Month: November 2018
MULTA DE 1.2 MILLONES PARA UBER POR ATRASO EN REPORTE DE INCIDENTE DE SEGURIDAD

Investigadores afirman que este incidente comprometió los buckets de Amazon S3 de la empresa
Uber Technologies decidió no revelar una violación de datos acontecida en 2016, decisión que sigue generando problemas para la plataforma de servicio de transporte.
Según reportes de expertos en forense digital, Uber ha sido multada por un monto de 1.2 millones de dólares, cantidad establecida por las autoridades reguladoras de datos de Reino Unido y Holanda, acusando a la empresa de políticas de seguridad de datos inadecuadas, así como por no informar en tiempo y forma sobre la violación de datos que la empresa sufrió. Las autoridades sostienen que este incidente, que la empresa tardó un año en reportar, expuso a los conductores y usuarios de Uber a un mayor riesgo de fraude cibernético.
El incidente comprometió la información personal de más de 50 millones de usuarios y 3 millones de conductores de Uber en todo el mundo, incluyendo nombres, direcciones de email y números de teléfono. Acorde a especialistas en forense digital, en algunos casos incluso se filtraron datos de ubicación, tokens de acceso y contraseñas de los usuarios. El incidente ocurrió en octubre de 2016, pero Uber la mantuvo en secreto hasta noviembre de 2017.
La Oficina del Comisionado de Información (ICO) del Reino Unido, encargada del cumplimiento con las leyes de protección de datos en territorio británico, ha multado a Uber con 385 mil libras. La ICO mencionó que el incidente ocurrió debido a “una serie de fallas” en la infraestructura de TI de Uber, agregando que cerca de 3 millones de usuarios de Uber en Reino Unido se vieron afectados por el incidente.
“La investigación de la ICO descubrió que la violación de datos fue posible gracias a la técnica de “relleno de credenciales” (credential stuffing), proceso mediante el cual los nombres de usuario y contraseñas se inyectan masivamente en un sitio web hasta que coinciden con una cuenta existente. Uber utiliza Amazon Web Services Simple Storage Service (S3), un servicio de almacenamiento basado en la nube, donde se resguarda su información.
Un atacante pudo acceder a múltiples buckets S3 de Uber debido a que el equipo de TI de la empresa dejó las credenciales de acceso a S3 en el código que fue cargado a GitHub, la popular plataforma de desarrollo y uso compartido de código. “El acceso a la cuenta en S3 de Uber se encontraba en un archivo de texto almacenado en GitHub”, mencionó la ICO.
Por su parte, Autoriteit Persoonsgegevens, la autoridad reguladora en materia de protección de datos de Holanda, impuso a Uber una multa de 600 mil libras por violar la legislación holandesa de seguridad de la información. “La empresa fue multada por no informar sobre la violación de datos dentro de las 72 horas posteriores al descubrimiento del incidente”, reportaron las autoridades de Holanda. Se calcula que cerca de 174 mil usuarios holandeses fueron afectados por el robo de datos.
La violación de datos ocurrió mientras Travis Kalanick se desempeñaba como CEO de Uber, pero se mantuvo en secreto hasta noviembre de 2017, luego de que Dara Khosrowshahi asumiera como CEO, quien ordenó se realizara una investigación forense digital.
A la postre, se supo que Uber había pagado 100 mil dólares a un joven hacker de Florida por concepto de un “reporte de bug” como parte de su programa de recompensas. Sin embargo, las autoridades creen que el hacker había descubierto la violación de datos, y el pago que realizó la empresa se trataba de un soborno para mantener el incidente en secreto.
La violación de datos ocurrió antes de la entrada en vigor del Reglamento General de Protección de Datos de la Unión Europea (GDPR), por lo que Uber fue sancionada acorde a lo establecido en la Ley de Privacidad de Datos de Reino Unido, promulgada en 1998. Las multas impuestas acorde a esta ley no pueden exceder los 500 mil dólares.
FILTRAR DATOS USANDO SMART BULBS

