Month: March 2022
RAGNARLOCKER RANSOMWARE ENCRYPTS THE INFORMATION OF 52 CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE AGENCIES IN THE US
RagnarLocker is a ransomware operation first detected in 2020 and has remained active despite constant changes and measures implemented by governments around the world against such groups.
Since the beginning of 2022, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) has identified at least 52 ransomware-infected organizations in 10 critical infrastructure sectors, including manufacturing, financial services, energy, information technology and government entities.

RagnarLocker is easily identifiable as it uses the “.RGNR_<ID>” extension, where <ID> is a hash of the computer’s NETBIOS name. Once the encryption process has been completed, threat actors leave a ransom note with instructions for making the payment and decrypting the affected information. RagnarLocker uses VMProtect, UPX, and custom packaging algorithms and is deployed within an attacker’s custom Windows XP virtual machine at a target’s site.
Ragnar Locker also uses the GetLocaleInfoW Windows API to identify the location of the infected machine. If the potential victim is identified as being of Azerbaijani, Armenian, Belarusian, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Moldovan, Tajik, Russian, Turkmen, Uzbek, Ukrainian, or Georgian origin, the process will be cut short.
The malware then iterates through all executed services and terminates the services employed by managed service providers for remote network administration. The malware will also attempt to remove all shadow copies, preventing victims from recovering the compromised files.
Finally, RagnarLocker encrypts all available files of interest. Instead of choosing which files to encrypt, RagnarLocker chooses which folders will be left unencrypted, so the affected devices will continue to work normally while hundreds of victims’ files are infected in the background.
The FBI considers RagnarLocker to be an active threat and whose activity could be highly damaging to critical U.S. infrastructure, so system administrators should implement some of the following recommendations:
- Enable offline backups of critical data
- Do not share critical information from a compromised network.
- Use multi-factor authentication and strong passwords, including for remote access services
- Keep computers, devices and applications always updated to the latest version available
The Agency also recommends not negotiating with cybercriminal groups, as this can sometimes result in a worst-case scenario for victims.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
3 XSS VULNERABILITIES IN IBM SECURITY QRADAR SOAR: UPDATE IMMEDIATELY
Cybersecurity specialists reported the detection of multiple vulnerabilities in IBM Security QRadar SOAR. According to the report, successful exploitation of these flaws would allow the deployment of severe attack scenarios.
Below are brief descriptions of the reported flaws, in addition to their tracking keys and scorings assigned according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
CVE-2021-41182: The insufficient sanitization of values passed as the `altField` option of the Datepicker widget would allow remote attackers to inject and run arbitrary JavaScript code in affected users’ browsers.
This is a medium severity flaw and received a CVSS score of 5.3/10.
CVE-2021-41183: The insufficient sanitization of user-supplied data when processing values of various `*Text` options would allow remote attackers to pass specially crafted inputs to the library, thus running arbitrary JavaScript code in affected users’ browsers.
The flaw received a 5.3/10 CVSS score.
CVE-2021-41184: Insufficient sanitization of values passed to the `of` option would allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript code in affected users’ browsers.
This is a medium severity flaw and received a CVSS score of 5.3/10.
Even though these vulnerabilities can be exploited by remote non-authenticated attackers via the Internet, there are no active exploitation reports related to the flaws described herein. Nonetheless, information security specialists recommend updating as soon as possible.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
IMPORTANT VULNERABILITY IN CYBERARK IDENTITY SECURITY SOLUTION
Cybersecurity specialists report the detection of a critical vulnerability in Cyberark Identity, a trusted partner for many leading organizations that allows implementing defense measures against cyberattacks, enabling digital businesses and boosting the operational efficiency of an organization. According to the report, exploiting this vulnerability would allow threat actors to access sensitive information.
Tracked as CVE-2022-22700, the flaw exists due to the exposure of the “X-CFY-TX-TM” response header in the “StartAuthentication” resource. This would allow remote threat actors to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information on the affected system.
This is a medium severity vulnerability and received a score of 4.8/10 according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
According to the report, the flaw lies in version 22.1 of Cyberark Identity.
While the flaw can be exploited remotely by unauthenticated threat actors, so far no active exploitation attempts or the existence of a malware variant associated with the attack have been detected. Still, users of affected deployments are encouraged to upgrade as soon as possible.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
3 CRITICAL VULNERABILITIES IN APC UPS COULD BE EXPLOITED TO SHOT DOWN THOUSANDS OF DATA CENTERS
Cybersecurity specialists report the detection of three zero-day vulnerabilities in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) devices developed by APC, a subsidiary of the well known tech company Schneider Electric. The set of vulnerabilities, dubbed as TLStorm, resides in APC Smart-UPS devices, very popular in sectors such as industry, commerce and computer security.
The security firm Armis, in charge of this finding, mentions that two of the reported flaws, tracked as CVE-2022-22805 and CVE-2022-22806 reside in the implementation of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, which connects Smart-UPS SmartConnect devices with the Schneider Electric management cloud.
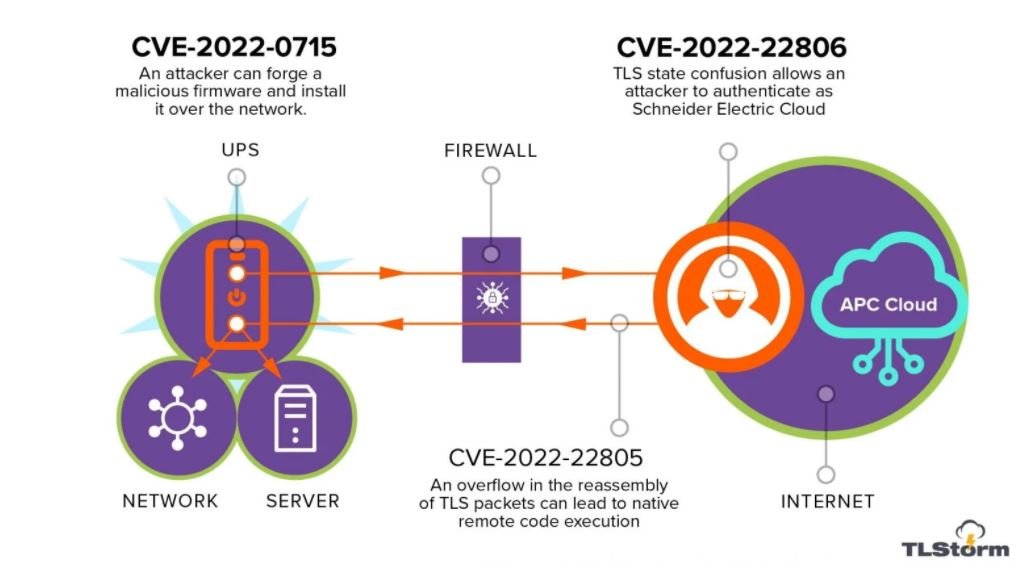
On the other hand, the flaw tracked as CVE-2022-0715 relates to the firmware of almost all Smart-UPS devices, which is not cryptographically signed and its authenticity cannot be verified during its installation on the system.
