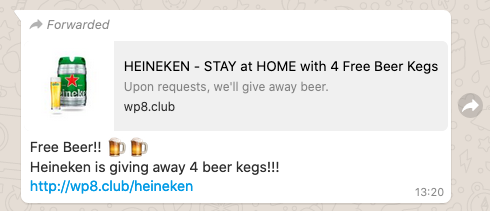
@Heineken got a link to this through a WhatsApp message, I assume it’s a scam thought you might want to know about it #stayathome #scam
Month: April 2020
NUEVO VIRUS DE WHATSAPP DE LA CERVEZA HEINEKEN INFECTA A MILES DE TELÉFONOS CELULARES. ¿CÓMO SE PROPAGA?
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/videos-noticias/nuevo-virus-de-whatsapp-de-la-cerveza-heineken-infecta-a-miles-de-telefonos-celulares-como-se-propaga/
El distanciamiento social debido al coronavirus está generando consecuencias inimaginables relacionadas con la ciberseguridad, aseguran expertos en cómputo forense. Un ejemplo es Reino Unido, que está entrando en su cuarta semana de aislamiento, por lo que miles de pubs y bares permanecen cerrados y dificultando a los ciudadanos la labor de conseguir algo de alcohol.
Al parecer un estafador, o grupo de estafadores, está tratando de sacar ventaja de eso, creando cuentas de redes sociales presuntamente operadas por la popular compañía cervecera Heineken, con sede en Holanda. Esos actores de amenazas engañan a los usuarios desprevenidos afirmando que pueden enviarles barriles de cerveza gratis con el propósito de extraer sus datos personales.
Durante los más recientes días, esta estafa se ha vuelto algo popular, especialmente en plataformas como WhatsApp. Esta treta consiste en una campaña de phishing que busca extraer la información personal de cientos de individuos con propósitos maliciosos; si bien esta campaña fue detectada hace un par de años, desde entonces sólo una persona ha sufrido el robo de su cuenta bancaria, mencionan expertos en cómputo forense.
A través de WhatsApp, las víctimas potenciales reciben un mensaje sobre una supuesta promoción en la que Heineken está regalando barriles de cerveza. En el mensaje se invita al usuario a hacer clic en un enlace que redirige a un sitio fraudulento llamado “Heineken Stay At Home with 4 FREE beer kegs”. Posteriormente se mostrará al usuario un formulario para ser uno de los ganadores de esta promoción.
Aunque los expertos en cómputo forense detectaron la estafa por primera vez en 2018, los actores de amenaza se tomaron el tiempo de actualizar el contenido de sus páginas fraudulentas, relacionándolo con el tema del coronavirus y la campaña de aislamiento emprendida por gobiernos de todo el mundo. En otras palabras, los hackers aseguran que la cerveza será regalada a las personas que se quedan en casa.
Cuando la primera campaña de phishing fue detectada, Heineken publicó el siguiente comunicado: “La supuesta promoción en la que se ofrecen barriles de cerveza es una estafa y no está relacionada con Heineken”. Se espera que la compañía se pronuncie sobre este nuevo incidente en breve.
Los expertos del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) mencionan que el phishing sigue siendo uno de los métodos de ataque más utilizados, pues requiere pocos recursos y conocimientos técnicos, además de que es relativamente fácil engañar a los usuarios menos familiarizados con temas de seguridad informática.
CÓMO HACKEAR LA RED AISLADA DEL REACTOR NUCLEAR CON GPU SIMPLE Y SEÑALES DE RADIO
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/seguridad-informatica/como-hackear-la-red-aislada-del-reactor-nuclear-con-gpu-simple-y-senales-de-radio/
Los sistemas y dispositivos aislados (conocidos como sistemas “air-gapped”) han sido objeto de análisis de investigadores y actores de amenazas por años, afirman especialistas en seguridad perimetral, lo que ha generado una gran cantidad de variantes y escenarios de ataque para comprometer estos sistemas.
Uno de estos ataques es el conocido como Stuxnet, un gusano informático empleado en las instalaciones de una compañía nuclear en Irán hace casi diez años. Esa fue la primera ocasión en que un grupo de hackers demostró que no es imposible comprometer un sistema air-gapped.
Especialistas en seguridad perimetral mencionan que, en esa ocasión, los actores de amenazas (el ataque fue atribuido a agencias de inteligencia israelíes) podrían haber empleado una variante de malware que comprometió las centrifugadoras en una planta de enriquecimiento de uranio. Al respecto, el especialista en hacking ético Mikhail Davidov formuló una pregunta: si bien es posible inyectar código malicioso en un sistema air-gapped, ¿es posible extraer datos de estas redes?
La respuesta a esta pregunta podría estar en el espectro de radio. Empleando una radio, una antena y un script de su propio desarrollo, el hacker descubrió cómo emplear una señal emitida por una unidad de procesamiento gráfico (GPU) de una computadora conectada a una red air-gapped y extraer datos confidenciales. El experto publicó sus hallazgos en un blog compartido en exclusiva con la firma CyberScoop.
El ataque fue lanzado desde detrás de una pared y a más de 15 metros de distancia de la computadora objetivo. El experto usó una antena para escanear el espectro de radiofrecuencia buscando variaciones que pudieran ser empleadas para extraer datos. Al percatarse de que la GPU emite un tipo de señal que es posible manipular, el hacker ético desarrolló un script para realizar esta acción. Controlando la duración de cada transmisión de radio de la GPU, y empleando una radio capaz de captar esta señal, pudo completar la extracción de datos de la página.
“Al pensar en la extracción de datos de redes air-gapped, llegué a esta conclusión. Muchas veces tenemos que pensar en cualquier posible escenario de utilidad para los actores de amenazas y descartar o confirmar esas posibilidades en un entorno controlado”, menciona el experto en seguridad perimetral.
Acorde a Davidov, esta investigación también es una invitación para la comunidad de la ciberseguridad para adoptar un enfoque más proactivo sobre las señales emitidas por los sistemas informáticos y la posibilidad de que sean comprometidos. El Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) menciona que las agencias de inteligencia nacionales también deben considerar este vector de ataque.