Un equipo de investigadores ha desarrollado un par de apps que se aprovechan de las funcionalidades de los smart bulbs para extracción de datos
Los investigadores una firma de ciberseguridad y forense digital desarrollaron dos aplicaciones móviles que explotan las características de los smart bulbs (bombillas inteligentes) para la exfiltración de datos, informan expertos del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética.
Los expertos utilizaron los smart bulbs Magic Blue, que cuentan con la característica de comunicación vía Bluetooth 4.0. Los dispositivos son fabricados por una compañía china, llamada Zengge y pueden ser controlados mediante aplicaciones de Android y iOS. La compañía cuenta con clientes importantes, como Philips, entre otras.
Los especialistas en forense digital centraron su estudio en dispositivos que utilizan el Protocolo de Atributos de Baja Energía (ATT) para establecer la comunicación.
El primer test llevado a cabo por los expertos consistió en detectar la comunicación entre los smart bulbs y la aplicación móvil de emparejamiento. El método de emparejamiento utilizado por los investigadores es Just Works.
Los expertos en forense digital emparejaron un teléfono móvil con sistema operativo Android con la aplicación iLight y comenzaron a detectar el tráfico mientras utilizaban la función de cambio de colores del smart bulb.
De esta manera, el equipo encargado de la investigación encontró los comandos enviados por la aplicación móvil a los smart bulbs. El equipo realizó una ingeniería inversa de la aplicación móvil utilizando una herramienta llamada jadx.
Una vez que consiguieron control completo sobre el dispositivo, los especialistas comenzaron a desarrollar una aplicación que se aprovecha de la luz de los smart bulbs para transferir información entre el dispositivo comprometido y el atacante.
En su informe de la prueba de concepto, los especialistas mencionaron: “Nuestro plan para la exfiltración de datos era usar la luz de estos dispositivos como un medio de transferencia de información desde el dispositivo comprometido hasta la ubicación del atacante. La luz alcanza distancias más amplias, que era nuestra principal meta”.
“Imaginemos el siguiente escenario: un smartphone BLE es comprometido con alguna variante de malware para robar las credenciales del usuario. La información robada podría ser enviada a un atacante utilizando un smart bulb BLE en una ubicación cercana”. En su ataque, los expertos utilizaron un smartphone conectado a un telescopio para recibir los datos filtrados sin levantar sospechas del usuario.
Fue necesaria la creación de dos apps para la filtración de datos, una se instaló en el smartphone de la víctima, y la otra en el dispositivo móvil del atacante para recibir e interpretar los datos filtrados.
“Creamos dos aplicaciones, la primera para enviar los datos exfiltrados y la segunda para recibirlos. La aplicación que transmite la información cambia la intensidad de la luz azul en el smartphone. La aplicación tiene dos modalidades: modo normal y modo silencioso. El primero puede ser visible para el ojo humano, pero el modo silencioso es muy difícil de detectar debido a las variaciones de los tonos de azul utilizados”, mencionaron los expertos.
“Estos métodos son funcionales en cada smart bulb que permita que un atacante tome control sobre esta. En el futuro, nos gustaría crear una mejor prueba de concepto que nos permita probar una base de datos de smart bulbs vulnerables, también hemos considerado la implementación de inteligencia artificial para aprender sobre otras clases de smart bulbs”, concluyeron los expertos.
FACEBOOK EXTIENDE SU PROGRAMA DE RECOMPENSAS POR REPORTE DE VULNERABILIDADES

La red social pagaría hasta 40 mil dólares por reportes de errores que permitan el robo de cuentas de usuarios
En medio de una crisis de imagen por las críticas de usuarios y autoridades reguladoras sobre su política de protección de datos, Facebook ha anunciado la expansión de su programa de recompensas por reporte de errores para expertos en hacking ético y forense digital. Los hackers de sombrero blanco podrían ganar hasta 40 mil dólares por reportar un bug, dependiendo de su gravedad e interacción del usuario requerida.
El anuncio fue publicado en la página de reporte de errores de la empresa, donde Facebook ha invitado a los hackers éticos a tratar de penetrar en la plataforma en cualquier forma imaginable para buscar errores antes de que los hackers maliciosos los encuentren. Aunque el programa de recompensas de Facebook lleva activo más de 7 años, la red social nunca ha estado exenta de ataques o fugas de información. Acorde a expertos en forense digital del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética, este es el más reciente esfuerzo de la empresa para evitar que sigan presentándose incidentes de seguridad que atenten contra su imagen.
“Para alentar a los investigadores de seguridad a trabajar en la búsqueda de problemas de alto impacto, hemos incrementado el pago promedio de los errores robo de cuentas. Nuestro objetivo es garantizar que estas vulnerabilidades, como la revelada en septiembre pasado, sean de conocimiento de Facebook de forma oportuna y responsable”, menciona el comunicado de la empresa.
Ahora la empresa pagará 40 mil dólares si el bug no requiere interacción del usuario para su explotación, en tanto que el pago por reportes de errores que requieren interacción mínima del usuario alcanzaría los 25 mil dólares.
Acorde a expertos en forense digital, este programa se extenderá a otros servicios propiedad de la red social, incluidos Instagram, WhatsApp y Oculus. No se requerirá que los hackers éticos presenten una cadena de explotación completa si el proceso requiere eludir el mecanismo Linkshism, de Facebook. La empresa quiere que los hackers puedan compartir la prueba de concepto de su error sin tener que vulnerar capas de seguridad adicionales.
“Incrementando las recompensas por vulnerabilidades de robo de cuentas y disminuyendo la carga técnica necesaria en cada reporte de bug, esperamos recibir un mayor número de solicitudes para el programa de recompensas, aumentando la calidad de los trabajos de investigación en colaboración con los hackers de sombrero blanco, ayudándonos a proteger a más de 2 mil millones de usuarios de los diferentes servicios de Facebook”, finaliza el comunicado.
$1.2M USD FINE FOR UBER BECAUSE OF DELAY OF DATA BREACH REPORT

