Month: January 2020
LAS NACIONES UNIDAS DECLARAN QUE WHATSAPP ES EXTREMADAMENTE INSEGURO DE USAR
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/tecnologia/las-naciones-unidas-declaran-que-whatsapp-es-extremadamente-inseguro-de-usar/
Para el desarrollo de sus operaciones cotidianas, la Organización de las Naciones Unidas (ONU) emplea múltiples desarrollos tecnológicos con los más altos estándares de seguridad informática, incluso cuenta con un programa de recompensas para reportar vulnerabilidades en las soluciones de software de uso común.
Debido al carácter confidencial de muchos asuntos tratados por la ONU, no cualquier software o tecnología es elegible para la organización. Tal parece ser el caso de WhatsApp, servicio de mensajería considerado por la ONU como muy poco seguro para establecer comunicación entre los líderes mundiales.
Acorde a un reporte mencionado por Farhan Haq, portavoz del secretario general de la ONU, una firma de seguridad informática aconsejó a la organización a evitar el uso de WhatsApp debido a sus bajos estándares de seguridad: “Los altos funcionarios de la ONU han sido instruidos para evitar el uso de WhatsApp, cuyos servicios no cuentan con los mecanismos de seguridad necesarios”, mencionó Haq, después de que un reportero cuestionara el uso de esta plataforma de mensajería entre jefes de estado.

Al recibir preguntas respecto al hackeo del CEO de Amazon, Jeff Bezos, presuntamente perpetrado por la corona de Arabia Saudita mediante WhatsApp, Haq sólo comentó: “Hemos prestado la suficiente atención a los hechos conocidos; supervisaremos el desarrollo de esta situación”.
Hace algunos meses, un reporte de seguridad informática publicado en The Guardian reveló que el smartphone de Bezos fue comprometido usando un archivo malicioso que el empresario recibió a través de un chat de WhatsApp con Mohammed bin Salam Al Saud, heredero al trono saudí.
Aunque Arabia Saudita ha negado esas acusaciones en repetidas ocasiones, Agnes Callamar y David Kaye, relatores especiales de la ONU, solicitaron una investigación inmediata sobre el presunto hackeo. Los resultados finales aún no son presentados a los altos mandos de la ONU.
A pesar de que Facebook, compañía propietaria de WhatsApp, asegura que el servicio de mensajería es completamente seguro, el Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) ha publicado múltiples reportes sobre métodos de ataque contra este servicio, principalmente explotando WhatsApp Web, la versión para equipos de escritorio. Si bien esta clase de ataques involucran una gran cantidad de factores, su explotación es completamente factible, por lo que descartar esta clase de reportes sería un gran error por parte de la organización
DETECTAN NUEVO MALWARE PARA MAC; MILES DE USUARIOS DE APPLE INFECTADOS A DIARIO
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/malware-virus/detectan-nuevo-malware-para-mac-miles-de-usuarios-de-apple-infectados-a-diario/
Durante 2019, especialistas en seguridad en redes de la firma Kaspersky emitieron reportes sobre miles de infecciones de Shlayer, una nueva familia de troyanos, logrando evitar ataques en uno de cada diez dispositivos Mac. Aunque parecía que la amenaza había sido contenida, recientes reportes aseguran que el malware sigue activo.
En su reporte, Kaspersky menciona que los atacantes emplean un ingenioso método de distribución, desplegando Shlayer mediante redes asociadas, sitios web de entretenimiento e incluso vía Wikipedia, por lo que no sólo los usuarios que navegan por sitios web inseguros están expuestos, sino que este malware también podría llegar a los visitantes de páginas legítimas.
Aunque macOS es considerado un sistema mucho más seguro que otras opciones ampliamente utilizadas, muchos grupos de actores de amenazas logran desarrollar métodos de ataque contra los usuarios de este sistema y, durante el año pasado, las infecciones de Shlayer fueron una muestra importante de esta tendencia.
Los expertos en seguridad en redes de Kaspersky afirman que Shlayer fue el malware más activo en cualquier sistema de Apple; dedicado a la instalación de adware, Shlayer recopila búsquedas en el navegador para posteriormente alterar los resultados mostrados al usuario objetivo con el fin de mostrar más anuncios invasivos.
Respecto al proceso de infección, Kaspersky detectó que está dividido en dos fases:
- Instalación de Shlayer e instalación de una variante de adware específica
- Descarga del programa malicioso; para esto, el atacante debe forzar a la víctima a realizar la descarga mediante el sistema de distribución del malware
Los actores de amenaza suelen ofrecer Shlayer como una opción para monetizar sitios web como parte de un programa de socios, además de asegurar a los administradores de sitios web que recibirán un pago relativamente alto por cada instalación de este adware.
Acorde a los expertos en seguridad en redes de Kaspersky, el esquema funciona de la siguiente forma:
- La víctima potencial busca contenido en línea (streaming de eventos deportivos, películas en sitios pirata, etc)
- Las páginas asociadas redirigen al usuario a falsas páginas de actualización de Flash Player
- Una vez en la página falsa, la víctima descarga el malware
No obstante, esta no es la única forma de completar la infección. Los atacantes también han logrado colocar enlaces a la página falsa de Adobe Flash en plataformas legítimas como descripciones de videos en YouTube o referencias en artículos de Wikipedia. En total, Kaspersky detectó 700 dominios (legítimos e ilegales) con enlaces al sitio de descarga del malware.
FUENTE: Kaspersky
A pesar de que la mayor parte de la actividad de Shlayer se concentra en Estados Unidos, también se han detectado una cantidad de ataques considerable en Alemania, Francia, Reino Unido y otros países de Europa.
Los especialistas en seguridad en redes del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) consideran que los ataques a usuarios del sistema macOS representan ganancias considerables para los atacantes, especialmente mediante campañas de ingeniería social, fáciles de desplegar incluso mediante plataformas legítimas. Por fortuna no todo son malas noticias, pues los expertos aseguran que los usuarios de este sistema operativo están menos expuestos a incidentes de robo de datos que los usuarios de sus contrapartes, aunque no está de más que los usuarios consideren el uso de otras medidas de seguridad.
PERSONAL INFORMATION OF 15,000 DETROIT GOVERNMENT EMPLOYEES HACKED
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/24/personal-information-of-15000-detroit-government-employees-hacked/
Another day, another incident related to data protection. The Detroit city government offered more than 15,000 public employees a free credit monitoring service after a data breach was revealed, which could have exposed confidential information.
The measure applies to both current and former city workers, Information Office Director Beth Niblock reported in an official statement. The director’s letter also mentions that less than 10% of the city’s accounts were compromised, although many of the affected accounts could contain sensitive details. The incident occurred during the early morning of January 16.
So far there have been no indications of malicious use of the compromised information, in addition, because the information exposed is encrypted, it is highly unlikely that hackers will be able to access a readable version of this data. However, the city government preferred not to leave loose ends and protect employees with this monitoring service, data protection experts mention.
Without going into detail, the city administration mentions that the exposed information also involves the personal data of at least 300 customers of the Detroit Department of Water and Sewerage. Affected users will also be able to access free credit monitoring services.