HEINEKEN BEER WHATSAPP VIRUS INFECTING THOUSAND OF MOBILE PHONES; HOW IT SPREADS?
ORIIGNAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/23/heineken-beer-whatsapp-virus-infecting-thousand-of-mobile-phones-how-it-spreads/
Social distancing due to coronavirus is generating unimaginable cybersecurity consequences, computer forensics experts say. One example is the UK, which is entering its fourth week of isolation, so thousands of pubs and bars remain closed and making it difficult for citizens to get some alcohol.
Apparently a scammer, or group of scammers, is trying to take advantage of that, creating social media accounts allegedly operated by the popular Dutch-based brewing company Heineken. Those threat actors deceive unsuspecting users by claiming that they can send them free beer kegs for the purpose of extracting their personal data.
Over the most recent days, this scam has become popular, especially on platforms like WhatsApp. This ruse consists of a phishing campaign that seeks to extract the personal information of hundreds of individuals for malicious purposes; although this campaign was detected a couple of years ago, since then only one person has suffered theft from their bank account, computer forensics experts mention.
Through WhatsApp, potential victims receive a message about an alleged promotion in which Heineken is giving away beer kegs. The message invites the user to click on a link that redirects to a fraudulent site called “Heineken Stay At Home with 4 FREE beer kegs”. The user will then be shown a form to be one of the winners of this promotion.
Although computer forensics experts first detected the scam in 2018, threat actors took the time to update the content of their fraudulent pages, linking it to the issue of coronavirus and the isolation campaign undertaken by governments around the world. In other words, hackers claim that beer will be given away to people who stay at home.
When the first phishing campaign was detected, Heineken published the following statement: “The alleged promotion in which beer kegs are offered is a scam and is not related to Heineken”. The company is expected to rule on this new incident shortly.
Experts at the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) mention that phishing remains one of the most widely used attack methods, requiring few resources and technical knowledge, and it is relatively easy to mislead users less familiar with information security issues.
HOW TO HACK NUCLEAR REACTOR ISOLATED NETWORK WITH A SIMPLE GPU & RADIO SIGNALS
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/23/how-to-hack-nuclear-reactor-isolated-network-with-a-simple-gpu-radio-signals/
Isolated systems and devices (known as “air-gapped” systems) have been the subject of analysis by researchers and threat actors for years, as network perimeter security specialists said, which has generated a large number of variants and attack scenarios to compromise these systems.
One such attack is the one known as Stuxnet, a computer worm used at a nuclear company’s facility in Iran nearly ten years ago. That was the first time a hacker group showed that it is not impossible to compromise an air-gapped system.
Network perimeter security specialists mention that, on that occasion, threat actors (the attack was attributed to Israeli intelligence agencies) could have employed a malware variant that compromised centrifuges at a uranium enrichment plant. In this regard, ethical hacking specialist Mikhail Davidov asked a question: while it is possible to inject malicious code into an air-gapped system, is it possible to extract data from these networks?
The answer to this question could be on the radio spectrum. Using a radio, antenna, and script from his own development, the hacker figured out how to use a signal emitted by a graphics processing unit (GPU) from a computer connected to an air-gapped network and extract sensitive data. The expert posted his findings on a blog shared exclusively with the firm CyberScoop.

The attack was launched from behind a wall and more than 15 meters away from the target computer. The expert used an antenna to scan the radio frequency spectrum for variations that could be used to extract data. Realizing that the GPU emits a type of signal that can be manipulated, the ethical hacker developed a script to perform this action. By controlling the duration of each GPU radio transmission, and using a radio capable of capturing this signal, it was able to complete the extraction of data from the page.
“When I thought about extracting data from air-gapped networks, I came to this conclusion. Many times we have to think about any possible scenario of usefulness for threat actors and discard or confirm those possibilities in a controlled environment,” the network perimeter security expert says.
According to Davidov, this research is also an invitation to the cybersecurity community to take a more proactive approach to signals emitted by computer systems and the possibility of them being compromised. The International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) mentions that national intelligence agencies should also consider this attack vector.
LIST OF HALF A MILLION ZOOM ACCOUNTS WITH NAME, EMAIL, MEETING URL AND HOST KEYS
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/14/list-of-half-a-million-zoom-accounts-with-name-email-meeting-url-and-host-keys/
A new security inconvenience for people working from home has been reported. Information security training experts report that nearly half a million Zoom accounts are on sale on various hacking forums hosted on dark web for less than a penny (even some are available for free).
According to reports, these login credentials are obtained from the method known as credential stuffing, using usernames and passwords obtained from previous data breach incidents.
Experts from information security training firm Cyble say these leaked accounts have been exposed since the beginning of April. This information is shared through various text-sharing forums in which cybercriminals generally post email addresses and possible passwords for improper and maliciously intended access.
Researchers collected a sample of 290 accounts related to various universities in the United States, including the University of Vermont, the University of Colorado, Dartmouth, Lafayette, University of Florida, among others. All of these accounts were published for free by threat actors.
After identifying one of the individuals who posted these ads, the information security training experts managed to contact them to try to purchase a larger sample of these login credentials. Researchers bought about 530,000 Zoom credentials for $0.0020 USD. After extensive analysis, the researchers concluded that some of the Zoom accounts on display belonged to reputable companies such as Chase or Citibank, as well as multiple academic institutions, among others.
According to the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), any company may be the victim of a credential stuff attack, so it is recommended to use unique passwords for any online platform you use. Credential stuffing necessarily requires the use of login credentials exposed in other data breach incidents and is a very common cybercriminal practice, but the use of unique passwords greatly limits the risk of being victims of this attack.
For any user willing to know if their information has been exposed in a similar cybersecurity incident, they can consult the online platform Have I Been Pwned, which has a huge database on known cybersecurity incidents. By simply entering their email address, users will be able to know if this information has been leaked previously.