Researchers claim that this incident compromised the company’s Amazon S3 buckets
Uber Technologies decided not to disclose a data breach in 2016, a decision that keeps bringing bad news for the transport service platform.
According to reports of experts in digital forensics, Uber has been fined for an amount of $1.2M USD, amount established by the data regulatory authorities of the United Kingdom and the Netherlands, accusing the company of inadequate data security policies, as well as for not properly reporting the data breach that the company suffered two years ago. The authorities argue that this incident, which the company took a year to report, exposed Uber drivers and users to an increased risk of cyber fraud.
The incident compromised the personal information of over 50 million users and 3 million Uber drivers worldwide, including names, email addresses and phone numbers. According to specialists in digital forensics, in some cases attackers even leaked location data, access tokens and user passwords. The incident occurred in October 2016, but Uber kept it undisclosed until November 2017.
The United Kingdom Information Commissioner Office (ICO), in charge of compliance with data protection laws in British territory, has fined Uber with £385k. The ICO mentioned that the incident occurred because of “a series of flaws” in Uber IT infrastructure, adding that about 3 million of Uber users in the UK were affected by the incident.
“The ICO research found that data breach was possible thanks to the “credential stuffing” technique, a process by which usernames and passwords are injected massively into a website until they match with an existing account. Uber uses Amazon Web Services Simple Storage Service (S3), a cloud-based storage service, where its information is protected.
An attacker was able to access multiple Uber S3 buckets because the company IT team left the S3 access credentials in the code that was uploaded to GitHub, the popular code development and sharing platform. “Uber S3 account accesses were in a plain text file stored on GitHub,” the ICO mentioned.
On the other hand, Autoriteit Persoonsgegevens, the regulatory authority on data protection in Netherlands, imposed Uber a fine of £600k for violating the Dutch information security law. “The company was fined for not reporting the data breach within 72 hours after the discovery of the incident,” the Dutch authorities reported. It is estimated that about 174k Dutch users were affected by data theft.
Data breach occurred while Travis Kalanick served as Uber’s CEO, but remained undisclosed until November 2017, after Dara Khosrowshahi emerged as CEO, who ordered a digital forensics investigation.
In the end, it was learned that Uber had paid $100k USD to a young hacker from Florida for a “bug report” as part of its vulnerability bounty program. However, the authorities believe that the hacker had discovered the data breach, and the payment made by the company was a bribe to keep the incident a secret.
The data breach occurred before the entry into force of the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), so Uber was sanctioned in accordance with the provisions of the United Kingdom Data Privacy Act, promulgated in 1998. Fines imposed in accordance with this law may not exceed $500k USD.
LEAKING DATA WITH SMART BULBS

A team of researchers has developed a couple of apps that take advantage of the functionalities of smart bulbs for data leaking
Researchers from a cybersecurity and digital forensics firm developed two mobile applications that exploit the characteristics of smart bulbs for data exfiltration, as reported by experts from the International Institute of Cyber Security.
The experts used the Magic Blue smart bulbs, which feature the communication via Bluetooth 4.0. The devices are manufactured by a Chinese company, called Zengge and can be controlled by Android and iOS applications. The company has important clients, such as Philips, among others.
Digital forensics specialists focused their study on devices that use the Low-Energy Attribute Protocol (ATT) to establish communication.
The first test carried out by the experts consisted in detecting the communication between the smart bulbs and the pairing mobile app. The pairing method used by researchers is Just Works.
Digital forensics experts paired a mobile phone with an Android operating system with the iLightapplication and began detecting traffic while using the smart bulb’s color-changing feature.
In this way, the research team found the commands sent by the mobile application to the smart bulbs. The computer reverse-engineered the mobile application using a tool called JADX.
Once they got full control over the device, the specialists began to develop an app that takes advantage of the smart bulbs light to transfer information between the compromised device and the attacker.
In their proof-of-concept report, the specialists mentioned: “Our plan for data exfiltration was to use the light of these devices as a mean for transferring information from the compromised device to the attacker’s location. Light reaches wider distances, which was our main goal.”
“Let’s imagine the next scenario: a BLE smartphone gets compromised with some malware variant to steal the user’s credentials. Stolen information could be sent to an attacker using a BLE smart bulb in a nearby location.” In their attack, the experts used a smartphone connected to a telescope to receive the leaked data without raising the user’s suspicion.
It was necessary to create two apps for data leaking, one was installed on the victim’s smartphone, and the other on the attacker’s mobile device to receive and interpret the leaked data.
“We created two applications, the first to send the leaked data and the second one to receive them. The application that transmits the information changes the intensity of the blue light on the smart bulb. The app has two modalities: normal mode and silent mode. The first can be visible to the human eye, but the silent mode is very difficult to detect due to the variations of the shades of blue used,” the experts mentioned.
“These methods are functional in every smart bulb that allows an attacker to take control of them. In the future, we would like to create a better proof of concept that allows us to test a database of vulnerable smart bulbs, we have also considered the implementation of artificial intelligence to learn about other classes of smart bulbs,” the experts concluded.
FACEBOOK WILL PAY YOU $40K USD FOR REPORTING BUG

