changes, which means that the flaw can affect resources beyond the security scope managed by the developers of the vulnerable component.
The flaw has already been addressed by the creators of the tool, so users of affected deployments are advised to upgrade as soon as possible.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
HACKERS STEAL $1 MILLION USD FROM RAZORPAY
Media outlets in India report that an unidentified hacker managed to steal around $1 million from Razorpay, a payment processing company. Apparently, the attacker remained hidden in the company’s systems for three months, manipulating security mechanisms to authenticate over 800 illegitimate transactions.
Razorpay Software Private Limited provides online payment services that allow businesses in India to collect payments via credit card, debit card, net banking, and even cryptocurrency wallets.
The malicious activity was detected when a team at Razorpay Software Private Limited was auditing the transactions. Company employees were unable to reconcile transaction files with funds in enterprise accounts.
Abhishek Abhinav Anand, in charge of legal disputes and legislative compliance at Razorpay, filed a complaint with the southeast Indian cybercrime unit earlier this week.
Authorities are trying to identify the hacker or hacker group responsible for the attack, based on recorded online transactions. Meanwhile, Razorpay also ordered an internal investigation, revealing that the attacker compromised and manipulated the transaction authorization process to complete the attack; as a result, threat actor approved a total of 831 failed transactions, which mean losses around $1 million.
Razorpay shared with law enforcement detailed information about these 831 illegitimate transactions, including date, time and IP address.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
HOW TO DOWNLOAD PAID APPLICATIONS FOR FREE FROM HUAWEI APPGALLERY: NEW VULNERABILITY FOUND
Since then-U.S. President Donald Trump signed an executive order to apply restrictions on Chinese technology companies, Huawei has seen its aspirations to become one of the world’s largest smartphone makers cut short. Still, millions of people still use Huawei phones, which facing with the impossibility of using the Google Play Store, include a set of services instead.
The main attraction of these services is Huawei AppGallery, the company’s own app store that works essentially in the same way as the Play Store. Specialist Dylan Roussel has investigated the operation of the Huawei app, discovering an API that takes the name of a package as a parameter and returns a JSON object with the details of the application. This finding aroused Roussel’s curiosity, so he decided to continue investigating until he knew what else he could find.
For his tests, the researcher tested the API with the app package name AppGallery:
| 123456789101112131415161718192021222324 | { "app": { ... "name": "AppGallery", "openCount": 0, "openCountDesc": "", "openurl": "", "permissions": [], "pkgName": "com.huawei.appmarket", "price": "0", "productId": "", "rateNum": "0", "recommImg": "", "releaseDate": "2022-04-20 17:03:53", "sha256": "2e1a1ce4e86cbfc87f05411a2585e557af78b893f6be85f8f6cb93f889faee05", "size": "50347219", "tagName": "", "updateDesc": "", "url": "https://appdlc-dre.hispace.dbankcloud.com/dl/appdl/application/apk/40/4037feaa91cf453ca2dd1ebf444aedaa/com.huawei.appmarket.2204201539.apk?sign=mw@mw1651866832368&maple=0&distOpEntity=HWSW", "version": "12.1.1.302", "versionCode": 120101302 }, ...} |
The API returns various details, including some IDs, app version, logos and other images, descriptions, system permissions, and pricing. In addition, the API also returns a URL to the app in AppGallery, from where it is possible to download the app.
After trying this search on a free app, it was time to try a paid app. Roussel used the package name of a paid app, also getting the download link with the same type of sign parameter at the end; at the conclusion of the test, the researcher was able to download the application and use it normally.
The researcher decided to continue with his tests to prove that this was not just a mistake. By using the package names of two apps and a mobile game, Russel was able to download and use these tools; It is worth mentioning that the game had a license check, which could not prevent the researcher from using the game without paying.
For Roussel, it is hard to believe that AppGallery is affected by such a simple error, considering that in repository stores the work of dozens of developers who seek profit through this medium.
The good news is that Huawei is already aware of this bug, although it will take a few more days to complete a functional solution. Everything is expected to be fixed by May 25.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
INDIA RELAXES CYBER SECURITY INCIDENTS REPORTING RULES AND SAYS NEW RULES APPLY TO MNCS
Cybersecurity agencies in India are slightly relaxing their controversial and complex requirements for reporting on information security incidents, although they reaffirm that the final version of these rules should apply to any multinational company operating on their territory.
These rules were announced overnight in late April, receiving criticism from major players in the industry because system administrators were required to report 22 types of cybersecurity incidents just six hours after their detection, in addition to establishing as a requirement the registration of VPN users and other controversial measures.