HACKERS LEAKED CONFIDENTIAL FILES OF BOEING, LOCKHEED MARTIN AND SPACEX AFTER RANSOM NOT PAID
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/13/hackers-leaked-confidential-files-of-boeing-lockheed-martin-and-spacex-after-ransom-not-paid/
Despite efforts to combat cybercrime, sometimes companies can’t do anything to prevent their information from being exposed. According to experts from a cyber security course, a data breach in a major company allowed the leaking of multiple internal documents from some of the world’s leading aerospace companies.
Everything points to the incident behind this incident are hackers from criminal group DoppelPaymer, who exposed this information in retaliation to an unpaid ransom. Among the confidential information exposed are the plans of multiple projects developed by firms such as Lockheed-Martin, Boeing and SpaceX.
Cyber security course specialists point out that these documents were extracted from the systems of Visser Precision, a U.S. manufacturing and design contractor. Among the company’s most prominent customers are Tesla, Blue Origin, Sikorsky, Joe Gibbs Racing, as well as the aforementioned firms.
DoppelPaymer was responsible for infecting Visser’s computers to encrypt your files, demanding a ransom in exchange for restoring access to the information. Upon expiry of the deadline for the ransom to be paid, threat actors posted a sample of the compromised documents on a website that, to date, remains online within the reach of any user.
In this regard, a spokesman for Lockheed Martin said, “We are aware of the Visser Precision incident, and we will conduct our own cybersecurity incident response protocols related to our supply chain.” On the other hand, Visser, SpaceX and Boeing still do not give official statements.
This is not the first time that DoppelPaymer hackers have been linked to a similar incident. What’s more, this group of threat actors is maintaining a website to publish the documents of companies that decide not to pay after suffering a ransomware infection. Most of the information exposed on this site (which is constantly updated) does not pose serious threats to the companies exposed, although the case of Visser and its partners is an exception, say experts from the cyber security course.
The latest reports related to DoppelPaymer mention that hackers agreed not to attack any hospital’s technological infrastructure during the combat period to the coronavirus pandemic; it remains to be seen whether this promise is honored.
Although the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) ensures that it is never advisable to pay hackers after a ransomware attack, multiple companies decide to take risks and pay the ransom due to the high costs arising from the recovery process of a similar incident, so that guides have even been developed for paying these extortions in the safest possible way.
LISTA DE MEDIO MILLÓN DE CUENTAS DE ZOOM CON NOMBRE, DIRECCIÓN EMAIL, URL DE REUNIÓN Y CLAVES DE HOST
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/hacking-incidentes/lista-de-medio-millon-de-cuentas-de-zoom-con-nombre-direccion-email-url-de-reunion-y-claves-de-host/
Un nuevo inconveniente de seguridad para las personas trabajando desde casa ha sido reportado. Expertos de un curso de seguridad informática reportan que cerca de medio millón de cuentas de Zoom se encuentran a la venta en diversos foros de hacking alojados en dark web por menos de un centavo de dólar (incluso algunas están disponibles de forma gratuita).
De acuerdo con los reportes, estas credenciales de inicio de sesión se obtienen a partir del método conocido como relleno de credenciales, empleando los nombres de usuario y contraseñas obtenidos en incidentes de brechas de datos anteriores.
Expertos del curso de seguridad informática de la firma Cyble afirman que estas cuentas filtradas comenzaron a exponerse desde inicios de abril. Esta información se comparte mediante diversos foros de intercambio de textos en los que los cibercriminales publican generalmente direcciones email y posibles contraseñas para acceder de forma indebida.
Los investigadores recolectaron una muestra de 290 cuentas relacionadas con diversas universidades en Estados Unidos, como la Universidad de Vermont, la Universidad de Colorado, Dartmouth, Lafayette, la Universidad de Florida, entre otras. Todas estas cuentas fueron publicadas de forma gratuita por los actores de amenazas.
Después de identificar a uno de los individuos que publicaron estos anuncios, los expertos del curso de seguridad informática lograron contactarlo para tratar de comprar una muestra más grande de estas credenciales de inicio de sesión. Los investigadores compraron alrededor de 530 mil credenciales de Zoom por 0.0020 centavos de dólar. Después de un exhaustivo análisis, los investigadores concluyeron que algunas de las cuentas de Zoom expuestas pertenecían a empresas de renombre como Chase o Citibank, además de múltiples instituciones académicas, entre otras.
Acorde al Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), cualquier compañía puede ser víctima de un ataque de relleno de credenciales, por lo que se recomienda emplear contraseñas únicas para cualquier plataforma en línea que use. El relleno de credenciales requiere forzosamente el uso de credenciales de inicio de sesión expuestas en otros incidentes de brecha de datos y es una práctica cibercriminal muy común, pero el uso de contraseñas únicas limita en gran medida el riesgo de ser víctimas de este ataque.
Cualquier usuario que desee saber si su información se ha visto expuesta en un incidente similar, puede consultar la plataforma Have I Been Pwned, que cuenta con una enorme bases de datos sobre incidentes de ciberseguridad conocidos. Con sólo ingresar su dirección email, los usuarios podrán saber si ésta información se ha filtrado anteriormente.
HACKERS EXTRAEN ARCHIVOS CONFIDENCIALES DE BOEING, LOCKHEED MARTIN Y SPACEX POR NO PAGAR EL RESCATE
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/hacking-incidentes/hackers-extraen-archivos-confidenciales-de-boeing-lockheed-martin-y-spacex-por-no-pagar-el-rescate/
A pesar de los esfuerzos por combatir el cibercrimen, en ocasiones las compañías no pueden hacer nada por evitar que su información sea expuesta. Acorde a expertos de un curso de ciberseguridad, una brecha de datos en una importante compañía permitió la filtración de múltiples documentos internos de algunas de las compañías aeroespaciales más importantes del mundo.
Todo apunta a que detrás de este incidente están los hackers del grupo criminal DoppelPaymer, quienes expusieron esta información en represalia a un rescate no pagado. Entre la información confidencial expuesta se encuentran los planos de múltiples proyectos desarrollados por firmas como Lockheed-Martin, Boeing y SpaceX.