This absence of signature would allow threat actors to create a malicious version of the firmware and deliver it as an update to the affected UPS devices, leading to a remote code execution (RCE) scenario.
During testing, the researchers were able to exploit the flaw and create a malicious APC firmware version that was accepted by Smart-UPS devices as an official update. The consequences of the attack vary depending on the affected device:
- Smart-UPS devices that feature SmartConnect cloud connection functionality can be upgraded from the cloud management console
- Older Smart-UPS devices that use the Network Management Card (NMC) can be upgraded over the local network
- Most Smart-UPS devices can also be upgraded via a USB drive
Vulnerable APC UPS units are used in approximately eight out of 10 companies, so malicious exploitation of these vulnerabilities could have a major impact on various industries. To increase the risk, Armis points out that the reported TLS failures appear to be much more serious than previously thought, as they could be exploited in zero-click attacks without the interaction of the target user.
Users of affected devices are advised to adhere to the recommendations issued by the firm to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
MOST WATCHED VIDEOS ON VEVO IN 2021
Although the official data hasn’t been updated in a while, we can safely say that Vevo is the world’s number one premium music video and original content provider. The platform has been working with artists to bring their music closer to a global audience. From industry legends to emerging artists, Vevo provides a global platform where everyone can find and grow their audience.
MOST POPULAR US AND GLOBAL VIDEOS ON VEVO IN 2021
As always, the world’s leading music video network recently released a review of the year behind us, highlighting the most viewed music videos of 2021. The platform also had a chance to work together with some of these artists and create original content exclusive to Vevo viewers.
Just as a reminder, the platform is available in the UK, United States, Australia, Brazil, Canada, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, Philippines, and Spain. If your country is not on this list, you can use Vevo proxies to access the platform and enjoy your favorite videos. You’ll also be helping your favorite artists since Vevo pays artists more than other platforms.
US TOP 10 VIDEOS BY VIEW COUNT
Weeknd’s “Save Your Tears” tops both lists, which is no surprise. The incredible Superbowl performance we all still remember, followed by Billboard, Juno, and BRIT award wins, significantly fueled the song’s popularity and ensured a stellar year for the global superstar. The list features a lot of first-timers, from Lil Nas X to Olivia Rodrigo, the only artist who took two slots this year. According to Vevo’s data, Olivia’s viewership increased eight times in 2021.
- The Weeknd with “Save Your Tears”, 102.9M views
- Lil Baby with “On Me”, 94.0M views
- Lil Nas X with “MONTERO (Call Me By Your Name)”, 91.3M views
- Polo G with “Rapstar”, 86.9M views
- DJ Khaled, Lil Baby, Lil Durk with “Every Chance I get”, 80.0M views
- Olivia Rodrigo with “Drivers License”, 79.9M views
- Olivia Rodrigo with “Good 4 U”, 64.8M views
- Doja Cat and SZA with “Kiss Me More”, 63.2M views
- Coi Leray and Lil Durk with “No More Parties (remix)”, 59.7M views
- Justin Bieber, Daniel Caesar, Giveon with “Peaches”, 442M views
GLOBAL TOP 10 VIDEOS BY VIEW COUNT
Moving on to the global list, the numbers get even more impressive. Weeknd still has a strong lead, followed by Latin superstars Karol G and Marian Angeliq, with Black Eyed Peas and Shakira at number three. “Peaches” by Justin Bieber, an instant fan favorite since its March 19 release, took fourth place, followed by the country music sensation Lil Nas X at number five.
- The Weeknd with “Save Your Tears”, 615M views
- KAROL G and Mariah Angeliq with “EL MAKINON”, 556M views
- Black Eyed Peas and Shakira with “GIRL LIKE ME”, 519M views
- Justin Bieber, Daniel Caesar, Giveon with “Peaches”, 442M views
- Lil Nas X with “MONTERO (Call Me By Your Name)”, 402M views
- J Balvin and Maria Becerra with “Qué Más Pues?”, 384M views
- The Kid LAROI and Justin Bieber with “STAY”, 371M views
- Sebastián Yatra and Myke Towers with “Pareja de Año”, 334M views
- KAROL G, Anuel AA, J Balvin with “LOCATION”, 331M views
- Olivia Rodrigo with “Drivers License”, 325M views
MORE VEVO STATS
If you watched your favorite music video online in the past decade, it’s probably thanks to Vevo. With over 26 billion views every month, one billion daily views, and users spending 1.5 billion hours watching videos on the platform, Vevo is a true music industry powerhouse. Most people know about it from the YouTube channels and subchannels.
However, that’s not all. Vevo also has a Roku channel with over 15,000 videos and playlists, an app for Apple TV, Samsung TV Plus, Alexa-enabled gadgets, Amazon Fire TV devices, Sky Q, Pluto TV, Now TV, and Xumo.
LET THE MUSIC PLAY
No matter how you look at it, streaming is growing. Video hosting sites are popping up faster than ever, so everyone can find something they can enjoy. It’s important to note that all of these platforms have limited availability and are often unavailable in different parts of the world. If you’re looking for a safe way to enjoy content on your favorite platform, be it Vimeo or any other, click here for more information.