The Government of India published an FAQ document related to these new rules and specifying that improvements and revisions will continue to apply. For example, India has clarified that minor security incidents, such as social media account takeover, will not have to be reported within six hours; on the other hand, only the most severe incidents, capable of disrupting operations in the affected organization, will have to be reported within this period.
Authorities also reversed the restriction of using only a couple of Indian Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers, specifying that the use of other NTP servers synchronized with local operators is also allowed.
The document also more clearly lists the requirements for entities that can operate in India without having a physical presence in the nation. As it reads, these companies must designate a point of contact to communicate with CERT-India, which administers the new rules. Non-Indian organizations can store certain data abroad, but must make it available to the CERT-In.
Indian officials avoided making any mention of the criticism the first version of this project received. The FAQ does not address objections to measures such as VPN user retention, in addition to frequently referencing that some of these measures were implemented for national security purposes, making it difficult to change specific aspects.
This document also does not offer any explanation as to how CERT-In will use the documents it collects to analyze security incidents, a matter of interest as organizations can submit reports in formats such as PDFs or faxes that do not lend themselves to automated ingestion or analysis.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
INVESTIGADOR DE SEGURIDAD ENCUENTRA NUEVA FORMA DE EXPLOTAR CVE-2022-22005, ERROR DE DESERIALIZACIÓN EN MICROSOFT SHARPOINT ABORDADO RECIENTEMENTE
A inicios de 2022, Microsoft abordó CVE-2022-22005, una vulnerabilidad de ejecución remota de código (RCE) que utilizaba las funciones de creación de sitios web en SharePoint, lanzando un parche de seguridad. A pesar de que la falla ya había sido corregida, un investigador de seguridad encontró una nueva forma de explotar el error de deserialización mediante la carga de archivos maliciosos en el servidor.
Muchos lenguajes usan serialización y deserialización para pasar objetos complejos a servidores y entre procesos. Si el proceso de deserialización no es seguro, los atacantes podrán explotarlo para enviar objetos maliciosos y ejecutarlos en el servidor. Nguyễn Tiến Giang, investigador de seguridad de StarLabs, descubrió que cuando los servidores se configuran en cierta forma, son propensos a los ataques de deserialización, que eventualmente llevarían a la ejecución de código.

En su blog, el experto explica que los hackers pueden explotar el error creando una SharePoint List en el servidor y cargando una cadena de dispositivos maliciosos con la carga útil de deserialización como un archivo adjunto PNG. Al enviar una solicitud de procesamiento para el archivo cargado, el atacante activará el error y ejecutará la carga útil en la implementación afectada.
La buena noticia es que la falla solo puede ser explotada por actores de amenazas autenticados, además de que se requiere una configuración desactivada por defecto. Esta variante de la vulnerabilidad, identificada como CVE-2022-29108, fue abordada en el parche de Microsoft para mayo.
El experto encontró la falla mientras analizaba CVE-2022-22005, descubriendo que había otra forma de desencadenar el ataque: “En realidad, este error es muy fácil de detectar. Hubo una publicación al respecto marzo; simplemente hay que seguir las instrucciones en esa publicación y las personas pueden detectar fácilmente la nueva variante de CVE-2022-22005. Es como beber un vino viejo de una botella nueva”, bromeó el experto.
Finalmente, el investigador conocido como hir0ot, quien había publicado un análisis detallado sobre CVE-2022-22005, menciona que hay dos formas principales de corregir las fallas de deserialización: limitando los endpoints que deserializan los datos no confiados, o bien usar una carpeta de tipo basada en una lista blanca.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
INVESTIGADORES ENCUENTRAN UNA NUEVA FORMA DE HACKEAR DISPOSITIVOS IPHONE INCLUSO CUANDO ESTÁN APAGADOS
Expertos en ciberseguridad publicaron una investigación detallando cómo las funciones inalámbricas Bluetooth, Near Field Communication (NFC) y las tecnologías de banda ultraancha (UWB) en los dispositivos iPhone permitirían desplegar algunas variantes de ciberataques, ya que permanecen activas incluso cuando los dispositivos afectados están apagados.
Estas características tienen acceso a Secure Element, que almacena información confidencial del dispositivo y permanece activa en los modelos más recientes de iPhone incluso con el teléfono apagado. Acorde a los especialistas de la Universidad Técnica de Darmstadt, Alemania, esto permitiría cargar malware en un chip Bluetooth ejecutado en un dispositivo inactivo.