Los especialistas del curso de ciberseguridad señalan que estos documentos fueron extraídos de los sistemas de Visser Precision, un contratista de fabricación y diseño de E.U. Entre los clientes más destacados de esta compañía se encuentran Tesla, Blue Origin, Sikorsky, Joe Gibbs Racing, además de las firmas antes mencionadas.
DoppelPaymer se encargó de infectar las computadoras de Visser para cifrar sus archivos, exigiendo un rescate a cambio de restablecer el acceso a la información. Al vencer la fecha límite para que el rescate fuera pagado, los actores de amenazas publicaron una muestra de los documentos comprometidos en un sitio web que, hasta la fecha, sigue en línea al alcance de cualquier usuario.
Al respecto, un portavoz de Lockheed Martin mencionó: “Estamos al tanto del incidente en Visser Precision, y llevaremos a cabo nuestros propios protocolos de respuesta a incidentes de ciberseguridad relacionados con nuestra cadena de suministro”. Por otra parte, Visser, SpaceX y Boeing siguen sin dar declaraciones oficiales.
Esta no es la primera vez que los hackers de DoppelPaymer son vinculados con un incidente similar. Es más, este grupo de actores de amenazas mantienen un sitio web para publicar los documentos de las compañías que deciden no pagar después de sufrir una infección de ransomware. La mayoría de la información expuesta en este sitio (el cual es actualizado de forma constante) no representa serias amenazas para las compañías expuestas, aunque el caso de Visser y sus socios es una excepción., aseguran expertos del curso de ciberseguridad.
Los últimos reportes relacionados con DoppelPaymer mencionan que los hackers acordaron no atacar la infraestructura tecnológica de ningún hospital durante el periodo de combate a la pandemia de coronavirus; está por verse si esta promesa se cumple.
A pesar de que el Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) asegura que nunca es recomendable pagar a los hackers después de un ataque de ransomware, múltiples compañías deciden arriesgarse y pagar el rescate debido a los altos costos derivados del proceso de recuperación de un incidente similar, por lo que incluso se han elaborado guías para el pago de estas extorsiones del modo más seguro posible.
FIX FOR CRITICAL ZERO-DAY LINUX VULNERABILITY AVAILABLE; PATCH IMMEDIATELY
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/06/fix-for-critical-zero-day-linux-vulnerability-available-patch-immediately/
Good news for Linux system administrators. Data security training experts have announced the release of a security patch to fix an operating system kernel vulnerability that was revealed to the public in the latest edition of the Pwn2Own ethical hacking contest. Exploiting this vulnerability would have allowed threat actors to perform an escalation of privileges to root Ubuntu Desktop.
The researchers who submitted this finding were rewarded with $270k USD. In addition to reporting this flaw in Ubuntu Desktop, experts presented examples of possible attack scenarios on Windows, Safari, Oracle VirtualBox, and Adobe Reader systems.
Regarding this flaw, data security training specialists submitted an exploit to scale local privileges on the affected system. Researchers demonstrated that they were able to abuse an incorrect input validation error in the Linux kernel to scale privileges at the root user level.
“To be more specific, this flaw is due to the management of eBPF programs; the vulnerability exists due to inadequate validation in eBPF programs provided by users before being executed. A threat actor could exploit the flaw to scale privileges and execute code in the context of the core,” said Manfred Paul, one of the investigators in charge of the report.
The flaw was tracked as CVE-2020-8835 and is considered high severity, according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) report. After receiving the report, kernel developers began working to correct the flaw; finally the corresponding updates have been released, as data security training specialists said. Potentially exposed system administrators are advised to update as soon as possible.
According to the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), Linux 5, 6, 7 and 8 systems are not affected by this failure, since the kernel version included in these versions does not support the confirmation that this condition generates. Other distributions, such as Fedora, could also be affected, so developers should pay attention to potential exploit attempts. Finally, the researchers noted that exploiting this failure could also lead to a kernel crash, triggering a denial of service (DDoS) condition. Additional technical details about the vulnerability are available on developer platforms
HACKER DESTROYS 15,000 SERVERS TO TAKE REVENGE WITH THE AUTHOR OF THE BOOK ABOUT HIM
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/06/hacker-destroys-15000-servers-to-take-revenge-with-the-author-of-the-book-about-him/
Specialists from an iOS pentesting course report that, over the most recent days, a hacker has been improperly breaking into Elasticsearch servers exposed on the Internet to remove their content, blaming a cybersecurity company. John Wethington, a cybersecurity expert who has been following up on the case, says I played off on March 24.
Apparently, the hacker behind this campaign has been using an automated script to scan the Internet for these protections-less Elasticsearch deployments, connecting to the databases to delete the content, and finally creating a new index (with no content) with the name nightlionsecurity.com. This index has also been found in some Elasticsearch deployments with intact content, so specialists believe the attack does not work in all cases.
The name of the index left by the hacker was immediately linked to Night Lion Security, a cybersecurity firm that teaches an iOS pentesting course. In this regard, Vinny Troia, founder of the company, says Night Lion has nothing to do with these attacks. In a later interview, Troia claims that these attacks are the responsibility of a hacker he has been investigating for years, who may be exacting revenge for a book Troia wrote.
Although at first many members of the cybersecurity community regarded these attacks as a joke, this is no longer funny. So far, at least 15,000 Elasticsearch deployments have been known; this is not the only concern in the community, as at least 35,000 Elasticsearch servers are known that might be exposed.
Researchers from an iOS pentesting course experts and security firms have already notified Elasticsearch as well as the competent authorities; the company is in the process of implementing some measures to mitigate the scope of these attacks.
As if that wasn’t enough, the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) has identified a second threat actor by attacking Elasticsearch deployments. The hacker (or group of hackers) behind this campaign compromises the security of the databases to leave a message informing administrators that they have been hacked, further leaving an email address to agree a payment in exchange for resetting access. Only 40 cases related to this campaign are known, although it is not ruled out that the number will increase in the coming days.