MILLIONS OF HP LAPTOPS, POINTS OF SALE MACHINES AND SERVERS AFFECTED BY 16 CRITICAL VULNERABILITIES
A report by cybersecurity firm Binarly points to the detection of 16 critical vulnerabilities in various implementations of Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), present in multiple HP enterprise devices. According to the researchers, threat actors can exploit these flaws to implant firmware capable of evading UEFI Secure Boot, Intel Boot Guard, and virtualization-based security measures.
Affected devices include HP enterprise deployments such as laptops, desktops, point-of-sale systems, and edge computing nodes: “Exploiting detected flaws would allow threat actors to execute privileged code on firmware and even deliver persistent malicious code that survives operating system reinstallations,” Binarly reports.
This is the list of vulnerabilities described in the report:
- CVE-2021-39297: DXE stack buffer overflow that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2021-39298: SMM call that would trigger privilege escalation
- CVE-2021-39299: DXE stack buffer overflow for arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2021-39300: DXE stack overflow that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2021-39301: DXE stack overflow for arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23924: SMM heap buffer overflow for arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23925: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23926: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23927: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23928: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23929: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23930: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23931: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
- CVE-2022-23932: SMM call that would allow privilege escalation
- CVE-2022-23933: SMM call that would allow privilege escalation
- CVE-2022-23934: SMM memory corruption that would allow arbitrary code execution
The most dangerous vulnerabilities in this report are memory corruption errors in the System Management Mode firmware feature. Threat actors could exploit these flaws to execute arbitrary code with high privileges on affected systems.
The company recommends installing HP UEFI firmware security updates, issued in February, to address the reported vulnerabilities.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
1 OUT OF 3 WORDPRESS PLUGINS DOES NOT RECEIVE SECURITY UPDATES; MILLIONS OF WEBSITES AT RISK
A report specialized in WordPress security points to a 150% increase in reported flaws during 2021 compared to the previous year, in addition to establishing that almost 30% of the vulnerabilities detected in plugins for WordPress do not receive updates.
Since this is the most widely used content management system (CMS) in the world, this should be a worrisome issue for tens of millions of website administrators.
According to Patchstack specialists, of all the flaws reported in 2021, only 0.58% resided in the WordPress core, while the rest affect themes and plugins created by dozens of developers. In addition, about 92% of these flaws are in free plugins, while paid plugins were affected by 8.6% of the failures reported last year.
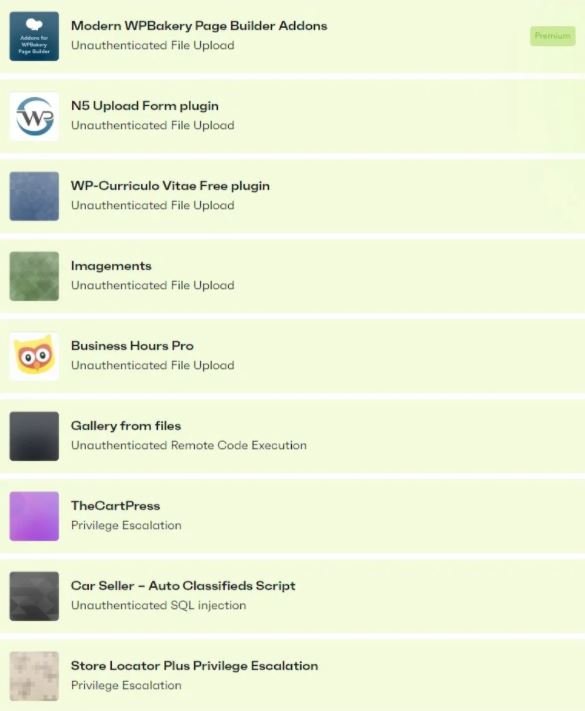
Of all the vulnerabilities reported in that time period, five critical bugs were detected in 55 WordPress themes, most of them related to the abuse of the file upload feature.

Regarding plugins, 35 critical vulnerabilities were reported, two of which could be present in up to 4 million websites.
Some of the security issues in WordPress that caught the most attention of researchers reside in Optimonster, a plugin used in about 1 million websites, and in All in One, an SEO plugin with more than 3 million active installations.
Although these critical vulnerabilities were fixed, nine other plugins with millions of installations never received updates for the severe security flaws detected over the past year. In addition to uploading potentially malicious files, these plugins are affected by privilege escalation flaws and SQL injections.
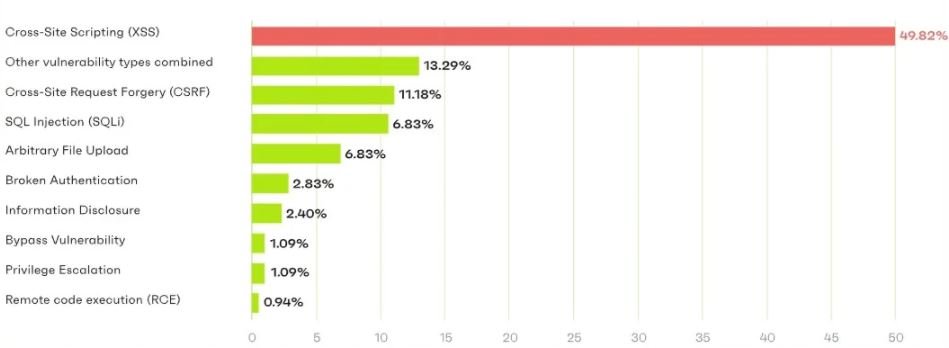
On the most common security issues in WordPress plugins, the researchers note that cross-site scripting (XSS) errors are the most reported, followed by request spoofing flaws, SQL injections, and arbitrary file loading into the system.
Faced with this situation, experts recommend that website administrators acquire paid versions of plugins, use as few tools as possible on their platform and keep their plugins always updated to the latest version available, which will considerably mitigate their exposure to this kind of security risks.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
VODAFONE HACKED BY LAPSUS$ CYBERCRIME GROUP? INVESTIGATION GOING ON
In a message shared with an international media outlet, phone operator Vodafone confirmed it is investigating reports of an alleged data breach revealed by hackers from cybercriminal group Lapsus$.