El compromiso de estas funciones permitiría a los actores de amenazas acceder a información protegida, incluyendo detalles de tarjetas de pago, información bancaria y otros detalles. Si bien este riesgo es considerado real y activo, los investigadores reconocen que la explotación de estas fallas es compleja, pues los hackers requerirían cargar malware en un iPhone objetivo cuando está encendido, para lo cual es necesaria una herramienta de ejecución remota de código (RCE).

Según el reporte, el error existe debido a la forma en que se implementa el modo de bajo consumo (LPM) en los chips inalámbricos de Apple: “La configuración LPM se activa cuando el usuario apaga su teléfono o cuando el sistema iOS se apaga automáticamente debido a la falta de batería”.
Los expertos consideran que, además de sus obvias ventajas, la implementación actual de LPM creó nuevos vectores de ataque. La compatibilidad con LPM se basa en el hardware del iPhone, por lo que errores como este no pueden ser corregidos con actualizaciones de software.
En un escenario de ataque, probado por los investigadores, se describe cómo el firmware del smartphone permitiría que los atacantes tuvieran acceso a nivel sistema para la ejecución remota de código empleando una vulnerabilidad Bluetooth conocida, como la popular Braktooth. La investigación fue compartida con Apple antes de su publicación. Aunque la compañía no comentó al respecto, los expertos propusieron que Apple agregue un interruptor basado en hardware para desconectar la batería, impidiendo que las funciones relacionadas con el error reciban energía con el dispositivo apagado.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
MÁS DE 200 APLICACIONES EN PLAY STORE CON MILLONES DE DESCARGAS ESTÁN ROBANDO INFORMACIÓN Y CONTRASEÑAS CONFIDENCIALES DE LOS USUARIOS
Investigadores de Trend Micro identificaron un conjunto de aplicaciones móviles disponibles en Google Play Store realizando tareas maliciosas en segundo plano, incluyendo el robo de credenciales de usuario y detalles bancarios de usuarios de Android. Algunas de estas aplicaciones tienen casi 100,000 descargas, por lo que el alcance del problema es considerable.
En total, el análisis reveló la detección de 200 aplicaciones maliciosas que ocultan código de peligrosas variantes de malware, capaces de poner en serios aprietos a los usuarios de los dispositivos afectados.
HERRAMIENTAS SIMPLES, PROBLEMAS COMPLEJOS
Una de las principales amenazas identificadas es Facestealer, una variante de spyware capaz de robar credenciales de acceso a Facebook, permitiendo posteriores campañas de phishing, ingeniería social y publicidad invasiva. Facestealer es actualizado constantemente y existen múltiples versiones, lo que facilita su entrada a Play Store.
Daily Fitness OL se describe como una herramienta fitness, ofreciendo rutinas de ejercicio y videos demostrativos. Aunque no parece haber nada malo con esta aplicación, un análisis a profundidad demuestra que el código de la app oculta una carga del spyware Facestealer.

Cuando un usuario abre esta aplicación, se envía una solicitud a hxxps://sufen168.space/config para descargar su configuración cifrada. Esta configuración envía al usuario un mensaje solicitando iniciar sesión en Facebook, después de lo cual la aplicación inicia un WebView para cargar una URL maliciosa. Posteriormente, se inyecta un fragmento de código JavaScript en el sitio web cargado, lo que permite el robo de las credenciales del usuario.
Una vez que el usuario ingresa en su cuenta de Facebook, la aplicación recopila las cookies y el spyware cifra la información recolectada para enviarla a un servidor remoto.

Otras apps maliciosas, como Enjoy Photo Editor o Panorama Camera, también ocultan cargas de Facestealer y cuentan con un proceso de ataque muy similar, aunque pueden variar en algunas etapas o métodos.

RIESGO PARA INVERSORES DE CRIPTOMONEDA
Los expertos también identificaron más de 40 apps fraudulentas de criptomoneda haciéndose pasar por herramientas legítimas, incluso tomando su imagen o usando nombres similares. Los desarrolladores de estas herramientas buscan que los usuarios afectados compren supuestas versiones Premium a altos costos con anuncios falsos.
Herramientas como “Cryptomining Farm Your Own Coin” no demuestran conductas invasivas incluso en entornos de prueba, por lo que evaden eficazmente los mecanismos de seguridad en Play Store. No obstante, al tratar de conectar una billetera Bitcoin a esta aplicación, aparece un mensaje solicitando al usuario ingresar su calve privada, una clara alerta de que algo está mal.

Una muestra del código fue desarrollada utilizando Kodular, una suite en línea gratuita para el desarrollo de aplicaciones móviles. Trend Micro señala que la mayoría de las apps falsas de criptomoneda utilizan el mismo marco de trabajo.