PARCHE PARA VULNERABILIDAD DÍA CERO EN LINUX YA DISPONIBLE; ACTUALICE DE INMEDIATO
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/vulnerabilidades/parche-para-vulnerabilidad-dia-cero-en-linux-ya-disponible-actualice-de-inmediato/
Buenas noticias para los administradores de sistemas Linux. Expertos en gestión de la seguridad de la información han anunciado el lanzamiento de un parche de seguridad para corregir una vulnerabilidad del kernel del sistema operativo que fue revelada al público en la más reciente edición del concurso de hacking ético Pwn2Own. La explotación de esta vulnerabilidad habría permitido a los actores de amenazas realizar una escalada de privilegios para rootear Ubuntu Desktop.
Los investigadores que presentaron este hallazgo fueron recompensados con 270 mil dólares. Además del reporte de esta falla en Ubuntu Desktop, los expertos presentaron ejemplos de posibles escenarios de ataque en sistemas Windows, Safari, Oracle VirtualBox y Adobe Reader.
Respecto a esta falla, los especialistas en gestión de la seguridad de la información presentaron un exploit para realizar una escalada de privilegios locales en el sistema afectado. Los investigadores demostraron ser capaces de abusar de un error de validación de entrada incorrecta en el kernel de Linux para escalar privilegios a nivel de usuario root.
“Para ser más específicos, esta falla se debe al manejo de los programas eBPF; la vulnerabilidad existe debido a una inadecuada validación en los programas eBPF proporcionados por los usuarios antes de ser ejecutados. Un actor de amenazas podría explotar la falla para escalar privilegios y ejecutar código en el contexto del núcleo”, mencionó Manfred Paul, uno de los responsables de la investigación.
La falla fue identificada como CVE-2020-8835 y se le considera de alta severidad, según el reporte del Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). Después de recibir el reporte, los desarrolladores del kernel comenzaron a trabajar para corregir la falla; finalmente las actualizaciones correspondientes han sido lanzadas, señalan los especialistas en gestión de la seguridad de la información. Se recomienda a los administradores de sistemas potencialmente expuestos actualizar a la brevedad.
Acorde al Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), los sistemas Linux 5, 6, 7 y 8 no se ven afectados por esta falla, puesto que la versión del kernel incluida en estas versiones no respalda la confirmación que genera esta condición. Otras distribuciones, como Fedora, podrían verse afectadas también, por lo que los desarrolladores deben prestar atención a potenciales intentos de explotación. Finalmente, los investigadores señalaron que la explotación de esta falla también podría conducir a un bloqueo del kernel, desencadenando una condición de denegación de servicio (DDoS). Mayores detalles técnicos sobre la vulnerabilidad están disponibles en las plataformas de los desarrolladores.
HACKER DESTRUYE 15 MIL SERVIDORES PARA VENGARSE DEL AUTOR DE UN LIBRO SOBRE ÉL
contenido original: https://noticiasseguridad.com/hacking-incidentes/hacker-destruye-15-mil-servidores-para-vengarse-del-autor-de-un-libro-sobre-el/
Especialistas de un curso de pentest reportan que, durante los más recientes días, un hacker ha estado irrumpiendo indebidamente en servidores de Elasticsearch expuestos en Internet para eliminar su contenido, culpando de ello a una empresa de ciberseguridad. John Wethington, experto en ciberseguridad que ha estado dando seguimiento al caso, asegura que toco comenzó el 24 de marzo.
Al parecer, el hacker detrás de esta campaña ha estado empleando un script automatizado para escanear en Internet en busca de estas implementaciones de Elasticsearch sin protecciones, conectándose a las bases de datos para eliminar el contenido y, finalmente, crear un nuevo índice (sin contenido alguno) con el nombre de nightlionsecurity.com. Este índice también ha sido encontrado en algunas implementaciones de Elasticsearch con contenido intacto, por lo que los especialistas creen que el ataque no funciona en todos los casos.
El nombre del índice dejado por el hacker fue inmediatamente vinculado con Night Lion Security, una firma de ciberseguridad que imparte un curso de pentest. Al respecto, Vinny Troia, fundador de la compañía, asegura que Night Lion no tiene nada que ver con estos ataques. En una entrevista posterior, Troia afirma que estos ataques son responsabilidad de un hacker que ha estado investigando desde hace años, quien podría estar cobrando venganza por un libro que escribió Troia.

Aunque al principio muchos miembros de la comunidad de la ciberseguridad consideraron estos ataques como una broma, esto ya ha dejado de ser gracioso. Hasta el momento, se conoce de al menos 15 mil implementaciones de Elasticsearch atacadas; esta no es la única preocupación en la comunidad, pues se conocen al menos 35 mil servidores de Elasticsearch que podrían estar expuestos.
Investigadores, expertos del curso de pentest y firmas de seguridad ya han notificado a Elasticsearch, así como a las autoridades competentes; la compañía está en proceso de implementar algunas medidas para mitigar el alcance de estos ataques.
Por si no fuera suficiente, el Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) ha identificado a un segundo actor de amenazas atacando implementaciones de Elasticsearch. El hacker (o grupo de hackers) detrás de esta campaña compromete la seguridad de las bases de datos para dejar un mensaje en el que se informa a los administradores que han sido hackeados, dejando además una dirección email para acordar un pago a cambio de restablecer el acceso. Sólo se conocen 40 casos relacionados con esta campaña, aunque no se descarta que el número incremente en los próximos días.
DO YOU WANT TO WORK WITH THE US DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE? THESE ARE THE CYBERSECURITY STANDARDS THAT WILL MAKE YOU ELIGIBLE
Private companies wishing to provide cyberdefense, among other services for the US Government must meet a new requirements framework. According to data security training experts, the US Department of Defense (DOD) has just unveiled a new cybersecurity certification model that sets new guidelines that companies will need to meet.
A few weeks ago, DOD officials submitted the final draft of the Cybersecurity Maturity Certification Model. According to the official communication platforms of the DOD, this new framework was designed to improve cybersecurity in each area of the agency; the new model focuses especially on the supply chain, one of the main cybersecurity challenges for any company.
Multiple data security training specialists agree that today’s supply chains are a complex issue for large private companies and government organizations, involving contractors, business partners, sellers, manufacturers and suppliers. Any link in a supply chain is exposed to cybersecurity incidents, compromising the rest of the participants in the process.