The Detroit city government will report directly to affected persons, sending a letter to their respective homes, as well as an email to their last address registered on the systems. In turn, the Information Office will be working with data protection experts, cybersecurity firms and federal law enforcement agencies to investigate the incident.
The causes of the incident are still unknown, so we will have to wait for the investigation to conclude to determine whether it is due to the intervention of any group of threat actors, or whether the leak is due to carelessness of the city’s IT staff. In the event of human error, the International Institute of Cyber Security mentions that persons in charge of the affected areas should be called to appear before the justified one.
THREE CRITICAL VULNERABILITIES IN SAMBA; PATCHES ALREADY AVAILABLE
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/24/three-critical-vulnerabilities-in-samba-patches-already-available/
This has been a complex and busy start of 2020 year for vulnerability testing specialists. This time, Samba, Microsoft’s shared file protocol just announced the release of some updates for security flaws tracked as CVE-2019-14902, CVE-2019-14097, and CVE-2019-19344.
The first of these security issues, CVE-2019-14902, is a medium severity security error involving the granting of a new right in the target system, in addition to the elimination of a previously granted right. If a user is allowed to make system modifications (such as password change), deleting this right would not be automatically reflected on all domain controllers.
The report, prepared by Samba vulnerability testing specialists, mentions that the update completely fixes this issue, although it is important that administrators verify full synchronization between all potentially affected domains.
The second vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2019-14907, is also a medium severity error that, if exploited, allows a crash after a failed character conversion at record level three (or higher) that affects any version of Samba after 4.0.
The vulnerability was detected on the Samba Active Directory domain controller and can cause long-running processes to be interrupted unexpectedly.
Last but not least, Samba revealed the existence of CVE-2019-19344, a use-after-free vulnerability generated during the removal of DNS zones on the Samba Active Directory domain controller in v4.9 and later. During the release of Samba 4.9, a default shutdown feature was included that allowed deleting dynamically created DNS records that had reached their expiration point.
The use-after-free issue could allow that read memory to be stored in the database in case the appropriate conditions are presented, vulnerability testing experts mention.
As already mentioned, update patches are now available on Samba’s official platforms; the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) recommends system administrators updating potentially affected systems as soon as possible to mitigate any exploitation risk.
RANSOMWARE SHUTS DOWN A 100-YEAR-OLD CAR PARTS MANUFACTURER; MORE THAN 4,000 JOBS LOST
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/24/ransomware-shuts-down-a-100-year-old-car-parts-manufacturer-more-than-4000-jobs-lost/
A new ransomware incident has harshly affected a major automotive company. Gedia Automotive Group, a German car parts manufacturer with nearly 5,000 employees in seven different countries, has confirmed a ransomware attack that forced all of its IT systems to be shut down; the company’s employees were sent home until further notices, as reported by ethical hacking specialists.
This firm is established in the German city of Attendorn and is more than 100 years old. Through a statement, the Gedia direction board reported that it will take a few weeks (or months, at worst) to its IT department to restore the operation of its entire infrastructure.
“At the beginning of this week, a massive cyberattack took place at Gedia’s headquarters in Attendorn. After detecting the incident, an internal investigation began, after which the immediate shutdown of the systems was determined as a security measure,” the company’s statement says.
Although many details about the incident are still unknown, Gedia mentions on its website that the group of threat actors in charge of this attack is also behind the ransomware incident that recently affected the systems of the currency exchange firm Travelex. According to experts in ethical hacking, this hacker group would have claimed the authorship of the attack on a dark web forum.
The company’s claim appears to be backed by a security firm that has tracked recent attacks using the Sodinokibi ransomware variant, also known as REvil. Operators of these attacks have threatened to publicly disclose company’s sensitive data.
The hackers’ announcement, allegedly posted on a clandestine hacking forum, threatens to post more than 50 GB of confidential information, including blueprints of future projects and confidential employee and customer information. The amount of ransom that hackers demand of Gedia is still unknown.
In response to the incident, the company implemented an emergency plan to ensure critical operations were still online. In addition, Gedia’s executives hired the services of an ethical hacking firm for the incident recovery process. Apparently the attack originated in some Eastern European country.
Specialists predict that it will be difficult to identify the threat actor behind this attack, as there are currently at least 40 groups of cybercriminals using the Sodinokibi ransomware, in addition to the attack methods employed by these criminal cells they’re very similar.
Experts in ethical hacking from the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) mention that among the main causes of ransomware attacks are the use of weak or preset passwords, security implementation errors and lack update internal resource management policies.
THE UNITED NATIONS HAS DECLARED WHATSAPP AS EXTREMELY UNSAFE TO USE
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/24/the-united-nations-has-declared-whatsapp-as-extremely-unsafe-to-use/
For the development of its day-to-day operations, the United Nations (UN) employs multiple technological developments with the highest information security standards, including a vulnerability bounty program to solve security flaws in commonly used software solutions.
Due to the confidential nature of multiple matters dealt with by the UN, not any software or technology is eligible for the organization. Such seems to be the case of WhatsApp, a messaging service called by the UN as very unsafe to establish communication between world leaders.
According to a report mentioned by Farhan Haq, a spokesperson for the UN secretary-general, an information security firm advised the organization to avoid the use of WhatsApp due to its low security standards: “The senior UN officials have been instructed to avoid the use of WhatsApp, whose services do not have the necessary security mechanisms,” Haq said, after a reporter questioned the use of this messaging platform between heads of state.

Upon receiving questions regarding the hacking of Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, allegedly perpetrated by the Crown of Saudi Arabia through WhatsApp, Haq commented only: “We have paid sufficient attention to known facts; we will monitor the development of this situation.”
A few months ago, an information security report published by The Guardian revealed that Bezos’ smartphone was compromised using a malicious file that the entrepreneur received via a WhatsApp chat with Mohammed bin Salam Al Saud, heir to the Saudi throne.
Although Saudi Arabia has repeatedly denied such accusations, Agnes Callamar and David Kaye, UN special rapporteurs, called for an immediate investigation into the alleged hack. The final results are not yet presented to the top UN officials.
Although Facebook, which owns WhatsApp, claims that the messaging service is completely secure, the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) has published multiple reports on methods of attacking this service, mainly exploiting WhatsApp Web, the desktop version. While such attacks involve a lot of factors, their exploitation is entirely feasible, so ruling out such reports would be a big mistake on the part of the organization.
NUEVA YORK TIENE UNA PRISIÓN ELECTRÓNICA POR HACKEAR IPHONES
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/seguridad-movil/nueva-york-tiene-una-prision-electronica-por-hackear-iphones/
Recientemente se volvió a encender la polémica respecto al uso de cifrado en los dispositivos inteligentes con iOS y Android. Por un lado, Apple y Google argumentan que el cifrado es la principal herramienta para la protección de datos de los usuarios, mientras que las agencias gubernamentales sostienen que implementar una forma de acceder a estos dispositivos representaría un gran avance en el combate a las actividades criminales.