La aplicación analizada solo carga un sitio web y ni siquiera cuenta con capacidades para simular procesos de minado o transacciones de criptomoneda.

En el sitio web cargado se menciona a los usuarios que pueden participar en un proyecto de minado en la nube con el fin de atraerlos al verdadero inicio del ataque. A continuación, los actores de amenazas piden a los usuarios vincular una billetera digital a este sitio web, en un intento de recolectar claves privadas, lo que además se procesa sin cifrado alguno.

Si bien las aplicaciones maliciosas fueron reportadas a Google y ya han sido eliminadas de la tienda oficial, los investigadores consideran que la compañía debe mejorar considerablemente las medidas de seguridad en Play Store, pues muchos desarrolladores de aplicaciones maliciosas siguen encontrando métodos para evadir la seguridad del repositorio de apps, poniendo en riesgo amillones de usuarios.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
APPLE LANZA ACTUALIZACIÓN DE EMERGENCIA PARA ABORDAR VULNERABILIDAD DÍA CERO EN DISPOSITIVOS MAC Y APPLE WATCH
Apple anunció el lanzamiento de actualizaciones para abordar una vulnerabilidad día cero que los actores de amenazas podrían explotar en ataques contra dispositivos Mac y Apple Watch. Como recordará, una falla día cero es un error de seguridad que los proveedores de software desconocen y aún han sido abordados; en casos específicos, pueden divulgarse exploits para vulnerabilidades antes de que sea emitido un parche.
En la alerta de seguridad publicada este lunes, se identifica la falla como CVE-2022-22675, descrita como un error de escritura fuera de límites en AppleAVD, un kernel de extensión para decodificar audio y video. Apple confirmó que la falla podría haber sido explotada activamente para la ejecución de código con privilegios de kernel.
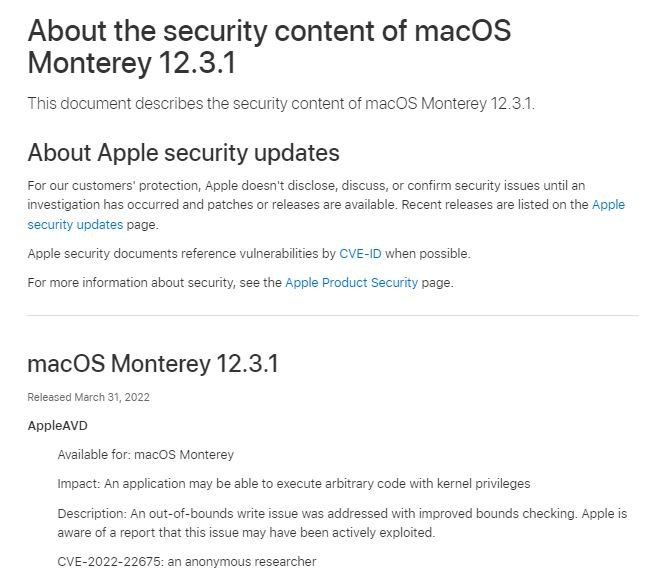
La vulnerabilidad fue reportada reside en dispositivos Apple Watch Series 3 y posteriores, Mac con macOS Big Sur, Apple TV 4K, Apple TV 4K de segunda generación, y Apple TV HD. Este problema fue abordado en macOS Big Sur 11.6., watchOS 8.6 y tvOS 15.5.
Apple no agregó más detalles sobre los intentos de explotación detectados hasta el momento, aparentemente como un intento de hacer llegar las actualizaciones al mayor número posible de usuarios antes de que se divulguen los detalles del ataque. Aunque especialistas en ciberseguridad creen que esta falla podría haber sido explotada solo en ataques dirigidos, se recomienda encarecidamente a los usuarios aplicar los parches de seguridad correspondientes.
Las fallas día cero se han convertido en un problema recurrente para Apple. En enero, la compañía abordó dos errores día cero que habrían permitido a los actores de amenazas ejecutar código arbitrario con privilegios de kernel y realizar actividades de seguimiento web en tiempo real.