This is a particularly troubling issue for defense and intelligence agencies, which routinely handle national security issues. Regarding how functional the adoption of this model might be, data security training specialists still have their reservations because they believe that, on the one hand, the DOD presents excellent ideas and raises the guidelines required to cover any vector related to cybersecurity at the agency. On the other hand, there are still no concrete signs of the implementation of any of these measures in practice.
One of the methods covered in this framework is the allocation of a score between 1 and 5 to each organization, mentioned by the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS). The more an organization adheres to the strict measures established by the DOD, the closer it will get to a score of 5; U.S. Defense agencies must also adhere to the framework.
It should be noted that, by themselves, these new processes and certifications will not protect the information of any private agency or company. The establishment of strict security measures and policies, ongoing staff training, and the use of secure and up-to-date software are critical to meeting security guidelines capable of addressing current threats.
USING THIS SOFTWARE, THE GOVERNMENT WILL TRACK PEOPLE DURING AND AFTER THE PANDEMIC. PRIVACY WILL NO LONGER EXIST
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/02/using-this-software-the-government-will-track-people-during-and-after-the-pandemic-privacy-will-no-longer-exist/
NSO Group is embroiled in a new privacy and surveillance scandal. The Israeli technology firm has been pointed out on multiple occasions by the alleged development of sophisticated spyware tools for sale to governments around the world, mentioning experts from a cyber security audit company. The company has even been accused of hacking attempts against Facebook & WhatsApp, accusations that NSO Group has always denied.
In the midst of the global crisis over the emergence of coronavirus, NSO Group would be trying to reach the West with new COVID-19 case-tracking software, trying to sell it to governments to collect as much information as possible about potential outbreaks or cases of infection based on metadata analysis.
It is rare for NSO Group to publicly state on any of its products or developments. However, this time the company has offered multiple demonstrations on how this new technology would work, as part of a marketing campaign aimed at the rulers of Western countries, mention specialists from a cyber security audit company.
While the reports ensure that this tool really is everything its creators say, so far no details have been leaked about how it works or whether it provides some measure of protection to the privacy of the target people. It is even mentioned that the Israeli government is ready to start using this tool on the smartphones of its citizens.
Sky News reporters say this software would be hosted on the government’s own client systems. In reality, NSO Group would not have access to the data uploaded to the system, which in turn would be provided by the governments themselves.
Citizens would be registered on this platform using a random identifier. In addition, their location movements would have a timestamp, which will allow platform administrators to track the latest locations of users infected with coronavirus to develop potential risk scenarios, experts from the cyber security audit company.
According to NSO Group, using this tool at the national level, governments could identify regions with the highest concentration of people exposed to COVID-19.
For obvious reasons, this is a project that violates user privacy under almost any data protection legislative framework. However, the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) notes that, due to the state of emergency in force in multiple countries, governments could take extraordinary steps to combat the pandemic, even if these measures conflict human rights.
Even Edward Snowden has spoken out on such measures, stating that governments could take advantage of the emergency to take authoritarian measures that could be instituted permanently without proper oversight of civil society.
¿DESEA TRABAJAR CON EL DEPARTAMENTO DE DEFENSA DE EU? ESTOS SON LOS ESTÁNDARES DE CIBERSEGURIDAD QUE LO HARÁN ELEGIBLE
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/seguridad-informatica/desea-trabajar-con-el-departamento-de-defensa-de-eu-estos-son-los-estandares-de-ciberseguridad-que-lo-haran-elegible/
Las empresas privadas que deseen proveer servicios de ciberdefensa para el gobierno estadounidense deberán cumplir con un nuevo marco de requisitos. De acuerdo con expertos en gestión de la seguridad de la información, el Departamento de Defensa de E.U. (DOD) acaba de revelar un nuevo modelo de certificación de ciberseguridad que establece nuevos lineamientos que las empresas deberán cumplir.
Hace algunas semanas, oficiales del DOD presentaron el borrador definitivo del Modelo de Certificación de Madurez en Ciberseguridad. Acorde a las plataformas oficiales de comunicación del DOD, este nuevo marco de trabajo fue pensado para mejorar la ciberseguridad en cada área de la agencia; el nuevo modelo se enfoca especialmente en la cadena de suministro, uno de los principales retos en ciberseguridad para cualquier empresa.

Múltiples especialistas en gestión de la seguridad de la información concuerdan en que las cadenas de suministro actuales son un asunto complejo para las grandes empresas privadas y organizaciones gubernamentales, pues involucran a contratistas, socios comerciales, vendedores, fabricantes y proveedores. Cualquier eslabón en una cadena de suministros está expuesto a incidentes de ciberseguridad, comprometiendo al resto de los participantes en el proceso.
Este es un tema especialmente preocupante para agencias de defensa e inteligencia, que manejan asuntos de seguridad nacional de forma rutinaria. Respecto a qué tan funcional podría ser la adopción de este modelo, los especialistas en gestión de la seguridad de la información aún tienen sus reservas pues consideran que, por un lado, el DOD expone excelentes ideas y plantea las pautas requeridas para cubrir cualquier vector relacionado con la ciberseguridad en la agencia. Por otra parte, aún no hay muestras concretas de la implementación de alguna de estas medidas en la práctica.
Uno de los métodos contemplados en este marco es la asignación de un puntaje entre 1 y 5 a cada organización, menciona el Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS). Entre más se apegue una organización a las estrictas medidas establecidas por el DOD, más se acercará a obtener un puntaje de 5; las agencias de Defensa de E.U. también deberán apegarse al marco.