Through their Telegram channel, the alleged hackers published a survey for their subscribers to decide what the next leak of the group would be after revealing confidential information from chipmaker NVIDIA. Among the options was a supposed 200 GB file storing Vodafone’s source code.
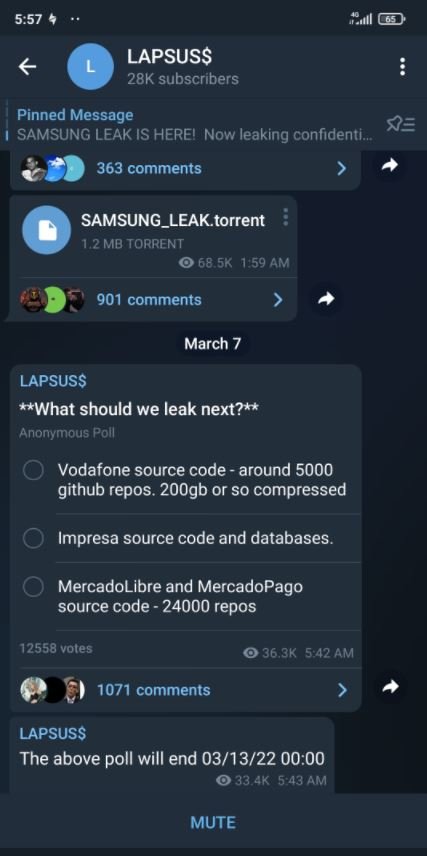
The survey also included as options the source code and databases of the Portuguese media firm Impresa, and the source code of MercadoLibre, the e-commerce giant based in Argentina. Subscribers to the Telegram channel seem to prefer that data be leaked from Vodafone, which was leading the vote at the time of writing.
In its message, the telecommunications company says it is aware of Lapsus$’s threats: “We are investigating these reports together with the police; at the moment we cannot affirm the veracity of this report. However, we are in a position to state that, in general, the types of repositories referenced in the complaint contain proprietary source code and do not contain data from our customers.”
Operating from somewhere in South America, Lapsus$ has hogged cybersecurity reports in recent weeks. In addition to the attack on NVIDIA, hackers reportedly managed to compromise Samsung’s systems, stealing snippets of the source code used in the Galaxy family of smartphones and other sensitive details.
To the misfortune of its users, Vodafone has become a frequent target for hacking groups. A few weeks ago, the firm confirmed that its branch in Portugal suffered a cyberattack that interrupted its services for a long time, ensuring that the leak did not involve personal information of its clients.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
A MEMBER OF ONE OF THE MOST DANGEROUS HACKING GROUPS HAS BEEN ARRESTED
A court in Ontario, Canada has sentenced Sebastien Vachon-Desjardins to seven years in prison after pleading guilty to participating as an affiliate in the dangerous NetWalker ransomware operation. The defendant reportedly pleaded guilty to five criminal charges, including data theft, extortion, conspiracy to commit fraud and illegal access to protected computer systems.
In addition to the time he must spend in prison, the accused must return a part of the damages caused by his attacks, accept the seizure of his property and spend a period of supervised release. Vachon-Desjardins would have been involved in at least 17 ransomware attacks, generating losses of about $2.8 million USD.
In 2020, Canadian authorities began receiving reports related to NetWalker’s activity, sent by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). Authorities in the U.S. believed there was a group affiliated with the ransomware operation working from Quebec. Thanks to the collection of IP addresses, online accounts, aliases, email addresses and logs from Apple, Google, Microsoft and Mega.nz, the researchers were able to identify Vachon-Desjardins.
The defendant was arrested in Florida a couple of months ago, when the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) released a report claiming that NetWalker’s unit in Canada managed to raise up to $27.5 million USD, targeting organizations such as Northwest Territories Power Corporation, College of Nurses of Ontario and a large local tire store.

Although the defendant claimed that about 1,200 Bitcoin passed through his electronic wallet, investigators have only been able to seize 720 cryptocurrencies from Vachon-Desjardins’ accounts, since the defendant managed to convert part of these assets into cash. During his arrest, Vachon-Desjardins had more than half a million dollars in cash in his possession.
For the authorities, this arrest and sentence are not minor incidents: “The defendant was not an insignificant actor in these and other crimes, as he played a dominant role and helped NetWalker and other affiliates improve their ability to extort money from their victims and launder their illegal profits,” says G. Paul Renwick, the Canadian judge in charge of the case.
Renwick notes that the defendant already had a criminal record related to drug charges, being sentenced to 3 1/2 years in prison in 2015.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CHECK THE INTEGRITY OF THE BROWSER EXTENSION USING THIS WHATSAPP TOOL BEFORE RUNNING WHATSAPP WEB
Users of the WhatsApp version for laptops and desktops will now be able to use a browser extension to check the integrity of the software running on their browser. This project was born as part of a collaborative project between Meta and Cloudflare.
End-to-end encryption in WhatsApp protects users’ messages from being read by intermediaries, although you can never have enough security, especially considering that things can change when users turn to the web version of the messaging app.
The extension was dubbed Code Verify and, according to Meta software engineer Richard Hansen, is based on a browser security feature called “subsource integrity,” which allows browsers to check if the files obtained have been altered in any way.
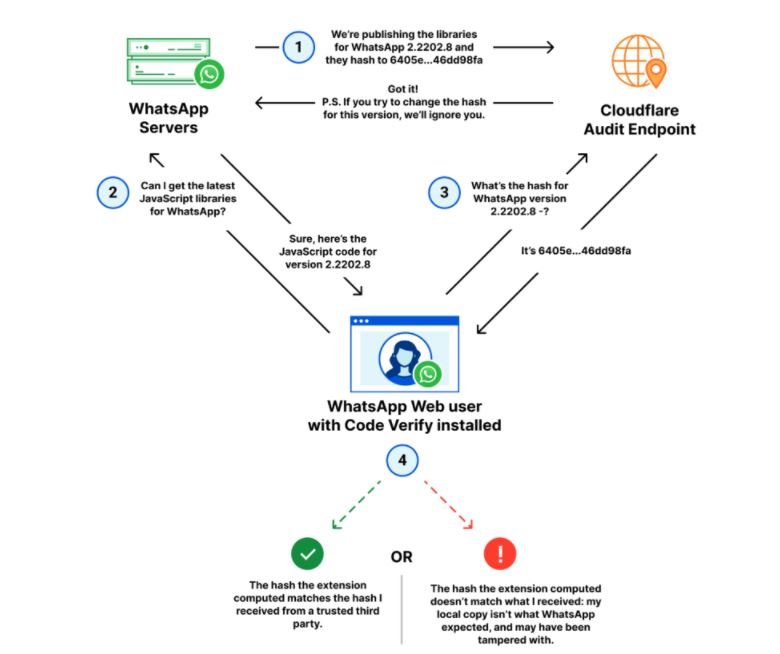
Code Verify analyzes the JavaScript code in WhatsApp Web, a process for which Cloudflare’s collaboration is required, since the high amount of resources required for a complete verification exceeds the capabilities of WhatsApp: “Cloudflare has a hash of the code that WhatsApp users should execute,” says the report on this extension.