Hace un par de meses, Apple abordó dos fallas día cero más, reconociendo que se habían detectado casos de explotación activa en dispositivos con sistemas macOS, watchOS 8.6 y tvOS 15.5.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VULNERABILIDAD CRÍTICA EN BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY (BLE) PERMITE HACKEAR FÁCILMENTE AUTOS TESLA, CERRADURAS INTELIGENTES Y MILLONES DE DISPOSITIVOS QUE UTILIZAN ESTA TECNOLOGÍA BLUETOOTH
Especialistas de la firma de seguridad NCC Group desarrollaron una herramienta capaz de desplegar ataques de relay contra Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), lo que permitiría evadir cualquier protección existente en el sistema objetivo, autenticándose sin problema alguno. Esta tecnología se usa en toda clase de productos, incluyendo smartphones, laptops, sistemas de control de acceso e incluso en autos Tesla Model 3 y Model Y.
En los ataques de relay, los actores de amenazas comienzan interceptando y manipulando las comunicaciones entre dos partes, como un auto sin llave y el dispositivo que abre sus puertas. Los atacantes deben colocarse en el medio de los dos extremos de la comunicación, transmitiendo una señal maliciosa para suplantar al usuario legítimo.
Los dispositivos tecnológicos que usan BLE para autenticación cuentan con medidas de seguridad contra ataques de relay por defecto, la mayoría basados en latencia y cifrado de capa de enlace. La herramienta desarrollada por los investigadores opera en la capa de enlace y cuenta con una latencia de 8ms, dentro del rango de respuesta Generic Attribute Profile (GATT).
Gracias a sus características, la herramienta puede reenviar PDUs de capa de enlace cifradas, además de detectar cambios encriptados en los parámetros de conexión para continuar retransmitiendo conexiones a través de cambios de parámetros. Es por ello que las protecciones BLE no funcionan contra este ataque.
Los expertos de NCC Group mencionan que toma alrededor de 10 segundos completar un ataque en cualquiera de los sistemas afectados, incluso en los autos Tesla Model 3 y Model Y, ya que usan un sistema de entrada basado en BLE.
Si bien no se han publicado los detalles técnicos detrás de este nuevo ataque, los investigadores reportaron haber probado esta herramienta en un Tesla Model 3 de 2020, a través de un iPhone 13 mini con la versión 4.6.1-891 de la aplicación Tesla. El ataque también fue replicado exitosamente en un modelo Tesla Model Y 2021, pues emplean tecnologías similares.
Los investigadores mencionan que es complicado implementar soluciones para este problema de seguridad debido a las características de BLE. Además, incluso si los miembros de la industria respondieran de forma inmediata y coordinada, las actualizaciones podrían demorar meses en llegar para todos los usuarios afectados.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
EL HACKER QUE SE INFILTRÓ EN LOS SISTEMAS DE LA NASA PARA ENCONTRAR PRUEBAS DE OVNIS
Un hacker asegura haber irrumpido en los sistemas informáticos de la NASA en busca de informes, fotos y pruebas sobre el fenómeno OVNI, descubriendo una imagen mostrando lo que él describe como una nave extraterrestre. Gary McKinnon, ciudadano británico experto en informática, fue acusado de comprometer casi un centenar de computadoras pertenecientes al gobierno de E.U.
Los fiscales en E.U. querían una sentencia de hasta 60 años para McKinnon, aunque Reino Unido ha bloqueado su extradición, no sin una correspondiente batalla legal que ya ha alcanzado los 10 años. El investigador simplemente argumenta que no hizo daño a nadie y sólo buscaba evidencia de ovnis ocultos por las autoridades estadounidenses.

En entrevista para The Sun, McKinnon asegura haber encontrado cosas insólitas durante su intrusión: “Es un hecho que en el cielo hay objetos que no entendemos, también es un hecho que hay científicos y departamentos militares y de inteligencia que estudian esos objetos”.
También conocido como “Solo” en el mundo del hacking, el investigador describe una de las fotos que más le sorprendieron: una nave no fabricada por el hombre (según su perspectiva), de forma alargada y parecida a un cigarrillo, capturada en imagen por un satélite. Poco después de ver esta imagen, McKinnon reporta haber perdido su conexión a los sistemas comprometidos, por lo que no pudo ver otras carpetas: “Estaba absolutamente atónito; esas carpetas tenían miles de imágenes más”, asegura.
El investigador también mencionó que su interés comenzó luego de escuchar el testimonio de Donna Hare, ex empleada de la agencia espacial que aseguraba que las imágenes satelitales con frecuencia son editadas por el personal del Centro Espacial Johnson para eliminar evidencia de ovnis.