Con el lanzamiento del sistema operativo iOS8, Apple comenzó a implementar cifrado en todos sus productos para proteger a los usuarios, pues estaban demasiado expuestos a la actividad de los hackers. Una medida idéntica fue implementada por Google poco después. Desde entonces comenzó una especia de carrera entre agentes del gobierno de E.U. tratando de obtener información de estos dispositivos y las compañías desarrolladoras, que implementan medidas de seguridad cada vez más estrictas.
La disputa entre el gobierno de E.U. y estas compañías está lejos de terminar; mientras tanto, las agencias policiales han encontrado una tercera vía para eludir el cifrado en estos dispositivos sin violar legislación de protección de datos. Cyrus Vance Jr., fiscal de distrito de Manhattan, y la Unidad de Cibercrimen de la ciudad, crearon una especie de prisión con un fin específico: extraer la información almacenada en algunos dispositivos inteligentes empleando tácticas de fuerza bruta antes de que sus dueños eliminen estos datos, que podrían ser útiles en investigaciones criminales.
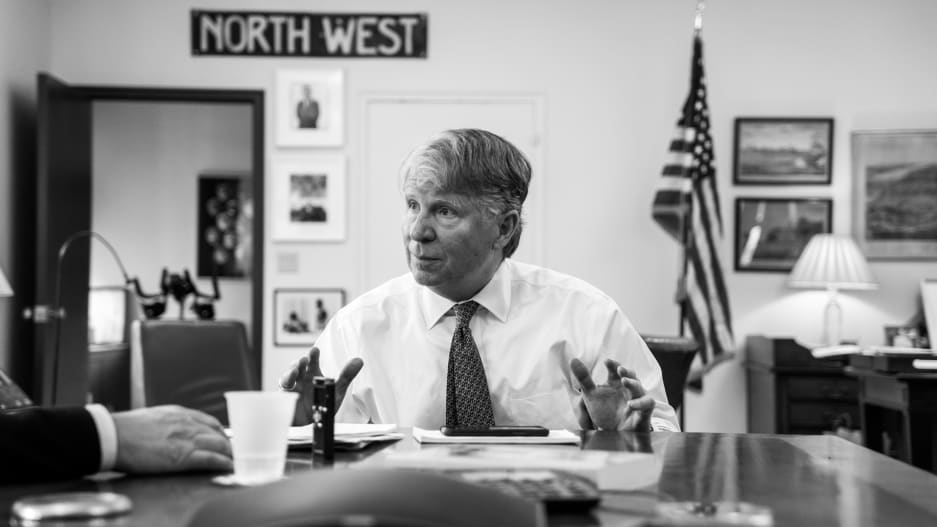

FUENTE: Fast Company
La entrada a esta “prisión” asemeja a la de un búnker. Esta instalación consiste en una cámara de aislamiento de radiofrecuencia protegida detrás de dos puertas de acero herméticamente cerradas. En las paredes de esta cámara, se encuentran conectados decenas de dispositivos de Apple (iPad/iPhone), todos confiscados durante la comisión de delitos en investigación.

FUENTE: Fast Company
Todos los dispositivos que se encuentran en estas instalaciones están conectados a dos computadoras con un poder de procesamiento masivo, dedicadas a la generación de secuencias de números aleatorios para tratar de descifrar los códigos de acceso a estos dispositivos confiscados. Los investigadores que aquí laboran incluso pueden aprovechar otros sistemas que no se usan de noche para crear una red local de súper computadoras, menciona una reseña de la revista de negocios Fast Company.
Durante la entrevista, Steve Moran, director de la Unidad de Análisis de Alta Tecnología, muestra como ejemplo del trabajo hecho en este laboratorio un iPhone en el que se han probado más de 10 mil combinaciones posibles: “Esto habría bastado para descifrar una contraseña de cuatro dígitos. Sin embargo, Apple lleva cinco años usando códigos de acceso de seis dígitos, lo que requiere probar un millón de combinaciones posibles”, mencionó.

FUENTE: Fast Company
Además, especialistas en protección de datos señalan que Apple restringe la cantidad de veces por minuto que puede ingresarse un código de acceso; aquí es donde entran los investigadores de estos posibles delitos. “Se requiere pensar en posibles combinaciones. Debemos saber algunos datos: fecha de nacimiento, aniversario de bodas, cumpleaños de esposas o hijos, incluso el número de su jugador de béisbol favorito puede ser útil para reducir el número de intentos necesarios para desbloquear los dispositivos de los sospechosos”, agrega Moran.
Esta no es la única variable que afecta las operaciones de este laboratorio, pues además del enorme número de combinaciones a probar, los investigadores también deben priorizar algunos dispositivos específicos. Para esto, Moran diseñó un flujo de trabajo que evalúa los casos más urgentes; actualmente hay más de 3 mil dispositivos considerados de baja prioridad resguardados en estas instalaciones.

FUENTE: Fast Company
Como ya se ha mencionado, el principal argumento de Apple y Google a favor del cifrado es la protección de datos, una postura totalmente justificada considerando que estas compañías abarcan casi el 99% del mercado mundial de los smartphones.
Si bien las compañías afirman que nadie, ni siquiera su personal interno, puede acceder a un dispositivo con cifrado, el fiscal Vance cree altamente probable que Apple tenga una especie de backdoor secreto. “Apple entra en nuestros dispositivos todo el tiempo: actualizaciones de SO, mensajes SMS, envío de enlaces, todo es parte de esa práctica invasiva”. A pesar de estas afirmaciones, compartidas por un número considerable de expertos en el tema, el discurso de la privacidad de los usuarios ha prevalecido sobre la exigencia de acceso a estos archivos.

FUENTE: Apple
Por otra parte, Vance considera que la petición de eliminar el cifrado no es exagerada, pues existen casos en los que la información almacenada en dispositivos inteligentes recuperados en escenas del crimen o allanamientos ha sido fundamental para cerrar casos complicados. Un ejemplo es el arresto y condena de Lamar Davenport, por el asesinato de E’Dena Hines, nieta del actor Morgan Freeman. El fiscal encargado del caso presentó como evidencia un video encontrado en el iPhone del acusado después de meses de internar acceder al dispositivo. “No solo eso; gracias a la actividad de este laboratorio hemos encontrado información suficiente para demostrar la inocencia de al menos 16 sospechosos en diversos crímenes”, añade el fiscal.
La campaña de Vance contra el cifrado no se ha limitado al ámbito local. El fiscal se ha reunido en diversas ocasiones con miembros de Europol, Interpol, ha publicado artículos en toda clase de revistas, además de tratar de establecer contacto con los representantes de las compañías tecnológicas.
El Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) menciona que, antes de 2014, las compañías tecnológicas parecían no tener problema con cooperar con las agencias policiales, señalando incluso que el trabajo de Apple era considerado destacado y eficaz. No obstante, esta labor de cooperación llegó a un punto de quiebre después de las revelaciones de Edward Snowden sobre la actividad de espionaje de la Agencia de Seguridad Nacional de E.U. Si bien todas las compañías tecnológicas señaladas por Snowden negaron colaborar con el gobierno de E.U., Apple optó por una demostración más enérgica de compromiso con la privacidad, lanzando el sistema iOS 8, que incluía el cifrado completo.