The social network would pay up to $40k USD for reporting errors that allow a single account takeover
In the middle of an image crisis because of critics of users and regulatory authorities on its data protection policy, Facebook has announced the expansion of its bug bounty program for experts in ethical hacking and digital forensics. White hat hackers could earn up to $40k USD for reporting a single bug, depending on its severity and required users’ interaction.
The announcement was posted on the company’s bounty program page, where Facebook has invited ethical hackers to try to get into its platform in any conceivable way, looking for never seen before bugs before malicious hackers find them. Although the Facebook bounty program has been active for over 7 years, the social network has never been free of attacks or information leaks. According to experts in digital forensics from the International Institute of Cyber Security, this is the most recent effort of the company to avoid continuing to present security incidents that threaten its image and business model.
“To encourage security investigators to work on the search for high-impact security issues, we have increased the average payment of account theft errors. Our goal is to ensure that these vulnerabilities, like the one revealed last September, are of Facebook knowledge in a timely and responsible way,” mentions the company’s statement.
Now the company will pay $40k USD if the bug does not require user interaction for its exploitation, while the payment for bug reports requiring minimum user interaction would reach $25k USD.
According to experts in digital forensics, this program will be extended to other services owned by the social network, including Instagram, WhatsApp and Oculus. Ethical hackers will not be required to present a full operating string if the process requires bypassing the Linkshism mechanism, by Facebook. The company wants hackers to be able to share the proof of concept of bug error without having to violate additional security layers.
“By increasing the rewards for account theft vulnerabilities and decreasing the required technical load in each bug report, we expect to receive a greater number of submits for the bounty program, increasing the quality of the work of research in collaboration with white hat hackers, helping to protect more than 2 billion users from the different Facebook services”, the statement ultimately mentions.
FOOTPRINTING USANDO DIG

El Domain Name Server (o Domain Name System) es un método distribuido que ayuda a las personas a recordar el nombre de cualquier sitio web. En general, los sitios web se alojan en servidores utilizando su dirección IP. Las personas no podrían recordar la dirección IP de un sitio (números) todo el tiempo. Ahí es donde el DNS ayuda. DNS convierte cualquier dirección IP en texto normal para que cualquiera pueda recordar la dirección de cualquier sitio web.
DNS actúa como una libreta de direcciones para Internet. Si conoce algún nombre de dirección en particular pero no conoce su dirección IP, puede buscarlo fácilmente en la libreta de direcciones. DNS funciona de la misma manera.
Por ejemplo, si un usuario visita (webimprints.com) en un navegador, la computadora utilizará el DNS para recibir la dirección IP del sitio web, que es 23.229.216.201.
Tipos de registro DNS
Los tipos de registro de DNS son generalmente utilizados por el editor de DNS (administradores de red) que realizan cambios en el servidor de nombres de dominio.
- A – MUESTRA LA DIRECCIÓN IP DEL HOST
- MX – MUESTRA SERVIDOR DE CORREO DE DOMINIO
- NS – MUESTRA EL SERVIDOR DE NOMBRE DEL HOST
- rDNS – MUESTRA EL REGISTRO DE DNS REVERSO
- VIEW ANY FILE – MAYORMENTE UTILIZADO EN BÚSQUEDA DE DNS
- PORT NO. – ESPECIFICANDO EL NUMERO DE PUERTO
- DNS PATH – MOSTRANDO EL DNS PATH
- IPV4 / IPV6 – MOSTRAR EN LAS DIRECCIONES IP
- SOA- MUESTRA EL REGISTRO DE SOA
Los tipos de registro DNS mencionados anteriormente se utilizan comúnmente para recopilar información sobre el sitio web.
DIG
DIG se utiliza para averiguar si el registro DNS está configurado correctamente o no.
Dig está disponible para Kali Linux por defecto.
- Para comenzar a usar Dig, vaya a Linux terminal. Simplemente escribiendo dig webimprints.com
- Escriba dig en el Terminal de Linux como se muestra en la captura de pantalla a continuación:

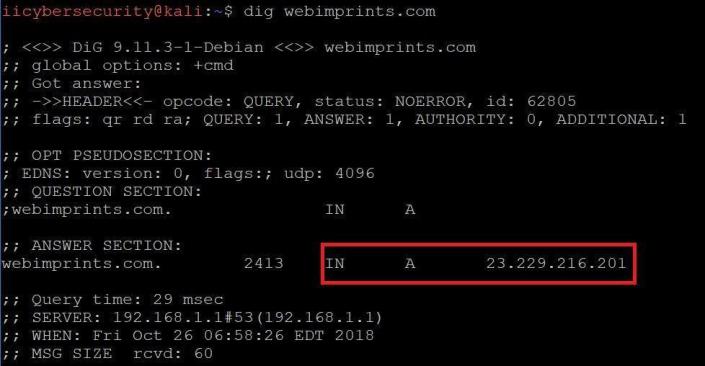
- En la pantalla de salida puede ver que webimprints.com muestra la dirección IP utilizando el registro A
Comprobar su servidor DNS en Linux
- Teclee cat /etc/resolv.conf.
- Puede ver más abajo las configuraciones DNS por defecto