Su curiosidad lo ha llevado a vivir un infierno legal, pues fue arrestado un par de veces entre 2002 y 2005 a solicitud de E.U. Aunque Reino Unido aprobó su extradición en 2006, McKinnon nunca desistió, apelando cada nueva decisión de la justicia británica hasta que en 2012 la entonces ministra del interior Theresa May bloqueó su extradición. McKinnon padece del síndrome de Asperger, elemento en el que sus abogados fundamentaron su defensa.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VULNERABILIDAD CRÍTICA EN FLUX2, UNA HERRAMIENTA DE ENTREGA CONTINUA DE KUBERNETES, PERMITE EL HACKING ENTRE IMPLEMENTACIONES VECINAS
Se ha detectado una vulnerabilidad en Flux, una popular herramienta de entrega continua (CD) para Kubernetes. Según se ha reportado, la explotación exitosa de la falla permitiría a los inquilinos saboteen las actividades de los “vecinos” que usan la misma infraestructura fuera de sus propias instalaciones.
Flux es una solución de CD abierta y extensible para mantener los clústeres de Kubernetes sincronizados con las fuentes de configuración, y es empleada por firmas de todos los ramos, incluyendo a Maersk, SAP, Volvo y Grafana Labs, entre muchas otras. En su más reciente versión (Flux2), se introdujo la compatibilidad con múltiples inquilinos, entre otras funciones.
La vulnerabilidad fue descrita como un error de ejecución remota de código (RCE) que existe debido a la validación incorrecta de los archivos kubeconfig, que definen comandos que se ejecutarán para generar tokens de autenticación bajo demanda: “Flux2 puede reconciliar el estado de un clúster remoto cuando existe un archivo kubeconfig con los derechos de acceso correctos”, señala un reporte publicado en GitHub.

Paulo Gomes, ingeniero de software que colabora en Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), que originó GitOps y brinda soporte para Flux y Kubernetes, menciona: “La herramienta puede sincronizar el estado declarado definido en un repositorio de Git con el clúster en el que se instala, que es el enfoque más utilizado, o bien puede apuntar a un grupo remoto”.
Gomes agrega que el acceso requerido para apuntar a clústeres remotos depende en gran medida del alcance previsto. Esto es completamente flexible y se basa en que el RBAC de Kubernetes tiene una amplia gama de granularidad. Esta conducta permite que un usuario malicioso con acceso de escritura a una fuente de Flux o acceso directo al clúster objetivo cree un archivo kubeconfig especialmente diseñado para ejecutar código arbitrario en el contenedor del controlador.
Al ser analizada acorde a la versión 2 del Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), esta vulnerabilidad fue considerada de severidad media y recibió una puntuación de 6.8/10, pues en implementaciones de un solo inquilino, el error es menos peligroso y los atacantes obtienen casi los mismos privilegios requeridos para la explotación.
No obstante, la falla recibe una puntuación de 9.9/10 según CVSS v3.1, pues esta versión incluye una métrica en torno a los cambios de ‘alcance’, lo que significa que la falla puede afectar a los recursos más allá del ámbito de seguridad gestionado por los desarrolladores del componente vulnerable.
La falla ya ha sido abordada por los creadores de la herramienta, por lo que se recomienda a los usuarios de implementaciones afectadas actualizar a la brevedad.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
AGENCIAS DE INVESTIGACIÓN EN ESPAÑA DESMANTELAN OPERACIÓN DE PHISHING QUE COMETIÓ FRAUDE POR CIENTOS DE MILES DE DÓLARES
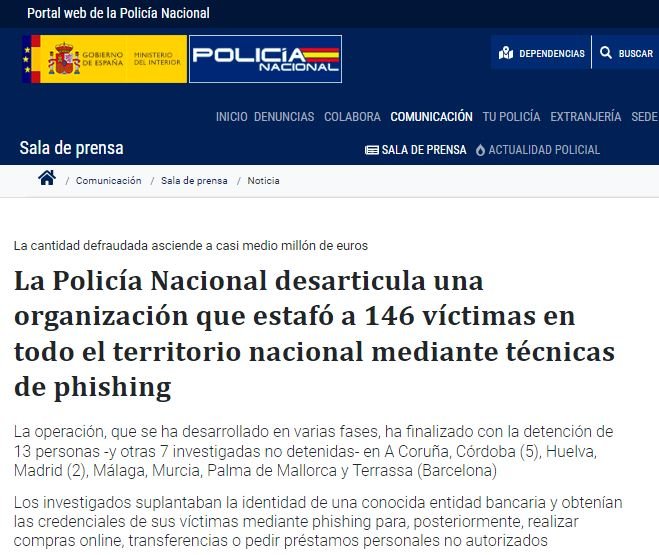
La Policía Nacional de España anunció el arresto de 13 individuos acusados de participar en un esquema de phishing con el que buscaban robar credenciales de acceso a cuentas bancarias en línea. La policía también inició una investigación sobre siete personas más.