When users run WhatsApp in their browser, WhatsApp’s code verification extension compares a hash of that code running in their browser to Cloudflare’s hash, allowing you to easily check if the code you’re running is the correct code.
At the moment, Code Verify is available for Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox, with plans to expand to Safari in the short term. The tool runs immediately after installation to start validating WhatsApp JavaScript libraries. The green indicator confirms that everything is valid, orange if the page needs to be updated or another extension interferes with Code Verify, and red if a hash discrepancy has been detected, indicating a possible compromise.
This integrity verification extension could make users of WhatsApp and other services that implement Code Verity less likely to install extensions that alter social media functions and raise potential security issues, strengthening the user experience in terms of cybersecurity.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
EL FBI ADVIERTE SOBRE GRUPOS DE ESTAFADORES HACIÉNDOSE PASAR POR FUNCIONARIOS GUBERNAMENTALES Y AGENCIAS COMO LA CRUZ ROJA PARA ROBAR MILLONES
Este lunes, el Buró Federal de Investigaciones (FBI), a través del Centro de Quejas de Delitos en Internet (IC3), emitió una alerta de seguridad sobre algunos grupos cibercriminales haciéndose pasar por funcionarios gubernamentales o agencias de la ley en un intento de extorsionar a los usuarios y robar información confidencial. La Agencia menciona que los estafadores están falsificando números de teléfono y nombres auténticos de funcionarios y agentes.
Este reporte asegura que los atacantes usan un tono agresivo y con sentido de urgencia, asegurando que enfrentan un problema legal y negándose a hablar o dejar un mensaje con cualquier persona que no sea el usuario afectado, además de que tratan de que las víctimas no hablen sobre este intento de extorsión con familiares, amigos o policías de verdad.
Los atacantes exigen pagos en diversas formas, incluyendo tarjetas prepagadas, transferencias electrónicas y depósitos bancarios en efectivo. En los casos de transferencias en efectivo, a menudo son enviadas a cuentas en el extranjero, haciendo muy difícil un posible rastreo.

En la mayoría de los casos, los falsos agentes aseguran a las víctimas potenciales que su identidad se usó en un delito, por lo que procederán a solicitar su número de seguro social y fecha de nacimiento. Algunas víctimas son amenazadas con arrestos o cargos penales si no brindan la información o realizan los pagos exigidos.
En otras ocasiones, los atacantes pueden incluso enviar mensajes de texto a las víctimas haciéndose pasar por agencias gubernamentales que necesitan un pasaporte o la información de la licencia de conducir del conductor para la renovación de documentos o una supuesta campaña de prevención de fraude o de recolección para la Cruz Roja.
El FBI ha reiterado en múltiples ocasiones que ni sus agentes ni otras agencias de investigación o entidades gubernamentales solicitan dinero o información confidencial de los usuarios, por lo que piden encarecidamente a las personas tener cuidado con quién comparten su información personal por teléfono y en línea.
Por otra parte, Erich Kron, especialista en ciberseguridad de KnowBe4, señaló que la ingeniería social y las estafas a menudo se basan en provocar un gran impacto emocional en las víctimas, lo que dificulta que las potenciales víctimas puedan responder adecuadamente ante el intento de extorsión: “Pocas agencias gubernamentales causan tanto miedo como las instituciones de impuestos, lo que hace que las personas cometan errores al interactuar con estos cibercriminales”.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
IMPORTANTE VULNERABILIDAD EN LA SOLUCIÓN DE SEGURIDAD CYBERARK IDENTITY
Especialistas en ciberseguridad reportan la detección de una vulnerabilidad en Cyberark Identity, un socio de confianza para muchas organizaciones líderes que permite implementar medidas de defensa contra ciberataques, habilitar negocios digitales e impulsar la eficiencia operativa de una organización. Según el reporte, la explotación de esta vulnerabilidad permitiría a los actores de amenazas acceder a información sensible.
Identificada como CVE-2022-22700, la falla existe debido a la exposición del encabezado de respuesta “X-CFY-TX-TM” en el recurso “StartAuthentication”. Esto permitiría a los actores de amenazas remotos obtener acceso no autorizado a información confidencial en el sistema afectado.
Esta es una vulnerabilidad de severidad media y recibió un puntaje de 4.8/10 según el Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
Según el reporte, la falla reside en la versión 22.1 de Cyberark Identity.
Si bien la falla puede ser explotada de forma remota por actores de amenazas no autenticados, hasta el momento no se han detectado intentos de explotación activa o la existencia de una variante de malware asociada al ataque. Aún así, se recomienda a los usuarios de implementaciones afectadas actualizar a la brevedad.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
“REGALO DEL DÍA INTERNACIONAL DE LA MUJER AMAZON 2022”: LA NUEVA ESTAFA CON LA QUE LOS CIBERCRIMINALES BUSCAN RECOLECTAR INFORMACIÓN DE MILLONES DE PERSONAS
Desde esta mañana, miles de usuarios de WhatsApp en todo el mundo han estado recibiendo mensajes supuestamente enviados por Amazon en los que se les ofrecen falsas ofertas por el Día Internacional de la Mujer, en lo que parece un intento más que obvio de fraude electrónico.