Este laboratorio es una de las principales herramientas para la investigación de casos criminales en la ciudad, pues cuenta con los recursos de hardware más complejos disponibles, además de software especialmente desarrollado para aplicar fuerza bruta a estos dispositivos. No obstante, con la aparición de nuevas versiones de los sistemas operativos móviles la labor de estos investigadores se hace cada vez más compleja. “Al comienzo de este proyecto, sólo el 52% de los smartphones analizados estaban bloqueados, mientras que actualmente la cifra de dispositivos bloqueados es del 82%”, menciona Moran, por lo que las agencias gubernamentales también apuestan por que la legislación en materia de cifrado en dispositivos móviles agilice esta labor.
SEATTLE, ESTADO EN E.U., PERMITIRÁ LA VOTACIÓN EN LÍNEA VÍA SMARTPHONE EN LAS ELECCIONES DE 2020
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/videos-noticias/seattle-estado-en-e-u-permitira-la-votacion-en-linea-via-smartphone-en-las-elecciones-de-2020/
Los avances tecnológicos siguen alcanzando nuevas aplicaciones, tanto en la vida cotidiana como en los aspectos sociales relevantes. Rumbo a las elecciones de 2020 en Estados Unidos, se ha anunciado que un distrito que abarca la mayor parte de la ciudad de Seatttle será el primero en el que el total de los electores podrá emitir su voto desde un smartphone, reportan expertos en ciberseguridad.
La agencia ambiental estatal King Conservation District, presente en Seattle y más de 30 ciudades, dará a conocer más detalles sobre este plan para permitir que más de 1 millón de ciudadanos emitan su voto de forma electrónica.
El plan será aplicado durante una elección de la Junta de Supervisores y los votos serán recibidos hasta el 11 de febrero, día de las elecciones. Bradley Tusk, CEO y fundador de Tusk Philantropies, organización sin fines de lucro dedicada a la expansión de la votación electrónica, mencionó: “Esta es la campaña de transformación más importante para el proceso democrático”. Esta organización financiará el programa piloto.
Los sistemas de votación en línea serán habilitados por Democracy Live, compañía con sede en Seattle especializada en el tema. Para ingresar a los sistemas, los votantes registrados deberán emplear su nombre y fecha de nacimiento. Después de llenar su boleta, el votante deberá verificar su envío mediante una firma electrónica.
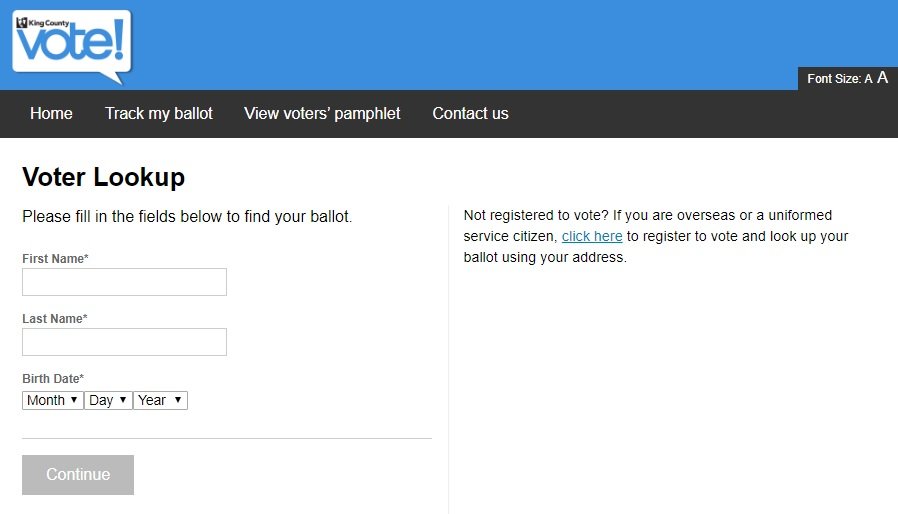
Acorde a los expertos en ciberseguridad, el envío de la boleta electrónica no es la única opción, pues los votantes podrán ingresar al sistema, completar la boleta y, en lugar de enviarla, podrán imprimirla y depositarla personalmente en las urnas o enviarla por correo tradicional.
Aunque la medida ya ha sido aplaudida y respaldada por un sector de la población, electores y entidades reguladoras también han expresado su preocupación por diversos motivos. Las elecciones locales en E.U. se caracterizan por una tasa de participación extremadamente baja, por lo que muchos analistas cuestionan la necesidad de implementar estos complejos planes. Por ejemplo, la pasada elección de la Junta de Supervisores registró una participación de menos del 1% de los posibles votantes.
Tusk considera que el poco interés de los electores a la larga se convierte en malos resultados entregados por los gobernantes, aunque la aplicación de la tecnología podría cambiar esto: “Si encontramos una forma de usar la tecnología para incrementar la participación de los electores, lograremos una mejor representación y, por lo tanto, mejores resultados de los políticos”, menciona.
Otro gran cuestionamiento respecto a estos planes tiene que ver con la ciberseguridad. Es por todos conocido que, durante las elecciones presidenciales de 2016, el gobierno ruso empleó ciberataques para inferir en el proceso electoral de E.U.

Si bien no existe evidencia de que estos ataques hayan alterado los sistemas electorales, sí se utilizaron técnicas de recolección de datos para mostrar publicidad altamente dirigida a usuarios específicos para influir en las tendencias electorales. Por si fuera poco, analistas políticos, de seguridad nacional y de ciberseguridad consideran altamente probable que las próximas elecciones de E.U. sean atacadas también.
Los expertos en seguridad han adoptado una postura en contra de la votación electrónica de forma casi unánime, pues consideran que, si bien es completamente factible implementar este método, la tecnología aún no avanza al punto de poder garantizar al 100% la integridad de este proceso: “Votar mediante el uso de un smartphone no es la idea más inteligente; existe un claro consenso entre la comunidad de la ciberseguridad”, asegura Duncan Buell, profesor de informática en la Universidad de Carolina del Sur.
Por otra parte, en el reporte del Comité de Inteligencia del Senado de E.U. sobre la injerencia de Rusia en las elecciones pasadas ha fijado una postura abiertamente en contra de la votación electrónica, afirmando que “E.U. debe resistir ante cualquier impulso a esta tecnología”.
El Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) señala que estas medidas no son del todo desconocidas para los sistemas electorales de E.U., pues durante los últimos 10 años han aparecido diversos planes para habilitar la votación a distancia. El primer gran intento ocurrió en Washington D.C., que en 2010 lanzó un programa de votación en línea, el cual fue hackeado antes de comenzar a operar en una situación real, por lo que fue rápidamente descartado.
Hace un par de años, Virginia usó una app móvil para permitir a los votantes en el extranjero participar en las elecciones intermedias; un ejemplo similar se presentó en Utah, donde se habilitó una plataforma en línea específicamente diseñada para recolectar los votos de los ciudadanos discapacitados y así evitar la necesidad de trasladarlos a las urnas físicas.