Según se ha reportado, los cibercriminales enviaban falsas alertas de seguridad a los usuarios afectados con el fin de interceptar sus credenciales de acceso. Una vez que accedían a las cuentas comprometidas, los atacantes realizaban compras en línea y transferencias a cómplices actuando como mulas.
Hasta el momento se han identificado a 146 víctimas de fraude electrónico, que sufrieron pérdidas por un total de $466,000 USD: “La operación, desarrollada en varias fases entre enero y abril de 2019, fue interrumpida con la detención de 13 personas – otras siete están siendo investigadas pero no fueron detenidas”, menciona el comunicado de la policía.
Las investigaciones comenzaron después de que algunas personas reportaran cargos no reconocidos en sus estados bancarios, muchos de estos rastreados en tiendas de electrónica en Francia, Alemania, Estados Unidos y Marruecos. Al indagar en el caso, los investigadores descubrieron que los actores de amenazas siempre estuvieron en España y solo estaban usando soluciones VPN para hacer parecer que las transacciones habían sido realizadas desde dichos países.
Sobre el esquema de phishing, la Policía Nacional menciona que los atacantes enviaban a los usuarios falsos mensajes bancarios, los cuales incluían un enlace a un sitio web fraudulento que aparentaba ser una plataforma bancaria oficial. Una vez en este sitio web, se pedía a los usuarios ingresar sus credenciales de inicio de sesión, que eran enviadas a un servidor controlado por los hackers.
Este ataque permitió a los criminales acceder a la información bancaria de las víctimas, además de obtener sus Claves de Comercio Electrónico Seguro, requeridas para realizar operaciones en línea.
El dinero robado era transferido a través de una red de mulas de dinero, la mayoría forzadas a participar en el esquema fraudulento, para finalmente ser enviado a cuentas bancarias en Costa de Marfil, de modo similar a una operación desmantelada por la Policía Nacional a finales de 2021, en la que los actores de amenazas transferían el dinero robado a Benín.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
CÓMO DESCARGAR GRATIS APLICACIONES DE PAGA DESDE HUAWEI APPGALLERY. NUEVA VULNERABILIDAD ENCONTRADA
Desde que el entonces presidente de E.U., Donald Trump, firmara una orden ejecutiva para aplicar restricciones a las compañías tecnologías chinas, Huawei vio cortadas sus aspiraciones de convertirse en uno de los fabricantes de smartphones más grandes del mundo. Aún así, millones de personas siguen usando teléfonos Huawei, que ante la imposibilidad de usar Google Play Store, incluyen un conjunto de servicios en su lugar.
El principal atractivo de estos servicios es Huawei AppGallery, la propia tienda de aplicaciones de la compañía que funciona esencialmente del mismo modo que Play Store. El especialista Dylan Roussel ha investigado el funcionamiento de la app de Huawei, descubriendo una API que toma el nombre de un paquete como parámetro y devuelve un objeto JSON con los detalles de la aplicación. Este hallazgo despertó la curiosidad de Roussel, por lo que decidió continuar indagando hasta saber qué más podía encontrar.
Para sus pruebas, el investigador probó la API con el nombre del paquete de la aplicación AppGallery:
| 123456789101112131415161718192021222324 | { "app": { ... "name": "AppGallery", "openCount": 0, "openCountDesc": "", "openurl": "", "permissions": [], "pkgName": "com.huawei.appmarket", "price": "0", "productId": "", "rateNum": "0", "recommImg": "", "releaseDate": "2022-04-20 17:03:53", "sha256": "2e1a1ce4e86cbfc87f05411a2585e557af78b893f6be85f8f6cb93f889faee05", "size": "50347219", "tagName": "", "updateDesc": "", "url": "https://appdlc-dre.hispace.dbankcloud.com/dl/appdl/application/apk/40/4037feaa91cf453ca2dd1ebf444aedaa/com.huawei.appmarket.2204201539.apk?sign=mw@mw1651866832368&maple=0&distOpEntity=HWSW", "version": "12.1.1.302", "versionCode": 120101302 }, ...} |
La API devuelve diversos detalles, incluyendo algunas ID, versión de la aplicación, logotipos y otras imágenes, descripciones, permisos en el sistema y precio. Además, la API también devuelve una URL a la aplicación en AppGallery, desde donde es posible descargar la aplicación.
Después de probar esta búsqueda en una aplicación gratuita, era momento de intentar con una aplicación de paga. Roussel usó el nombre del paquete de una aplicación de paga, obteniendo igualmente el enlace de descarga con el mismo tipo de parámetro sign al final; al concluir la prueba, el investigador pudo descargar la aplicación y usarla con normalidad.