Cabe mencionar que, por sí mismos, estos nuevos procesos y certificaciones no protegerán la información de ninguna agencia o empresa privada. El establecimiento de estrictas medidas y políticas de seguridad, la capacitación constante del personal y el uso de software seguro y actualizado son fundamentales para cumplir con los lineamientos de seguridad capaces de hacer frente a las amenazas actuales
USANDO ESTE SOFTWARE, EL GOBIERNO DARÁ SEGUIMIENTO A LAS PERSONAS DURANTE Y DESPUÉS DE LA PANDEMIA. LA PRIVACIDAD YA NO EXISTIRÁ
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/tecnologia/usando-este-software-el-gobierno-dara-seguimiento-a-las-personas-durante-y-despues-de-la-pandemia-la-privacidad-ya-no-existira/
NSO Group está envuelta en un nuevo escándalo de privacidad y vigilancia. La firma de tecnología israelí ha sido señalada en múltiples ocasiones por el supuesto desarrollo de sofisticadas herramientas de espionaje (spyware) para su venta a los gobiernos de todo el mundo, mencionan expertos de una empresa de ciberseguridad. La compañía incluso ha sido acusada de intentos de hacking contra Facebook y WhatsApp, acusaciones que NSO Group siempre ha desmentido.
En plena crisis mundial por la irrupción del coronavirus, NSO Group estaría tratando de llegar a occidente con un nuevo software de seguimiento de casos de COVID-19, tratando de venderlo a los gobiernos para recolectar toda la información posible sobre potenciales brotes o casos de infección con base en el análisis de metadatos.
Es poco común que NSO Group se pronuncie públicamente respecto a alguno de sus productos o desarrollos. No obstante, en esta ocasión la compañía ha ofrecido múltiples demostraciones sobre cómo funcionaría esta nueva tecnología, como parte de una campaña de marketing dirigida a los gobernantes de países occidentales, mencionan especialistas de una empresa de ciberseguridad.
Si bien los reportes aseguran que esta herramienta realmente es todo lo que dicen sus creadores, hasta ahora no se han filtrado detalles acerca de su funcionamiento o si es que brinda alguna medida de protección a la privacidad de las personas objetivo. Incluso se menciona que el gobierno israelí está listo para empezar a emplear esta herramienta en los smartphones de sus ciudadanos.
Corresponsales de la agencia Sky News aseguran que este software sería alojado en los propios sistemas de los clientes del gobierno. En realidad, NSO Group no tendría acceso a los datos cargados al sistema, que a su vez serían proporcionados por los propios gobiernos.
Los ciudadanos serían registrados en esta plataforma utilizando un identificador aleatorio. Además, sus movimientos de ubicación contarían con una marca de tiempo, lo que permitirá a los administradores de la plataforma rastrear las últimas ubicaciones de los usuarios infectados con coronavirus para desarrollar escenarios de riesgo potencial, señalan los expertos de la empresa de ciberseguridad.
Según NSO Group, empleando esta herramienta a escala nacional, los gobiernos podrían identificar las regiones con mayor concentración de personas expuestas a contraer COVID-19.
Por obvias razones, este es un proyecto que viola la privacidad de los usuarios bajo casi cualquier marco legislativo de protección de datos. No obstante, el Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) señala que, debido al estado de emergencia vigente en múltiples países, los gobiernos podrían tomar medidas extraordinarias para el combate a la pandemia, aunque estas medidas entren en conflicto con los derechos humanos.
Incluso Edward Snowden se ha pronunciado respecto a esta clase de medidas, afirmando que los gobiernos podrían aprovecharse de la emergencia para adoptar medidas autoritarias que podrían ser instituidas de forma permanente sin la adecuada vigilancia de la sociedad civil
THE MOST SECURE CLOUD BACKUP COMPANY WAS HACKED; 135 MILLION FILES LEAKED JUST ON WORLD BACKUP DAY
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/02/the-most-secure-cloud-backup-company-was-hacked-135-million-files-leaked-just-on-world-backup-day/
Although supposedly “unhackeable” products and solutions constantly appear in the market, cyber security consulting experts and even cybercriminals are responsible for demonstrating that there is no such thing. This is what happened to a cloud backup service provider, marketed as “the most secure in the world”, which has leaked a considerable amount of information from its individual and corporate customers, right at the commemoration of World Security Backup Day.
SOS Online Backup, headquartered in California, US, is a cloud services company with presence on the five continents. According to reports from vpnMentor researchers, the company’s staff accidentally exposed online the personal records of more than 135 million of its users.
Cyber security consulting specialists discovered more than 70 GB of company-operated data, including details such as:
- Full names
- Usernames
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Internal business customer details

SOURCE: vpnMentor
Specialists find the company’s stance on the incident particularly disturbing. Although the information leak was detected in November 2019, the company never responded to alerts sent by cyber security consulting experts; access to compromised information was also not disabled after its discovery. The experts sent two subsequent alerts in December 2019, which were also not answered.
Finally, the database was secured by SOS Online Backup during the last days of 2019. It is not known whether any unauthorized users accessed the information before access was disabled.
Among the undesirable scenarios, the worst is that this information ends up for sale in some hacking forum hosted on dark web, mentioned the researchers of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS).
On the possible causes of the incident, it most likely occurred due to misconfiguration of security. Cybersecurity specialist Raif Mehmet predicts that these errors will continue to be present as long as companies ignore the implementation of appropriate IT security policies. Configuration errors have been, without, and will continue to be the main causes of these incidents.
IT SEEMS THAT HACKERS ALWAYS HAD A BACKDOOR AT MARRIOTT; ONCE AGAIN, PRIVATE DATA OF MILLIONS OF CUSTOMERS IS LEAKED
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/04/01/it-seems-that-hackers-always-had-a-backdoor-at-marriott-once-again-private-data-of-millions-of-customers-is-leaked/
Nearly two years ago, researchers from a pentesting course company revealed that the Marriott hotel chain had been the victim of one of the largest data breach incidents recorded so far, compromising personal information of around 500 million customers of the Starwood subsidiary.
When everyone thought Marriott would have already implemented the necessary measures to prevent these incidents from happening again, a report has been leaked stating that the company has suffered a new data breach that compromised the information of nearly 2.5 millions of users.