Especificar servidor de nombre
- Después del comando anterior, teclee dig @ 192.168.1.1 webimprints.com


- En la salida anterior podemos ver el servidor de nombres especificado. En el nivel de raiz, debe haber algún servidor de nombres confiable configurado para responder a las consultas contra un nombre de dominio
- Los servidores de nombres que han sido designados por el registrador llevan el archivo de zona para el dominio. Los subdominios se configuran en servidores de nombres
Mostrando servidores de correo
- Teclee dig @192.168.1.1 webimprints.com MX


- En la captura de pantalla anterior se ve el servidor de correo webimprints.com. Este registro MX significa que el sitio web de webimprints.com tiene un registro de intercambio de correo
- Cada registro MX tiene su propia preferencia y los números más bajos tienen una preferencia más alta. Por lo tanto, cuando se envía el correo, se utiliza el registro MX con la preferencia más baja, si no se puede acceder al registro MX de la preferencia más baja que el registro MX con la siguiente preferencia alta. Sin embargo, si los registros tienen el mismo valor de preferencia MX, ambos registros MX se utilizarán simultáneamente
Registro DNS reverso
- Teclee dig –x 23.229.216.201 (direcciónnIP)


- El registro PTR permite que la consulta rDNS coincida con la dirección IP de un dominio. Funciona a la inversa del registro A
- El registro PTR permite la consulta RDNS (DNS inverso) para hacer coincidir la dirección IP con un dominio. Funciona frente a un registro A (Dirección). Tomemos por ejemplo 2 hosts:
Para 172.16.0.1:
Tipo: PTR
Host: 2Apunta a: host2.ejemplo.com
Para 172.16.0.2:
Tipo: PTRHost: 2
Apunta a: host2.ejemplo.com
Los registros de PTR se mostrarán en el Panel de control de esta manera:


- Después del registro PTR, asegúrese siempre de que los hosts mencionados deben tener registros A. En el ejemplo anterior, host1.example.com debe tener un registro apuntado a 172.16.0.1 y host2.ejemplo.com con 172.16.0.2
Ver un archivo
- Teclee dig –f query.txt +short


- Tiene que crear cualquier archivo. En ese archivo puede ingresar cualquier nombre de dominio. Este comando es útil en búsquedas masivas de DNS
- –f se usa en la lectura del archivo. + short se usa para ver solo las direcciones IP
Indicar cualquier número de puerto
- Teclear dig @8.8.8.8 –p 21 webimprints.com


- En la captura de pantalla anterior, puede especificar un puerto alternativo. Por alguna razón, un servidor de nombres externo está configurado para un puerto no estándar
- El servidor de nombres externo realmente escucha el tráfico en el puerto (21) especificado, y su firewall también debe permitir el tráfico, de lo contrario, la búsqueda fallará. Como puede ver, el tiempo de espera de la conexión se debe a que 8.8.8.8 no está configurado en un puerto aleatorio que es 21 como se muestra arriba en la captura de pantalla
Rastreo de DNS
- Teclee dig @8.8.8.8 webimprints.com +trace


- En la captura de pantalla anterior, al consultar webimprints.com, puede ver cómo el DNS hace su ruta. Primero irá a los servidores de nombres raíz, luego al dominio .com
Usar IPV4 o IPV6
- Teclee dig @8.8.8.8 -4 webimprints.com


- En la captura de pantalla anterior, utilice la consulta ipv4 para obtener el ipv4. Si quiere consultar ipv6 puedes -6 en lugar de -4
- Si desea ver el ipv6, debe configurar la red ipv6 para que funcione correctamente
Obtener el SOA
- Ingrese el comando dig @8.8.8.8 webimprints.com SOA


En la captura de pantalla anterior, el uso de la consulta SOA (State of Authority) muestra información simple sobre el dominio, la frecuencia con la que se actualiza y la última vez que se actualizó. Un archivo de zona solo puede contener un registro SOA
Según investigadores en hacking ético del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética, Dig es muy útil para el administrador de red en la fase de recopilación de información.
VIOLACIÓN DE DATOS EN OSISOFT