Recientemente, el Comité Nacional del Partido Demócrata descartó un plan para registrar votantes en Iowa y Nevada de forma remota. Otros estados de la unión americana, además de múltiples países, han demostrado su interés en incursionar en la votación electrónica, aunque los expertos en ciberseguridad consideren que las condiciones para implementar estos planes aún no son las óptimas.
NEW YORK HAS AN ELECTRONIC PRISON FOR HACKING IPHONES
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/23/new-york-has-an-electronic-prison-for-hacking-iphones/
The controversy over the use of encryption in iOS and Android smart devices was recently rekindled. First, Apple and Google argue that encryption is the main tool for users’ data protection, while government agencies claim that implementing a way to access these devices would represent a major step forward in combating criminal activities.
With the release of the iOS8 operating system, Apple began implementing encryption on all of its products to protect users, as they were too exposed to malicious hacking activity. An identical measure was implemented by Google soon after. Since then it began somewhat a race between US government agents trying to obtain information from these devices and the developer companies, which were increasingly implementing stringent security measures.
The dispute between the US government and these companies is far from be over; meanwhile, law enforcement agencies have found a third way to bypass encryption on these devices without violating data protection legislation. Cyrus Vance Jr., Manhattan district attorney, and the city’s Cybercrime Unit, created a kind of prison for a specific purpose: extracting information stored on some smart devices using brute force tactics before their owners delete this data, which could be useful in criminal investigations.

SOURCE: Fast Company
The entrance to this “prison” resembles that of a bunker. This installation consists of a radio frequency isolation chamber protected behind two hermetically sealed steel doors. On the walls of this camera are connected dozens of Apple devices (iPad/iPhone), which were confiscated during the commission of currently investigated crimes.

SOURCE: Fast Company
All devices found in these facilities are connected to a set of massive processing power computers, dedicated to generate random number sequences to try to decrypt the access codes to these confiscated devices. Researchers working here can even take advantage of other systems that aren’t used at night to create a local supercomputer network, mentions a review of the business magazine Fast Company.
During the interview, Steve Moran, director of the High Technology Analysis Unit, shows as an example of the work done in this lab an iPhone in which more than 10k possible combinations have been tested: “This would have been enough to decrypt a four-digit password. However, Apple has been using six-digit access codes for the last five years, which requires a million possible combinations to be tested,” he said.

SOURCE: Fast Company
In addition, data protection specialists point out that Apple restricts the number of times per minute an access code can be entered; this is where investigators of these possible crimes come in. “It is required to think about possible combinations. We need to know some facts: date of birth, wedding anniversary, birthday of wives or children, even the number of favorite baseball player can be helpful in reducing the number of attempts needed to unlock the devices of the suspects” , adds Moran.
This is not the only variable that affects the operations of this lab, because in addition to the huge number of combinations to test, researchers should also prioritize some specific devices. To this, Moran designed a workflow that evaluates the most urgent cases; there are currently more than 3,000 low-priority devices sheltered in these facilities.

SOURCE: Fast Company
As already mentioned, Apple and Google’s main argument for encryption is data protection, a position entirely justified considering that these companies cover almost 99% of the global smartphone market.
While companies claim that no one, not even their internal staff, can access a device with encryption, prosecutor Vance believes it highly likely that Apple will have some kind of secret backdoor. “Apple accesses our devices all the time: OS updates, SMS messages, external links, it’s all part of that invasive practice.” Despite these claims, shared by a considerable number of experts on the subject, the user privacy speech has prevailed over the demand for access to these files.

SOURCE: Apple
On the other hand, Vance considers that the request to remove encryption is not exaggerated or unfounded, as there are cases where information stored on smart devices recovered at crime scenes or raids has been instrumental to solve complex cases. An example is the arrest and conviction of Lamar Davenport for the murder of E’Dena Hines, granddaughter of actor Morgan Freeman. The prosecutor in charge of the case presented as evidence a video found on the defendant’s iPhone after months of investigation to access to the device. “Not only that; thanks to the activity of this laboratory we have found useful information to prove the innocence of at least 16 suspects in various crimes,” he adds.
Vance’s anti-encryption campaign has not been limited to his local environment. The prosecutor has met on several occasions with members of Europol, Interpol, besides publishing articles in all kinds of magazines, in addition to trying to establish contact with the representatives of the technology companies.
The International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) points out that, before 2014, technology companies seemed to have no problem cooperating with law enforcement agencies, even noting that Apple’s collaboration was considered outstanding and effective. However, this cooperative work came to a breaking point after Edward Snowden’s revelations about the US National Security Agency’s espionage activity. While all of the tech companies mentioned by Snowden denied collaborating with the US government, Apple opted for a more vigorous demonstration of privacy engagement, launching the iOS 8 system, which included full encryption for the first time.
This laboratory is one of the main tools for the investigation of criminal cases in the city, as it has the most complex hardware resources available, in addition to specially developed software to apply brute force to these devices. However, with the emergence of new versions of mobile operating systems, the work of these researchers becomes increasingly complex. “At the beginning of this project, only 52% of the smartphones analyzed were locked, while the number of locked devices is currently 82%,” Moran says, so government agencies also bet on legislation on encryption on mobile devices streamlines this work.
US STATE SEATTLE WILL ALLOW ONLINE VOTING BY SMARTPHONE IN 2020 ELECTIONS
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/23/us-state-seattle-will-allow-online-voting-by-smartphone-in-2020-elections/
Technological advances keep reaching new applications, both in everyday life and in relevant social aspects. Heading to the 2020 US election, it has been announced that a district that encompasses most of the city of Seattle will be the first in which total voters will be able to cast their ballots from a smartphone, cybersecurity experts report.
The state environmental agency King Conservation District, present in Seattle and more than 30 cities, has released more details about this plan to allow more than 1 million citizens to cast their ballots electronically.
The plan will be implemented during an election of the Board of Supervisors and votes will be received until February 11, Election Day. Bradley Tusk, CEO and founder of Tusk Philantropies, a nonprofit organization dedicated to the expansion of electronic voting, said, “This is the most important transformation campaign for the democratic process.” This organization will fund the pilot program.
Online voting systems will be enabled by Democracy Live, a Seattle-based company specializing in the subject. To enter the systems, registered voters must use their name and date of birth. After filling out their ballot, the voter must their submission via an electronic signature.