According to the experts of the pentesting course company, this incident occurred in mid-January because a threat actor managed to extract the login credentials of one of the employees of the hotel chain, entering multiple systems of guest storage. Among the data presented are details such as:
- Full names
- Addresses
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Dates of birth
- Booking data
Anomalous activity went unnoticed by Marriott’s IT security teams for weeks; Finally, during the last days of February, the company detected the intrusion, disabled compromised access and began an investigation into the incident to notify all potentially affected users.
Although no one denies that the hotel chain should be held accounted for for the security of its users’ information, it should be noted that these recent incidents initiated as attacks against third-party companies providing some administrative services to Marriott, so they didn’t compromise their internal networks. As experts from a pentesting course company point out, the 2018 incident was due to the attack on Starwood databases, which would be acquired by Marriott shortly thereafter.
The International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) says the most recent incident affected about 5.2 million customers in the chain, all members of its loyalty program; the company is in the process of notifying potentially affected customers.
Users concerned about the security status of their personal information may also check the platform Marriott has put online to resolve questions related to this incident, although this may not be the best of the ideas given by the recent history of data protection of the company.
LA EMPRESA DE RESPALDO EN LA NUBE MÁS SEGURA FUE HACKEADA; FILTRAN 135 MILLONES DE ARCHIVOS JUSTO EL DÍA MUNDIAL DEL RESPALDO DE SEGURIDAD
Aunque constantemente aparecen productos y soluciones supuestamente “inhackeables”, los expertos en consultoría de ciberseguridad e incluso los cibercriminales se encargan de demostrar que no existe tal cosa. Esto le ha ocurrido a un proveedor de servicios de respaldo en la nube, promocionado como “el más seguro del mundo”, el cual ha filtrado una cantidad considerable de información de sus clientes, justo en la conmemoración del Día Mundial del Respaldo de Seguridad.
SOS Online Backup, con sede en California, E.U., es una empresa de servicios en la nube con presencia en los cinco continentes. De acuerdo con los reportes de investigadores de vpnMentor, el personal de la compañía expuso en línea los registros personales de más de 35 millones de sus usuarios.
Los especialistas en consultoría de ciberseguridad descubrieron más de 70 GB de datos resguardados por la compañía, entre los que se encuentran detalles como:
- Nombres completos
- Nombres de usuario
- Direcciones email
- Números telefónicos
- Detalles internos de clientes empresariales

FUENTE: vpnMentor
A los especialistas les parece especialmente preocupante la postura adoptada por la compañía respecto al incidente. A pesar de que la fuga de información fue detectada en noviembre de 2019, la compañía nunca respondió a las alertas enviadas por los expertos en consultoría de ciberseguridad; el acceso a la información comprometida tampoco fue inhabilitado después de su descubrimiento. Los expertos enviaron dos alertas posteriores en diciembre de 2019, que tampoco fueron respondidas.
Finalmente, la base de datos fue asegurada por SOS Online Backup durante los últimos días de 2019. Se desconoce si algún usuario no autorizado accedió a la información antes de que el acceso fuera inhabilitado.
Entre los escenarios indeseables, el peor es que esta información termine a la venta en algún foro de hacking alojado en dark web, mencionan los investigadores del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
Sobre las posibles causas del incidente, lo más probable es que haya ocurrido debido a una configuración de seguridad errónea. Raif Mehmet, especialista en ciberseguridad, prevé que estos errores seguirán presentándose en tanto las empresas pasen por alto la implementación de adecuadas políticas de seguridad informática. Los errores de configuración han sido, sin, y seguirán siendo las principales causas de estos incidentes.
PARECE QUE LOS HACKERS SIEMPRE TUVIERON UN BACKDOOR EN MARRIOTT; UNA VEZ MÁS, SE FILTRAN DATOS PRIVADOS DE MILLONES DE CLIENTES
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/hacking-incidentes/parece-que-los-hackers-siempre-tuvieron-un-backdoor-en-marriott-una-vez-mas-se-filtran-datos-privados-de-millones-de-clientes/
Hace casi dos años, investigadores de una empresas de pentest revelaron que la cadena hotelera Marriott había sido víctima de uno de los incidentes de brechas de datos más grandes registrados hasta ahora, comprometiendo la información personal de alrededor de 500 millones de clientes de la subsidiaria Starwood.
Cuando todos pensaban que Marriott ya habría implementado las medidas necesarias para evitar que estos incidentes ocurrieran de nuevo, se ha filtrado un reporte que afirma que la compañía ha sufrido una nueva brecha de datos que comprometió la información de casi 2.5 millones de usuarios.
De acuerdo con los expertos de la empresa de pentest, este incidente ocurrió a mediados de enero debido a que un actor de amenazas logró extraer las credenciales de inicio de sesión de uno de los empleados de la cadena hotelera, ingresando a múltiples sistemas de almacenamiento de información de los huéspedes. Entre los datos expuestos se encuentran detalles como:
- Nombres completos
- Domicilios
- Direcciones email
- Números de teléfono
- Fechas de nacimiento
- Datos de reservaciones
La actividad anómala pasó desapercibida para los equipos de seguridad TI de Marriott por semanas; finalmente, durante los últimos días de febrero, la empresa detectó la intrusión, inhabilitó el acceso comprometido y comenzó una investigación sobre el incidente para notificar a todos los usuarios potencialmente afectados.
A pesar de que nadie niega que la cadena hotelera deba responder por la seguridad de la información de sus usuarios, cabe señalar que estos recientes incidentes iniciaron como ataques contra compañías de terceros que prestaban algunos servicios administrativos a Marriott, por lo que no se comprometieron sus redes internas. Como señalan expertos de una empresa de pentest, el incidente de 2018 se debió al ataque a las bases de datos de Starwood, la cual sería adquirida por Marriott poco tiempo después.
El Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) asegura que el más reciente incidente afectó a alrededor de 5.2 millones de clientes de la cadena, todos miembros de su programa de lealtad; la compañía está en proceso de notificar a los clientes potencialmente afectados.
Los usuarios preocupados por el estado de la seguridad de su información personal también pueden consultar la plataforma que Marriott ha puesto en línea para resolver las dudas relacionadas con este incidente, aunque puede que esta no sea la mejor de las ideas dado el historial reciente de protección de datos de la empresa.