La empresa de software ha sufrido una violación de datos que habría comprometido todas las cuentas de dominio
OSIsoft ha emitido una alerta sobre una violación de seguridad que afecta a empleados, pasantes, consultores y contratistas, informan especialistas en seguridad informática y forense digital del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética.
La empresa ofrece soluciones de gestión de datos en tiempo real; su producto principal es la infraestructura de empresa abierta, PI System, que permite conectar datos, sistemas y personas con base en sensores. Los clientes de OSIsoft utilizan PI System para recopilar, analizar y visualizar datos para mejorar sus procesos internos, acorde a expertos en ciberseguridad y forense digital.
Los actores maliciosos utilizaron credenciales robadas para acceder de forma remota a los sistemas de la compañía, según lo reportado en la notificación del incidente que realizó la compañía, presentada ante la Oficina del Fiscal General de California.
“OSIsoft está experimentando un incidente de seguridad que podría afectar a empleados, pasantes, consultores y contratistas. Las credenciales robadas se utilizaron para acceder de forma remota a las computadoras de OSIsoft”, se menciona en el aviso de la violación de datos.
“Los expertos de forense digital de OSIsoft alertaron al equipo de TI sobre acciones anómalas en los sistemas de la empresa. Nuestro proveedor de servicios de seguridad informática ha recolectado evidencia directa del ataque, así como del robo de accesos, situación que involucra a 29 computadoras y 135 cuentas. La evidencia nos ha permitido concluir que todas las cuentas de dominio OSI han sido afectadas”.
Los hackers habrían accedido al nombre de la cuenta de inicio de sesión del dominio OSI, la dirección email y la contraseña del usuario. Aunque Active Directory (AD) utiliza métodos de protección criptográficos, las credenciales personales de los usuarios pueden haber sido comprometidas.
Gracias a la notificación que la empresa presentó ante el fiscal de California se ha podido saber que la empresa desconoce con exactitud cuándo se presentó el incidente, pues OSIsoft ha declarado que éste ocurrió en algún momento entre el 23 de marzo de 2017 y el 26 de julio de 2018.
La compañía todavía está investigando la violación de seguridad, mientras tanto, ha desarrollado una estrategia de mitigación de riesgos.
OSIsoft está restableciendo las contraseñas comprometidas, también exhorta a los usuarios afectados a cambiar sus contraseñas para otras plataformas en caso de que sean las mismas contraseñas que usan para su cuenta de OSI, además invitan al usuario a informar a la empresa sobre actividades sospechosas, además de desactivar o restringir las funciones de acceso remoto y uso compartido de archivos en sus dispositivos.
ESTADOS UNIDOS PIDE A NACIONES ALIADAS BOICOTEAR EMPRESAS CHINAS

El gobierno estadounidense se dice preocupado por la seguridad de su información
Acorde a reportes de especialistas en forense digital del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética, el gobierno estadounidense ha instado a sus aliados a dejar de utilizar cualquier dispositivo de telecomunicaciones desarrollado por Huawei, pues consideran que la empresa china representa una amenaza para la seguridad de su información y telecomunicaciones.
Fuentes cercanas al problema informan que los funcionarios estadounidenses están presionando a los países que albergan bases militares estadounidenses para prohibir el uso del equipo de Huawei en sus redes inalámbricas e Internet.
El ejército de Estados Unidos utiliza redes seguras para sus comunicaciones que involucran el envío de información más sensible, pero las autoridades se han mostrado preocupadas, pues gran parte de su tráfico aún se desplaza a través de redes comerciales en países como Alemania, Italia y Japón, reportan los especialistas en forense digital. Funcionarios estadounidenses se han reunido en reiteradas ocasiones con representantes gubernamentales y ejecutivos de telecomunicaciones en otros países, invitándolos a dejar de utilizar productos de Huawei en sus redes, ya sean de uso comercial o gubernamental.
Las autoridades estadounidenses consideran que los equipos de Huawei son más propensos a los ciberataques, además de que podrían permitir que el gobierno chino espíe las comunicaciones o deshabilite las conexiones de Internet de las Cosas (IoT).
Un funcionario estadounidense, que ha solicitado permanecer en el anonimato, declaró: “Nos encontramos colaborando continuamente con países de todo el mundo para establecer lineamientos sobre amenazas cibernéticas contra nuestras estructuras de telecomunicaciones. El panorama de seguridad informática se vuelve más complejo con la transición a la tecnología 5G, que está llevándose a cabo por múltiples gobiernos”.
Por su parte, Huawei ha declarado que sus equipos son utilizados por clientes en cerca de 200 países, además, 46 de las 50 empresas de telecomunicaciones más grandes del mundo han implementado el uso de dispositivos Huawei, por lo que no se le puede considerar una empresa poco confiable.
“En Huawei nos ha sorprendido la postura que ha adoptado el gobierno estadounidense. EU está tratando de extender esta postura más allá de su jurisdicción, lo que consideramos reprobable. Huawei cree firmemente que nuestros socios y clientes tomarán la decisión correcta basándose en su propio juicio y en el historial que respalda a la empresa”, mencionó recientemente un portavoz.
Los funcionarios de inteligencia de EU, por su parte, han expresado su preocupación por la seguridad de los productos fabricados por Huawei, además de ZTE, otra empresa china. Acorde a especialistas en forense digital, el Pentágono ordenó a las tiendas en sus bases militares que dejaran de vender los productos desarrollados por estas dos empresas, principalmente smartphones, pues los consideran amenazas a la seguridad cibernética estadounidense.
Algunos otros países aliados de EU ya han tomado medidas para limitar la participación de Huawei en sus infraestructuras. En agosto pasado, Huawei dio a conocer que el gobierno australiano había impedido su participación en las licitaciones para la implementación de tecnología 5G en su infraestructura de telecomunicaciones.
Esta situación se presenta en medio de un conflicto entre China y Estados Unidos, pues cada país ha impuesto tarifas arancelarias a los productos del otro. Los jefes de gobierno de ambos países se reunirán en breve.
USE DIG FOR FOOTPRINTING