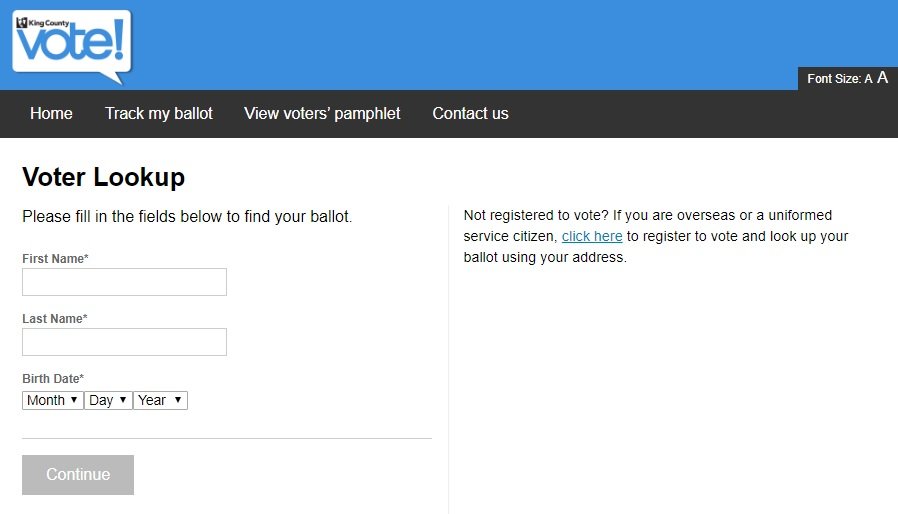
According to cybersecurity experts, sending the e-ballot is not the only option, as voters will be able to enter the system, complete the ballot and, instead of sending it, they will be able to print it and drop it personally in the ballot box or send it through traditional mail.
This measure has been backed and supported by electors and civilian organizations; however voters and democratic watchdogs have also expressed their concern on several issues. Local elections in the US are characterized by an extremely low participation rate so many analysts question the need to implement these complex plans. For example, the last election of the Board of Supervisors recorded a turnout of less than 1% of potential voters.
Tusk believes that the poor interest of voters in the process renders poor results delivered by governors, although the application of the technology could change this: “If we find a way to use technology to increase the participation of voters, we will achieve better representation and therefore better results from politicians,” he says.
Another big question about these plans has to do with cybersecurity. It is well known that, during the 2016 presidential election, the Russian government used cyberattacks to infer in the US democratic process.

While there is no evidence that these attacks have disrupted or altered electoral systems, data collection techniques were used to send highly targeted advertising to specific users aiming to influence election trends. As if that weren’t enough, political, national security and cybersecurity analysts consider it highly likely that the next US election will be attacked as well.
Security experts have taken a firm position against electronic voting almost unanimously, as they believe that, while it is entirely feasible to implement this method, the technology is not yet moving to the point of being able to guarantee 100% the integrity of this process: “Voting by using a smartphone is not the smartest idea; there is a clear consensus among the cybersecurity community,” says Duncan Buell, professor of computer science at South Carolina University.
On the other hand, in the report of the US Senate Intelligence Committee on Russia’s interference in past elections, has been set an open stance against electronic voting, stating that “The US must resist any push for this technology.”
The International Institute Cyber Security (IICS) notes that these measures are not entirely unknown to US electoral systems, as various plans to enable remote voting have appeared over the past 10 years. The first big attempt occurred in Washington, DC, which in 2010 launched an online voting program, which was hacked before it began operating in a real situation, so it was quickly dumped.
A couple of years ago, Virginia used a mobile app to allow voters abroad to participate in intermediate elections; a .similar example was presented in Utah, where an online platform specifically designed to collect the votes of disabled citizens was enabled to avoid the need to move them to the physical ballot box.
Recently, the Democratic Party National Committee dismissed a plan to register voters in Iowa and Nevada remotely. Other states of the American Union, in addition to multiple countries, have shown an interest in entering into electronic voting, even if cybersecurity experts consider that the conditions for implementing these plans are not yet optimal.
UN NUEVO RANSOMWARE ESTÁ HACKEANDO A LOS CIRUJANOS PLÁSTICOS PARA CHANTAJEARLOS Y PUBLICAR FOTOS DE ANTES Y DESPUÉS DE SUS PACIENTES
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/malware-virus/un-nuevo-ransomware-esta-hackeando-a-los-cirujanos-plasticos-para-chantajearlos-y-publicar-fotos-de-antes-y-despues-de-sus-pacientes/
Hace algunos días una clínica especializada en cirugías estéticas reveló que fue víctima de un incidente de ransomware. Estos ataques se han vuelto muy comunes, no obstante, ningún experto en seguridad de aplicaciones web pudo prever las inusuales consecuencias de este incidente.
Según se ha revelado, los atacantes están extorsionando a los pacientes que han pasado por esta clínica, amenazándolos con revelar sus fotos anteriores y posteriores a las cirugías plásticas a menos que paguen un rescate.
El doctor Richard Davis, encargado del Center for Facial Restoration, dijo sentirse preocupado e impotente debido a este incidente: “Ahora no tenemos que preocuparnos sólo de recuperar nuestros archivos, sino que también nuestros pacientes sufrieron las consecuencias del ataque”.
Por lo pronto, el personal de seguridad de aplicaciones web que colabora con la clínica se dispuso a corregir las debilidades de seguridad que permitieron el ataque, mencionando que la administración espera que las actualizaciones implementadas sirvan para mitigar el alcance del incidente, aunque son consientes de que el daño ya está hecho: “Aunque esta actualización no ayudará a las víctimas, trataremos de que el número de incidentes se mantenga al mínimo posible”, agregó el doctor Davis. Al parecer, el incidente ha afectado a los pacientes que enviaron sus fotografías a la clínica vía email.
Este es un ejemplo más del especial interés que los hackers han mostrado por comprometer los sistemas de instituciones de salud, tendencia que ha incrementado notablemente desde hace al menos un año. Este no es un problema menor, ya que una infección de ransomware podría paralizar los sistemas de un hospital mientras se llevan a cabo cirugías u otras operaciones críticas, comprometiendo seriamente la integridad de los pacientes.
Acorde a los expertos en seguridad de aplicaciones web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), la principal razón por la que los hackers apuntan contra los servicios médicos es la necesidad de mantener sus sistemas siempre en línea para poder acceder a historiales clínicos, sistemas de consulta médica, diagnósticos, medicación e incluso algunos sistemas relacionados con la operación de dispositivos como máquinas de rayos X, respiradores artificiales, monitores cardiacos, entre otros.
CEO DE UNA COMPAÑÍA DE CIBERSEGURIDAD ACUSADO DE HAKCEAR A SUS CLIENTES PARA VENDER SUS SERVICIOS
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/hacking-incidentes/ceo-de-una-compania-de-ciberseguridad-acusado-de-hakcear-a-sus-clientes-para-vender-sus-servicios/
Al igual que en cualquier otro contexto, confiar a ciegas en alguien puede ser mala idea en términos de ciberseguridad. Un individuo originario de Georgia, E.U., se ha declarado culpable de contratar una plataforma de denegación de servicio (DDoS) para lanzar ataques a diversos sitios web. Lo insólito del caso es que el acusado es CEO y cofundador de una compañía que brinda servicios de protección contra ataques DDoS.
En los documentos de la corte se menciona que Tucker Preston, de 22 años, ha sido hallado culpable de un cargo de “daño a computadoras protegidas empleando un programa, código o comando”. Como se ha mencionado anteriormente, un ataque DDoS consiste en saturar un sitio web en específico mediante tráfico falso, impidiendo que los usuarios legítimos accedan al sitio atacado.