Especialistas en ciberseguridad mencionan que estos mensajes contienen un enlace que redirige a los usuarios a un sitio web donde se les ofrece participar en una breve encuesta para tener la oportunidad de ganar un regalo en conmemoración de este día. El sitio web donde se aloja la encuesta no está asociado a Amazon en ninguna forma.

Según los expertos, existen múltiples indicios que sugieren que esta es una campaña fraudulenta:
- El nombre de dominio asociado a la campaña fueron registrados apenas hace un par de días
- Se han notado múltiples redirecciones entre los enlaces
- El sitio web ofrece un premio demasiado atractivo a cambio de prácticamente nada
- Hay errores gramaticales notables en el sitio web de la encuesta
Una vez completada esta encuesta, aparecerá un formulario solicitando a los usuarios engañados algunos datos adicionales, incluyendo nombres completos, direcciones email, números telefónicos y otros detalles de identificación personal. Los investigadores señalan que, a todas luces, esta debe ser considerada una campaña de recolección de información.
Por el momento no hay evidencia de que esta campaña también involucre el uso de malware para desplegar ataques posteriores en los dispositivos afectados.
Durante las pruebas, los expertos notaron que el enlace redirige a los usuarios a una página de ERROR 404 si el enlace es abierto en una laptop o computadora de escritorio. Sin embargo, si el enlace se abre en un dispositivo móvil, la campaña funciona bien, lo que indica que los cibercriminales a cargo de esta campaña se dirigen principalmente a los usuarios de telefonía móvil.
Los especialistas recomiendan a los usuarios de telefonía móvil evadir esta clase de mensajes, ya que un ataque exitoso podría comprometer todo el sistema, permitiendo a los actores de amenazas tomar control de funciones fundamentales en el dispositivo o acceder a información confidencial.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
3 VULNERABILIDADES CRÍTICAS EXPLOTABLES EN APC UPS PERMITIRÍAN CERRAR MILES DE CENTROS DE DATOS
Especialistas en ciberseguridad reportan la detección de tres vulnerabilidades día cero en los dispositivos de suministro de energía ininterrumpida (UPS) desarrollados por APC, firma subsidiaria de Schneider Electric. El conjunto de vulnerabilidades, identificadas como TLStorm, reside en los dispositivos APC Smart-UPS, muy populares en sectores como la industria, el comercio y la seguridad informática.
La firma de seguridad Armis, a cargo de este hallazgo, menciona que dos de las fallas reportadas, identificadas como CVE-2022-22805 y CVE-2022-22806 residen en la implementación del protocolo Transport Layer Security (TLS), que conecta los dispositivos Smart-UPS SmartConnect con la nube de gestión Schneider Electric.

Por otra parte, la falla conocida como CVE-2022-0715 se relaciona con el firmware de casi todos los dispositivos Smart-UPS, el cual no está firmado criptográficamente y su autenticidad no se puede verificar durante su instalación en el sistema.
Esta ausencia de firma permitiría a los actores de amenazas crear una versión maliciosa del firmware y entregarla como una actualización a los dispositivos UPS afectados, llevando a un escenario de ejecución remota de código (RCE).
Durante las pruebas, los investigadores pudieron explotar la falla y crear una versión de firmware de APC maliciosa que fue aceptada por los dispositivos Smart-UPS como una actualización oficial. Las consecuencias del ataque varían dependiendo del dispositivo afectado:
- Los dispositivos Smart-UPS que cuentan con la funcionalidad de conexión a la nube SmartConnect se pueden actualizar desde la consola de administración de la nube
- Los dispositivos Smart-UPS más antiguos que usan la tarjeta de administración de red (NMC) se pueden actualizar a través de la red local
- La mayoría de los dispositivos Smart-UPS también se pueden actualizar mediante una unidad USB
Las unidades UPS de APC vulnerables se utilizan en aproximadamente ocho de cada 10 empresas, por lo que la explotación maliciosa de estas vulnerabilidades podrís tener un gran impacto en diversas industrias. Para incrementar el riesgo, Armis señala que las fallas TLS reportadas parecen ser mucho más graves de lo que se pensaba, pues podrían ser explotadas en ataques de cero clics sin la interacción del usuario objetivo.
Se recomienda a los usuarios de dispositivos afectados apegarse a las recomendaciones emitidas por la firma para mitigar el riesgo de explotación.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
MILLONES DE LAPTOPS, PUNTOS DE VENTA Y SERVIDORES HP AFECTADOS POR 16 VULNERABILIDADES CRÍTICAS
Un reporte de la firma de ciberseguridad Binarly señala la detección de 16 vulnerabilidades críticas en diversas implementaciones de interfaz de firmware extensible unificada (UEFI), presentes en múltiples dispositivos empresariales de HP. Según los investigadores, los actores de amenazas pueden explotar estas fallas para implantar un firmware capaz de evadir el arranque seguro UEFI, Intel Boot Guard y las medidas de seguridad basadas en la virtualización.
Entre los dispositivos afectados se incluyen implementaciones empresariales de HP como laptops, equipos de escritorio, sistemas de punto de venta y nodos informáticos perimetrales: “La explotación de las fallas detectadas permitiría a los actores de amenazas realizar ejecutar código privilegiado en el firmware e incluso entregar un código malicioso persistente que sobrevive a las reinstalaciones del sistema operativo”, reporta Binarly.
Esta es la lista de vulnerabilidades descritas en el reporte:
- CVE-2021-39297: Desbordamiento de búfer de pila DXE que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2021-39298: llamada de SMM que desencadenaría una escalada de privilegios
- CVE-2021-39299: Desbordamiento de búfer de pila DXE para la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2021-39300: Desbordamiento de pila DXE que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2021-39301: Desbordamiento de pila DXE para la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23924: Desbordamiento del búfer de almacenamiento dinámico de SMM para la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23925: Corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23926: corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23927: corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23928: corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23929: corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23930: corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
- CVE-2022-23931: corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de códigoarbitrario
- CVE-2022-23932: llamada de SMM que permitiría la escalada de privilegios
- CVE-2022-23933: llamada de SMM que permitiría la escalada de privilegios
- CVE-2022-23934: corrupción de memoria SMM que permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario
Las vulnerabilidades más peligrosas en este reporte son errores de corrupción de memoria en la función del firmware System Management Mode. Los actores de amenazas podrían explotar estas fallas para ejecutar código arbitrario con altos privilegios en los sistemas afectados.