Domain Name Server or we can say Domain Name System is a distributed method that helps humans to remember name of any website. Generally websites are hosted on servers using their IP Address. Humans cannot remember IP Address (numbers) all the time. That’s where DNS helps. DNS make any IP Address into normal text so anyone can remember the address of any website.
DNS acts like an Address book for the internet. If you know any particular address name but don’t know their IP Address you can easily look it up in the address book. DNS works the same way.
For Instance it can be taken if user visits (webimprints.com) in a browser, computer will use DNS to receive the website IP Address which is 23.229.216.201.
DNS RECORD TYPES:-
DNS record types are generally used by DNS editor (Network Admins) who make changes in Domain Name Server.
- A – SHOWS HOST IP ADDRESS
- MX – SHOWS TO DOMAIN MAIL SERVER
- NS – SHOWS HOST NAME SERVER
- rDNS – SHOWS REVERSE DNS LOOKUP
- VIEW ANY FILE – MOSTLY USED IN BULD DNS LOOKUPS.
- PORT NO. – SPECIFYING THE PORT NUMBER.
- DNS PATH – SHOWING THE DNS PATH.
- IPV4/IPV6 – SHOW IN THE IP ADDRESSES.
- SOA- SHOWS THE SOA RECORD.
The above mentioned DNS record types are commonly used to gather information about the website.
NOW THE DIG:-
DIG is used to figure out whether DNS record are configured properly or not.
By default Dig is available for Kali linux.
- To start using dig, go to linux terminal. By simply typing dig webimprints.com
- Type dig in the Linux Terminal as shown in screen shot below:

- In the output screen you can see that webimprints.com showing the IP address using A record.
TO CHECK YOUR DNS SERVER IN LINUX:-
- Type cat /etc/resolv.conf.
- You can see below the default configured DNS configures.

SPECIFYING NAME SERVER:-
- After above command type dig @192.168.1.1 webimprints.com

- In the above output we can see specified name server. At rooting level there should be some trustworthy name server configured to respond to queries against a domain name.
- NS which have been designated by registrar carries zone file for domain. Subdomain are configured in name servers.
SHOWING DOMAIN MAIL SERVERS:-
- Type dig @192.168.1.1 webimprints.com MX

- In the above screen shot you see webimprints.com mail server. This MX record means that website of webimprints.com is having mail exchange record.
- Each MX record have its own preference and the lower numbers have a higher preference. So when mail is sent is uses MX record with the lowest preference, if lowest preference MX record is not reachable than MX record with the next high preference will be used. However if the records have same value MX preference, both MX records will be used simultaneously.
SHOWING REVERSE DNS LOOKUP:-
Type dig –x 23.229.216.201 (IP address)

- PTR record allows rDNS query to match IP address to a domain. It works opposite to an A record.
- PTR record allows RDNS (Reverse DNS) query, to match IP address to a domain. It works opposite to an A (Address) record. Take for example 2 hosts:
- For 172.16.0.1:
Type: PTR
Host: 1
Points to: host1.example.com
- For 172.16.0.2:
Type: PTR
Host: 2
Points to: host2.example.com
The PTR records will be shown in Control Panel like this:

- After PTR record, always make sure that the hosts mentioned should have A records. In above example, host1.example.com should have A record pointed to 172.16.0.1 and host2.example.com with 172.16.0.2
VIEWING A FILE:-
Type dig –f query.txt +short.

- You have to create any file. In that file you can enter any domain name. This command is useful in bulk DNS lookups.
- –f is used in reading the file. +short is used to only see the IP addresses.
INDICATE ANY PORT NUMBER:-
Type dig @8.8.8.8 –p 21 webimprints.com

- In the above screenshot, you can specify an alternate port. For some reason an external name server is configured for non-standard port.
- External name server actually listening to traffic on port (21) specified, and its firewall also need to allow the traffic, otherwise lookup will fail. As you can see the connection time out because 8.8.8.8 is not configured on random port which is 21 as above in screenshot.
DNS TRACING:-
- Type dig @8.8.8.8 webimprints.com +trace

- In the above screen shot, querying webimprints.com you can see how DNS make its path. First it will go to root name servers, then .com domain.
USING IPV4 OR IPV6:-
- Type dig @8.8.8.8 -4 webimprints.com.