Al parecer las actividades ilícitas de Preston se remontan al año 2016, cuando una firma de ciberseguridad describió el modo de operación de BackConnect Security, la compañía co-fundada por el acusado. Según el reporte, esta compañía tenía el inusual hábito de lanzar ataques de denegación de servicio para posteriormente ofrecer a los administradores de sitios web sus servicios de protección contra esta práctica.
Las prácticas ilegales de Preston fueron evidentes después de que las autoridades clausuraran vDOS, que entonces era el servicio de alquiler de ataques DDoS más popular y poderoso del mundo. Los administradores de vDOS fueron arrestados y se expuso una base de datos con toda la información que hacía posible las operaciones de esta plataforma ilícita, incluyendo los datos de sus usuarios, entre ellos Preston, quien entonces tenía sólo 19 años.
Además del cierre de esta plataforma, expertos en ciberseguridad mencionan que otros factores, como el uso de un pseudónimo asociado al creador de Mirai, una de las botnets más grandes jamás creadas, contribuyeron a la localización, arresto y juicio de Preston, quien fue encontrado poco después de que las autoridades federales clausuraron vDOS.
Acorde a un reporte del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), Preston enfrenta una condena de hasta 10 años de cárcel por el delito que cometió, además de una multa de hasta 250 mil dólares, o bien del doble de las ganancias generadas por sus actividades ilícitas. El acusado escuchará su sentencia definitiva el próximo 7 de mayo.
EJÉRCITO DE E.U. HACKEÓ AL GRUPO TERRORISTA ISIS DESPUÉS DE MUCHOS AÑOS
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/tecnologia/ejercito-de-e-u-hackeo-al-grupo-terrorista-isis-despues-de-muchos-anos/
En 2016 el ejército de E.U. logró detener una campaña masiva de propaganda en línea desplegada por el Estado Islámico. Para esto, las fuerzas armadas diseñaron una compleja operación de hacking en contra de múltiples servidores de ISIS, afirma un reporte de hacking ético elaborada a partir de documentos recientemente desclasificados.
En el informe, retomado por Yahoo News se menciona que el Comando Cibernético de E.U. logró interrumpir los esfuerzos de difusión en línea del mensaje radical de ISIS mediante la Operación Glowing Symphony, la primera operación de hacking reconocida abiertamente por el Pentágono. Además, se menciona que el Comando Cibernético de E.U. tuvo serios contratiempos burocráticos para poder comenzar el despliegue de esta operación.
En ocasiones anteriores, funcionarios del gobierno de E.U. ya habían admitido el uso de armas cibernéticas y métodos de hacking ético como parte del combate al terrorismo, aunque estas recientes publicaciones revelan más detalles sobre las acciones del ejército americano en contra del conocido grupo terrorista.
“Estos documentos fueron revelados en cumplimiento de la Ley de Libertad de la Información, y demuestran la complejidad y planeación sin precedentes dedicada a esta operación”, mencionan los especialistas en hacking ético.
Esta operación de hacking es, en la práctica, una respuesta enérgica al avance de los grupos extremistas y su mensaje a través de plataformas en línea como foros, redes sociales y anunciantes; según el reporte, las plataformas en línea son empleadas por ISIS y otros grupos terroristas con fines de reclutamiento y radicalización de las posturas ideológicas de los interesados en el tema.
Acorde al Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) estos documentos desclasificados también ofrecen algunas pistas sobre cómo operaron los comandos cibernéticos de E.U. para combatir la posible intrusión de actores extranjeros en las elecciones pasadas. Para esto, Paul Nakasone, líder de los comandos cibernéticos de E.U., ordenó la formación de un nuevo grupo conocido como Small Russia, dedicad por completo a la atención de potenciales amenazas al proceso electoral americano.
Aunque la más reciente operación contra ISIS culminó con la muerte de su líder, los especialistas aún prevén posibles intentos de ciberataque contra algunos de los sistemas informáticos más importantes de E.U.
BANCO RUSO SUFRE EL MAYOR ATAQUE DDOS VÍA DISPOSITIVOS IOT DE LA HISTORIA
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/hacking-incidentes/banco-ruso-sufre-el-mayor-ataque-dos-en-la-historia-de-los-dispositivos-iot/
El equipo de seguridad informática de Sberbank, el banco más importante de Rusia y uno de los más importantes de Europa, acaba de repeler un ataque de denegación de servicio (DoS) contra sus redes; acorde al informe del banco, este fue el intento de ataque DoS más grande del que se tenga registro.
El intento de ataque se llevó a cabo empleando millones de dispositivos de Internet de las Cosas (IoT) hackeados, mencionó Stanislav Kuznetsov, funcionario de Sberbank, durante el Foro Económico Mundial de Davos.
Kuznetsov afirma que el ataque tuvo lugar durante los primeros días del año, aunque la institución cuenta con un protocolo de defensa contra esta clase de incidentes desde el 2019, cuando se registraron los primeros intentos de ataque empleando recursos mucho menos avanzados que en esta ocasión: “Durante el otoño pasado detectamos indicios de actividad anormal en nuestras redes, por lo que comenzamos a prepararnos contra un potencial ataque. Nuestros expertos aseguran que este intento de ataque fue unas 30 veces más potente que los ataques DoS convencionales”.
El equipo de seguridad informática del banco asegura que el ataque no generó consecuencia alguna en sus sistemas; después de detener el incidente, los directivos del banco notificaron a la policía y se dijeron dispuestos a colaborar en la investigación. Aún se desconoce el método empleado por los hackers, su país de procedencia o las tácticas usadas por el banco para repeler el ataque.
Especialistas en seguridad informática afirman que el número de dispositivos IoT ya triplica el número de habitantes en todo el mundo. Aunado a esto, sus débiles características de seguridad los vuelven blanco atractivo para los hackers, que comprometen estos dispositivos para integrar enormes botnets empleadas en ataques como este. Por otra parte, el Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) afirma que dentro de cinco años el número de dispositivos IoT activos en el mundo será cinco veces mayor que el número de habitantes en la tierra. Los pronósticos respecto al uso de dispositivos IoT son poco alentadores, por lo que es urgente que los fabricantes comiencen a diseñar mejores estrategias para la seguridad y mantenimiento de estos equipos.
ICLOUD NO TENDRÁ CIFRADO COMPLETO; APPLE Y EL GOBIERNO TENDRÁN ACCESO A TUS FOTOS EN LA NUBE
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/tecnologia/icloud-no-tendra-cifrado-completo-apple-y-el-gobierno-tendran-acceso-a-tus-fotos-en-la-nube/
Esta es una revelación muy grave para la privacidad y protección de datos de los usuarios de Apple. Medios internacionales reportan que, después de recibir una queja del FBI, la compañía tecnológica abandonó sus planes para implementar un cifrado completo en los respaldos de seguridad de sus usuarios en iCloud. La agencia del gobierno de E.U. habría argumentado que este cifrado entorpece su labor de investigación.