La compañía recomienda instalar las actualizaciones de seguridad de HP UEFI Firmware, emitidas en febrero, para abordar las vulnerabilidades reportadas.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
1 DE CADA 3 PLUGINS DE WORDPRESS NO RECIBE ACTUALIZACIONES DE SEGURIDAD; MILLONES DE SITIOS WEB EN RIESGO
Un reporte especializado en seguridad de WordPress señala un incremento del 150% en las fallas reportadas durante 2021 en comparación con el año anterior, además de establecer que casi el 30% de las vulnerabilidades detectadas en plugins para WordPress no reciben actualizaciones.
Dado que este es el sistema de administración de contenido (CMS) más usado del mundo, este debería ser un problema preocupante para decenas de millones de administradores de sitios web.
Acorde a los especialistas de Patchstack, de todas las fallas reportadas en 2021, solo el 0.58% residían en el núcleo de WordPress, mientras que el resto afectan a los temas y plugins creados por decenas de desarrolladores. Además, cerca del 92% de estas fallas se encuentran en plugins gratuitos, mientras que los plugins de paga se vieron afectados por el 8.6% de las fallas reportadas el año pasado.
De entre todas las vulnerabilidades reportadas en ese periodo de tiempo, se detectaron cinco errores críticos en 55 temas de WordPress, la mayoría de ellos relacionados con el abuso a la función de carga de archivos.

Respecto a los plugins, se informaron 35 vulnerabilidades críticas, dos de las cuales podrían estar presentes en hasta 4 millones de sitios web.

Algunos de los problemas de seguridad en WordPress que más llamaron la atención de los investigadores residen en Optimonster, un plugin usado en unos 1 millón de sitios web, y en All in One, un plugin SEO con más de 3 millones de instalaciones activas.
A pesar de que estas vulnerabilidades críticas fueron corregidas, otros nueve plugins con millones de instalaciones nunca recibieron actualizaciones para los severos errores de seguridad detectados a lo largo del año pasado. Además de la carga de archivos potencialmente maliciosos, estos plugins se ven afectados por fallas de escalada de privilegios e inyecciones SQL.

Sobre los problemas de seguridad más comunes en plugins para WordPress, los investigadores señalan que los errores de scripts entre sitios (XSS) son los más reportados, seguidos por las fallas de falsificación de solicitudes, inyecciones SQL y carga arbitraria de archivos en el sistema.
Ante esta situación, los expertos recomiendan a los administradores de sitios web adquirir las versiones de paga de los plugins, usar el menor número de herramientas posible en su plataforma y mantener sus plugins siempre actualizados a la más reciente versión disponible, lo que mitigará considerablemente su exposición a esta clase de riesgos de seguridad.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
¿VODAFONE HACKEADA POR LAPSUS$ GROUP? INVESTIGACIÓN EN CURSO
En un mensaje compartido con un medio de comunicación internacional, la operadora telefónica Vodafone confirmó que está investigando los reportes sobre una presunta brecha de datos revelada por los hackers del grupo cibercriminal Lapsus$.
A través de su canal de Telegram, los presuntos hackers publicaron una encuesta para que sus suscriptores decidieran cuál sería la siguiente filtración del grupo después de revelar información confidencial del fabricante de chips NVIDIA. Entre las opciones destacaba un supuesto archivo de 200 GB almacenando el código fuente de Vodafone.

En la encuesta también se incluían como opciones el código fuente y las bases de datos de la firma de medios portuguesa Impresa, y el código fuente de MercadoLibre, el gigante del e-commerce con sede en Argentina. Los suscriptores al canal de Telegram parecen preferir que se filtren los datos de Vodafone, que encabezaba la votación al momento de redacción de este artículo.
En su mensaje, la compañía de telecomunicaciones dice estar al tanto de las amenazas de Lapsus$: “Estamos investigando estos reportes junto con la policía; por el momento no podemos afirmar la veracidad de este reporte. Sin embargo, estamos en condiciones de afirmar que, en general, los tipos de repositorios a los que se hace referencia en el reclamo contienen un código fuente patentado y no contienen datos de nuestros clientes”.
Operando desde algún punto en Sudamérica, Lapsus$ ha acaparado los reportes de ciberseguridad durante las últimas semanas. Además del ataque a NVIDIA, los hackers habrían logrado comprometer los sistemas de Samsung, robando fragmentos del código fuente usado en la familia de smartphones Galaxy y otros detalles confidenciales.
Para infortunio de sus usuarios, Vodafone se ha convertido en un objetivo frecuente para los grupos de hacking. Hace unas semanas, la firma confirmó que su rama en Portugal sufrió un ciberataque que interrumpió sus servicios de forma prolongada, asegurando que la filtración no involucró información personal de sus clientes.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
SITIOS WEB DE LAS AGENCIAS FEDERALES RUSAS FUERON HACKEADOS EN UN ATAQUE DE CADENA DE SUMINISTRO MEDIANTE UN PROGRAMA UTILIZADO PARA EL CONTEO DE USUARIOS
Múltiples agencias federales en Rusia han sufrido interrupciones en sus servicios desde hace días como parte de los ciberataques en represalia a la invasión rusa en Ucrania. Según un reporte oficial reciente, la mayoría de estas interrupciones fueron producto del hackeo contra un sistema de monitoreo de sitios web estatales, mantenido por el Ministerio de Desarrollo Económico.
El Ministerio de Desarrollo Digital, Comunicaciones y Medios de Comunicación de Rusia asegura que estos sistemas han sido restablecidos en su totalidad: “Los sitios web de las agencias estatales están bajo una seria protección y vigilancia las 24 horas por parte de los equipos de ciberseguridad. Es difícil comprometer estos sitios web directamente, por lo que los hackers atacan los recursos a través de servicios externos”, mencionó un portavoz del Ministerio en entrevista para Interfax.