- In the above screen shot, using the ipv4 query to get the ipv4. If you want to query ipv6 you can -6 instead -4.
- If you want to see the ipv6 you have to configure ipv6 network to work correctly.
GETTING THE SOA:-
- Type dig @8.8.8.8 webimprints.com SOA.

- In the above screen shot, using the query SOA(State of authority) shows simple information about the domain like, how often it is updated, when it was last updated. A zone file can contain only one SOA record.
As per ethical hacking researcher of international institute of cyber security, dig is quite helpful for network administrator in information gathering phase.
DATA BREACH IN OSISOFT

The software company has suffered a data breach that would have compromised all the domain accounts
OSIsoft has issued an alert on a security breach affecting employees, interns, consultants and contractors, as reported by information security and digital forensics specialists from the International Institute of Cyber Security.
The company offers real-time data management solutions; its main product is the open enterprise infrastructure, PI System, which allows connecting data, systems and people based on sensors. OSIsoft customers use PI System to collect, analyze, and view data to improve their internal processes, according to experts in cybersecurity and digital forensics.
Malicious actors used stolen credentials to remotely access the company’s systems, as reported in the company’s incident notification, filed with the California Attorney General Office.
“OSIsoft is experiencing a security incident that could affect employees, interns, consultants and contractors. Stolen credentials were used to remotely access OSIsoft’s computers”, the company mentioned in the data breach notification.
“OSIsoft’s digital forensics experts alerted the IT team about anomalous actions in the company’s systems. Our information security service provider has collected direct evidence of the attack, as well as access theft, a situation involving 29 computers and 135 accounts. The evidence has allowed us to conclude that all OSI domain accounts have been affected”.
Threat actors would have accessed the OSI domain logon account name, email address, and user password. Although Active Directory (AD) uses cryptographic protection methods, users’ personal credentials may have been compromised.
Thanks to the notification that the company presented to the California prosecutor, it has been possible to know that the company is not exactly aware of when the incident was presented, since OSIsoft has stated that it occurred sometime between March 23 2017 and July 26 2018.
The company is still investigating the security breach, meanwhile, has developed a risk mitigation strategy.
OSIsoft is re-establishing committed passwords, also encourages affected users to change their passwords for other platforms if they are the same passwords they use for their OSI account, and invite the user to inform the enterprise on suspicious activities, as well as disabling or restricting remote access and file sharing functions on users’ devices.
U.S. ASKS ALLIES TO BOYCOTT CHINESE COMPANIES

The American Government is concerned about its information security
According to reports of specialists in digital forensics from the International Institute of Cyber Security, the US government has urged its allies to stop using any telecommunications device developed by Huawei, as they consider that the Chinese company poses a threat to the security of its information and telecommunications.
Sources close to the problem report that US officials are pressuring countries that host American military bases to prohibit the use of Huawei equipment on their wireless networks and Internet.
The United States Army uses secure networks for its communications involving the most sensitive information, but the authorities have been worried, as much of its traffic is still shifted through commercial networks in countries like Germany, Italy and Japan, reported the digital forensics specialists. US officials have repeatedly met with government representatives and telecom executives in other countries, inviting them to stop using Huawei products on their networks, whether for commercial or government use.
The US authorities believe that Huawei devices are more prone to cyberattacks, and that they could allow the Chinese government to spy on communications or disable the Internet of Things(IoT) connections.
An American official, who has requested to remain anonymous, stated: “We are continually collaborating with countries around the world to establish guidelines on cyberthreats against our telecommunications structures. The information security landscape becomes more complex with the transition to 5G technology, which is being carried out by multiple governments.”
On the other hand, Huawei has stated that its equipment is used by customers in about 200 countries; in addition, 46 out of the 50 largest telecom companies in the world have implemented the use of Huawei devices, so it cannot be considered an untrustworthy company.
“At Huawei we were surprised by the posture that the US government has taken. The US is trying to extend this stance beyond its jurisdiction, which we consider reprehensible. Huawei firmly believes that our partners and customers will make the right decision based on their own judgment and on the company’s background,” a spokesperson recently mentioned.
US intelligence officials have expressed concern about the safety of products manufactured by Huawei, in addition to ZTE, another Chinese company. According to specialists in digital forensics, last August the Pentagon ordered stores in their military bases to stop selling the products developed by these two companies, mainly smartphones, as they consider threats to American cybersecurity.
Some other EU-allied countries have already taken steps to cut Huawei’s involvement in their infrastructures. Last August, Huawei announced that the Australian Government had banned its participation in the bidding for the implementation of 5G technology in its telecommunications infrastructure.
This situation is present in the midst of a conflict between China and the United States, as each country has imposed tariff rates on the other’s products. The presidents of both countries will meet soon.