La decisión habría sido tomada hace un par de años, aunque no había sido revelada previamente. A diferencia de los actos públicos de Apple, con los que pretende mostrarse como una compañía que siempre esta de lado del consumidor, esta decisión demuestra que Apple está dispuesta a colaborar en las investigaciones de esta agencia, sin importar que esto incluya pasar por encima de la privacidad de los usuarios, sean culpables o inocentes.
En su momento, especialistas en protección de datos del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) filtraron información sobre un plan para cifrar cualquier respaldo en iCloud; al inicio esto fue pensado como un método para combatir el hacking, no obstante, al llegar a oídos del FBI, la agencia se opuso a este cifrado, pues su implementación habría significado perder acceso a los respaldos en iCloud aún con una orden legal de por medio.
La polémica respecto a las agencias gubernamentales y su deseo por obtener una forma de acceder a la información en un dispositivo cifrado volvió a encenderse luego de que William Barr, fiscal general de E.U., pidiera públicamente a Apple desbloquear dos dispositivos iPhone, propiedad de un agente de Arabia Saudita que asesinó a tres oficiales americanos en Pensacola, Florida.
Esta solicitud se convirtió en crítica a la compañía cuando el presidente Donald Trump acusó a Apple de encubrir a “asesinos, traficantes de droga y otros criminales”, empleando como pretexto la protección de datos del resto de los usuarios para no desbloquear un dispositivo potencialmente útil en una investigación criminal. Por si fuera poco, congresistas de ambos partidos han comenzado a analizar la posibilidad de legislar en contra del uso del cifrado en los dispositivos tecnológicos.
Por su parte, la compañía afirma que las copias de seguridad en iCloud del responsable del tiroteo en Pensacola sí fueron entregadas a las autoridades, rechazando las versiones oficiales que afirmaban que Apple se negó a colaborar en la investigación.
NEW RANSOMWARE IS HACKING PLASTIC SURGEONS TO BLACKMAIL THEM TO PUBLISH BEFORE AND AFTER PICS OF CLIENTS
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/21/new-ransomware-is-hacking-plastic-surgeons-to-blackmail-them-to-publish-before-and-after-pics-of-clients/
A few days ago a clinic specializing in cosmetic surgeries revealed that it was the victim of a ransomware incident. These attacks have become very common; however, no web application security expert could foresee the unusual consequences of this incident.
The attackers are reportedly extorting patients who have passed through this clinic, threatening to reveal their pre- and post-plastic surgery photos unless they pay a ransom.
Dr. Richard Davis, in charge of the Center for Facial Restoration, said we were worried and helpless about this incident: “Now we don’t have to worry just about recovering our files, but also our patients suffered consequences of the attack.”
For the time being, the web application security personnel working with the clinic set out to correct the security weaknesses that enabled the attack, mentioning that management expects the deployed updates to mitigate the extent of the incident, while they are aware that the damage is already done: “While this update will not help victims, we will try to keep the number of incidents to the minimum possible,” Dr. Davis added. The incident appears to have affected patients who sent their photographs to the clinic via email.
This is yet another example of the special interest that hackers have shown in compromising health institution systems, a trend that has increased markedly for at least a year. This is not a minor problem, as a ransomware infection could paralyze a hospital system while performing surgeries or other critical operations, seriously compromising the integrity of patients.
According to web application security experts from the International Cyber Security Institute (IICS), the main reason hackers target medical services is the need to keep their systems always online in order to access clinical histories, medical consultation systems, diagnostics, medication and even some systems related to the operation of devices such as x-ray machines, artificial respirators, heart monitors, among others.
CEO OF A CYBERSECURITY COMPANY ARRESTED OF HACKING CLIENTS TO SELL HIS SERVICES
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/21/ceo-of-a-cybersecurity-company-arrested-of-hacking-clients-to-sell-his-services/
As in any other context, blind trusting someone can be a bad idea in terms of cybersecurity. An individual originally from Georgia, US, has pleaded guilty to hiring a denial-of-service (DDoS) platform to launch attacks on various websites. The unusual thing about the case is that the defendant was the CEO and co-founder of a company that provides DDoS attack protection services.
The court documents mention that Tucker Preston, 22, has been found guilty of a charge of “damage to protected computers using a program, code, or command.” In case you don’t remember, a DDoS attack consists of saturating a specific website using fake traffic, preventing legitimate users from accessing the attacked site.
Preston’s illicit activities appear to date back to 2016, when a cybersecurity firm described the mode of operation of BackConnect Security, the company co-founded by the defendant. According to the report, this company had an unusual habit of launching denial-of-service attacks and then offering website administrators its services to protect against this practice.
Preston’s illegal practices were evident after authorities shut down vDOS, which was then the world’s most popular and powerful DDoS-for-hire service. The administrators of vDOS were arrested and a database was exposed with all the information that made possible the operations of this illicit platform, including the data of its users, including Preston, who was then only 19 years old.
In addition to the closure of this platform, cybersecurity experts mention that other factors, such as the use of a pseudonym associated with the creator of Mirai, one of the largest botnets ever created, contributed to the location, arrest and trial of Preston, who was found shortly after federal authorities closed vDOS.
According to a report by the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), Preston faces a sentence of up to 10 years in prison for the crime he committed, in addition to a fine of up to $25k USD, or double the profits generated by his Illicit activities. The defendant will hear his final sentence on May 7.
US ARMY HACKED TERRORIST GROUP ISIS AFTER SO MANY YEARS
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/01/21/us-army-hacked-terrorist-group-isis-after-so-many-years/
Back in 2016, the US Army managed to stop a massive online propaganda campaign deployed by the Islamic State. For this, the armed forces designed a complex hacking operation against multiple ISIS servers, as claimed by an ethical hacking report drawn up from recently declassified documents.
The report, mentioned by Yahoo News, explains details about how the US Cyber Command managed to disrupt efforts to disseminate ISIS’ radical message online through “Operation Glowing Symphony”, the first operation openly recognized by the Pentagon. In addition, it is mentioned that the US Cyber Command had serious bureaucratic setbacks in order to begin the deployment of this operation.
On previous occasions, US government officials had already admitted the use of cyber weapons and ethical hacking methods as part of the fight against terrorism, although these recent publications reveal more details about the army’s actions American against the notorious terrorist group.
“These documents were disclosed in compliance with the Freedom of Information Act, and demonstrate the unprecedented complexity and planning dedicated to this operation,” ethical hacking specialists say.
This hacking operation is, in practice, an energetic response to the advancement of extremist groups and their message through online platforms such as forums, social networks and advertisers; according to the report, online platforms are used by ISIS and other terrorist groups for the purpose of recruiting and radicalizing the ideological positions of those interested in the subject.
According to the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) these declassified documents also offer some clues on how US cyber commandos operated to combat the possible intrusion of foreign actors into elections Past. For this, Paul Nakasone, leader of US Cyber Command, ordered the formation of a new group known as Small Russia, dedicated entirely to the attention of potential threats to the American electoral process.
Although the most recent operation against ISIS culminated in the death of its leader, specialists still foresee possible attempts to cyberattack some of the most important US computer systems.