Anonymous y otros grupos responsables de estos ataques habrían comprometido un widget instalado en los sitios web de los organismos estatales desde una fuente externa. En este caso, los hackers abusaron de un widget usado para recopilar las estadísticas de visitantes: “Después de hackear el widget, los atacantes pudieron publicar contenido incorrecto en las páginas de los sitios web. El incidente fue identificado y contenido de inmediato”, agrega el informe.
Actualmente, los sitios web de las agencias estatales rusas se mantienen funcionando correctamente. El contenido, incluyendo las solicitudes de los usuarios y los datos personales, permaneció intacto y bajo una protección total de sus respectivos administradores, señala el Ministerio de Desarrollo Digital.
En días anteriores se reportó que múltiples grupos de hacking habían atacado con éxito los sitios web del Servicio Penitenciario Federal, el Servicio Federal de Alguaciles, el Servicio Federal Antimonopolio, el Ministerio de Cultura, el Ministerio de Energía, el Servicio de Estadísticas del Estado Federal y otras plataformas.
Además de estos ataques, se reportaron incidentes contra algunos canales de televisión pública en Rusia y contra dos plataformas de streaming locales, cuyas señales fueron explotadas para transmitir imágenes de la invasión en Ucrania.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
UN MIEMBRO DE UNO DE LOS GRUPOS DE HACKING MÁS PELIGROSOS HA SIDO ARRESTADO
Un tribunal de Ontario, Canadá ha sentenciado a siete años de prisión a Sebastien Vachon-Desjardins después de declararse culpable de participar como afiliado a la peligrosa operación de ransomware NetWalker. Según se ha reportado, el acusado se declaró culpable de cinco cargos criminales, incluyendo robo de datos, extorsión, conspiración para cometer fraude y acceso ilegal a sistemas informáticos protegidos.
Además del tiempo que deberá pasar en la cárcel, el acusado deberá restituir una parte de los daños provocados por sus ataques, aceptar la incautación de sus bienes y pasar un periodo de libertad supervisada. Vachon-Desjardins habría estado involucrado en al menos 17 ataques de ransomware, generando pérdidas por unos $2.8 millones USD.
En 2020, las autoridades canadienses comenzaron a recibir informes relacionados con la actividad de NetWalker, enviados por el Buró Federal de Investigaciones (FBI). Las autoridades en E.U. creían que había un grupo afiliado a la operación de ransomware trabajando desde Quebec. Gracias a la recopilación de direcciones IP, cuentas en línea, alias, direcciones email y registros de Apple, Google, Microsoft y Mega.nz, los investigadores lograron identificar a Vachon-Desjardins.
El acusado fue arrestado en Florida hace un par de meses, cuando el Departamento de Justicia de E.U. (DOJ) publicóun informe afirmando que la unidad de NetWalker en Canadá logró recaudar hasta $27.5 millones USD, atacando a organizaciones como Northwest Territories Power Corporation, College of Nurses of Ontario y una gran tienda de neumáticos local.

Aunque el acusado aseguraba que por su billetera electrónica pasaron unos 1,200 Bitcoin, los investigadores solo han podido incautar 720 criptomonedas de las cuentas de Vachon-Desjardins, ya que el acusado logró convertir parte de estos activos en efectivo. Durante su arresto, Vachon-Desjardins tenía más de medio millón de dólares en efectivo en su posesión.
Para las autoridades, este arresto y sentencia no son incidentes menores: “El acusado no era un actor insignificante en estos y otros delitos, pues desempeñó un papel dominante y ayudó a NetWalker y a otros afiliados a mejorar su capacidad para extorsionar a sus víctimas y lavar sus ganancias ilegales”, menciona G. Paul Renwick, juez canadiense a cargo del caso.
Renwick señala que el acusado ya tenía antecedentes penales relacionados con cargos de drogas, siendo sentenciado a 3 años y medio de prisión en 2015.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VERIFIQUE LA INTEGRIDAD DE SU NAVEGADOR USANDO ESTA HERRAMIENTA ANTES DE EJECUTAR WHATSAPP WEB
Los usuarios de la versión de WhatsApp para laptops y equipos de escritorio ahora podrán usar una extensión de navegador para verificar la integridad del software ejecutado en su navegador. Este proyecto nace como parte de un proyecto de colaboración entre Meta y Cloudflare.
El cifrado de extremo a extremo en WhatsApp protege los mensajes de los usuarios para que no sean leídos por intermediarios, aunque nunca se puede tener suficiente seguridad, especialmente considerando que las cosas pueden cambiar cuando los usuarios recurren a la versión web de la app de mensajería.
La extensión fue bautizada como Code Verify y, según el ingeniero de software de Meta Richard Hansen, está basada en una característica de seguridad del navegador llamada “integridad de subfuente”, que permite a los navegadores verificar si los archivos obtenidos han sido alterados de algún modo.

Code Verify analiza el código JavaScript en WhatsApp Web, un proceso para el que se requiere la colaboración de Cloudflare, pues la alta cantidad de recursos requeridos para una verificación completa sobrepasa las capacidades de WhatsApp: “Cloudflare tiene un hash del código que los usuarios de WhatsApp deberían ejecutar”, señala el reporte sobre esta extensión.
Cuando los usuarios ejecutan WhatsApp en su navegador, la extensión de verificación de código de WhatsApp compara un hash de ese código que se ejecuta en su navegador con el hash de Cloudflare, permitiendo comprobar fácilmente si el código que se está ejecutando es el código correcto.
Por el momento, Code Verify está disponible para Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge y Mozilla Firefox, con planes para expandirse a Safari a corto plazo. La herramienta se ejecuta inmediatamente después de su instalación para comenzar a validar las bibliotecas de JavaScript de WhatsApp. El indicador verde confirma que todo es válido, naranja si la página debe actualizarse u otra extensión interfiere con Code Verify y rojo si se ha detectado una discrepancia de hash, lo que indica un posible compromiso.
Esta extensión de verificación de integridad podría hacer que los usuarios de WhatsApp y otros servicios que implementan Code Verity sean menos propensos a instalar extensiones que alteran funciones de las redes sociales y plantean posibles problemas de seguridad, fortaleciendo la experiencia de usuario en términos de ciberseguridad.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