El investigador decidió continuar con sus pruebas para demostrar que esto no era solo un error. Al usar los nombres de paquetes de dos aplicaciones y un juego para móviles, Russel pudo descargar y usar estas herramientas; cabe mencionar que el juego tenía una verificación de licencia, la cual no pudo impedir que el investigador usara el juego sin pagar.
Para Roussel, es difícil de creer que AppGallery se vea afectada por un error tan simple, considerando que en repositorio almacena el trabajo de decenas de desarrolladores que buscan ganancias a través de este medio.
La buena noticia es que Huawei ya está al tanto de este error, aunque demorará algunos días más en completar una solución funcional. Se prevé que todo esté solucionado para el 25 de mayo.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
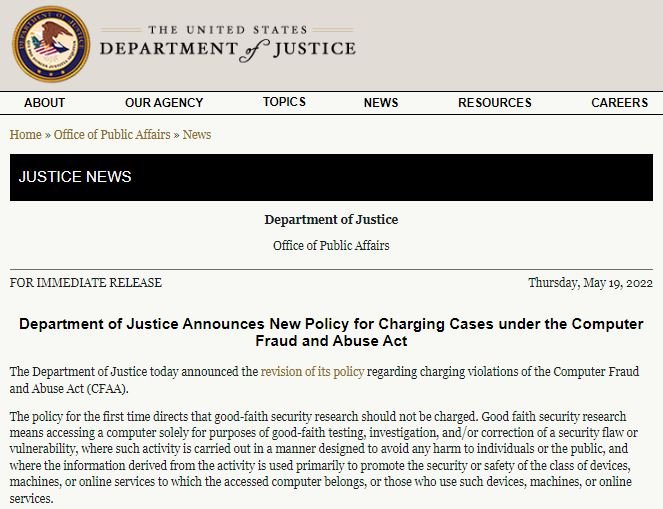
GOBIERNO DE E.U. DEJARÁ DE INVESTIGAR A LOS HACKERS ÉTICOS QUE REALICEN TRABAJOS Y ANÁLISIS LEGÍTIMOS
El Departamento de Justicia de E.U. (DOJ) comenzará a revisar sus políticas para la presentación de casos criminales derivados de infracciones a la Ley de Abuso y Fraude Informático (CFAA), lo que beneficiará directamente a la comunidad del hacking ético.
Las nuevas políticas establecerán una separación clara entre los casos de investigación “de buena fe”, de cualquier caso de hacking con fines maliciosos, que antes eran separados por una línea tremendamente difusa, por lo que muchos hackers éticos con intenciones legítimas terminaban siendo investigado como cibercriminales.
Bajo estas nuevas políticas, la investigación, pruebas de software, el análisis de fallas de seguridad y las brechas de seguridad en dispositivos o servicios con fines legales dejarán de ser objeto de investigación federal.
Lisa Monaco, fiscal general adjunta de E.U., menciona: “La investigación en seguridad informática es un factor clave para mejorar la seguridad en general. El DOJ nunca ha estado interesado en enjuiciar la investigación de seguridad informática de buena fe como un delito, y el anuncio de hoy promueve la seguridad cibernética al brindar claridad a los investigadores de seguridad”.
La investigación de seguridad de buena fe se define como “el acceso a una computadora únicamente con fines de pruebas legítimas, investigación y corrección de una falla o vulnerabilidad de seguridad, cuando dicha actividad se lleva a cabo de tal forma que se evita cualquier daño a individuos o al público, además de emplear los hallazgos derivados de estas investigaciones para promover la seguridad de dispositivos, sistemas y redes.
La nueva política se centra específicamente en las violaciones deliberadas de las limitaciones de acceso en computadoras y redes o incluso en cuentas en línea de otros usuarios. Estas políticas no pasarán por alto cualquier intento de hacking bajo el argumento de realizar investigaciones legítimas, por lo que los investigadores deberán seguir teniendo cuidado con su trabajo.
Son muchos los ejemplos de investigadores que se han visto en problemas con la CFAA a causa de su trabajo. Hace unos meses, el ingeniero de seguridad en la nube Rob Dyke reportó una filtración de datos afectando a una organización no gubernamental, lo que lo llevó a ser investigado por presunto uso indebido de sistemas informáticos.
Se espera que el DOJ publique un reporte completo sobre esta revisión de políticas en el futuro cercano.
Para más información sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware, riesgos de ciberseguridad y cursos de seguridad de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
