Month: December 2021
CONTI RANSOMWARE HITS 120 VMWARE ESXI SERVERS ON SHUTTERFLY NETWORKS
Photography-focused platform Shutterfly confirmed that it has suffered a Conti ransomware attack that would have encrypted thousands of devices and exposed sensitive information. Shutterfly is one of the world’s leading photo and photo-sharing services firms, working through brands such as GrooveBook, BorrowLenses, Shutterfly.com, Snapfish and Lifetouch.
Conti is a Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) operation in which a core team develops ransomware, maintains payment sites and data breaches, while its affiliates handle the deployment of attacks and the theft of sensitive information.
The first reports about this incident appeared on Friday afternoon, when an alleged internal actor revealed that the firm suffered the massive attack a couple of weeks ago, compromising some 4,000 devices and more than 100 VMware ESXi servers. Although more details about the attack are unknown, the informant assures that the hackers are demanding a millionaire ransom in exchange for restoring the affected systems.
Typically, ransomware groups do not initiate an infection immediately after entering the target system, but spend at least a couple of weeks collecting sensitive information on the affected networks. The stolen data is often used as a way to force victims to pay the ransom, as hackers threaten to reveal the compromised information if their financial demands are not met.
This appears to be the case with Shutterfly, as Conti has created a private data breach page containing screenshots of files allegedly stolen during the attack, in what specialists know as the “double extortion” tactic. In addition, the hackers claim to have the source code of the Shutterfly store, but it is unclear whether the ransomware band refers to Shutterfly.com or another website run by the company.
After a couple of days of uncertainty, the company confirmed the attack: “Shutterfly recently experienced a ransomware attack in some areas of the network. This incident has not affected sites such Shutterfly.com, Snapfish, TinyPrints or Spoonflower. However, parts of the Lifetouch and BorrowLenses, Groovebook businesses have experienced disruptions.”
It is still unknown whether the affected company is willing to negotiate with threat actors or whether they will restore the affected systems on their own.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
DATA BREACH AFFECTS MAJOR LOGISTICS FIRM; MILLIONS OF RECORDS LEAKED
Website Planet researchers report the finding of a data breach affecting D.W. Morgan, a U.S.-based multinational logistics firm. According to the report, the leak is due to an Amazon Web Services (AWS) bucket completely exposed online, accessible without any security measures.
The database contained more than 100 GB worth of data with 2.5 million files detailing financial, shipment, transportation, personal and sensitive records of fortune 500 companies leaked.
The exposed AWS bucket included five folders storing five specific file classifications, the researchers were able to detect:
- Transportation plans and agreements
- Process photos
- Attachments
- Signatures
- Unidentified documents
Below we will give a brief review of the characteristics of each folder exposed during this incident.
TRANSPORTATION PLANS AND AGREEMENTS
This first folder includes data on the company’s transportation plans and agreements; this information includes the agreed course of action for delivery drivers, warehouse and security personnel. Among the exposed records are:
- Process details
- Facility locations
- Full names
- Customers’ business email addresses
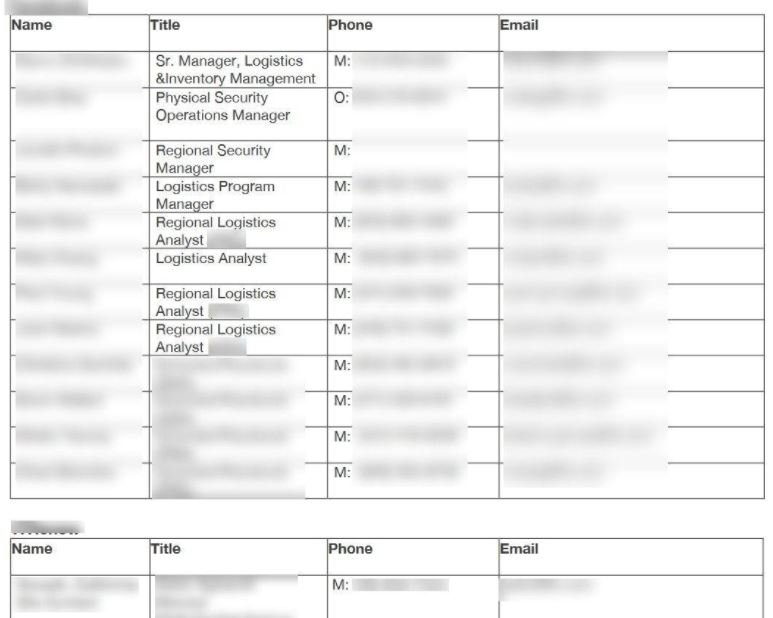
PROCESS PHOTOS
This folder stored at least 800,000 illustrative images about various parts of the shipping process at the company. These images were probably captured by employees to record shipments and documents.
ATTACHMENTS
It includes all kinds of invoices, shipping labels, and packing lists that are likely to come from the company’s email systems. In total, there were more than 10,000 of these files in this specific folder.

SIGNATURES
Although many details about the signatures found in the bucket are unknown, they are likely related to the multiple delivery processes in the company. The folder stores more than 4.5 million files.
UNIDENTIFIED DOCUMENTS
More than 100,000 files that appear unrelated to each other, though they include personally identifiable information and corporate customer details.

Investigators immediately notified the company, which rushed to revoke insecure access to the compromised information. However, it is unknown how long this information may have been exposed.
As in any other similar incident, affected employees and corporate customers could be exposed to phishing attacks, identity fraud and complex social engineering campaigns, so it is critical that the company implements the necessary prevention mechanisms to address the incident.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
SEVERE REMOTE CODE EXECUTION VULNERABILITY IN APACHE HTTP SERVER
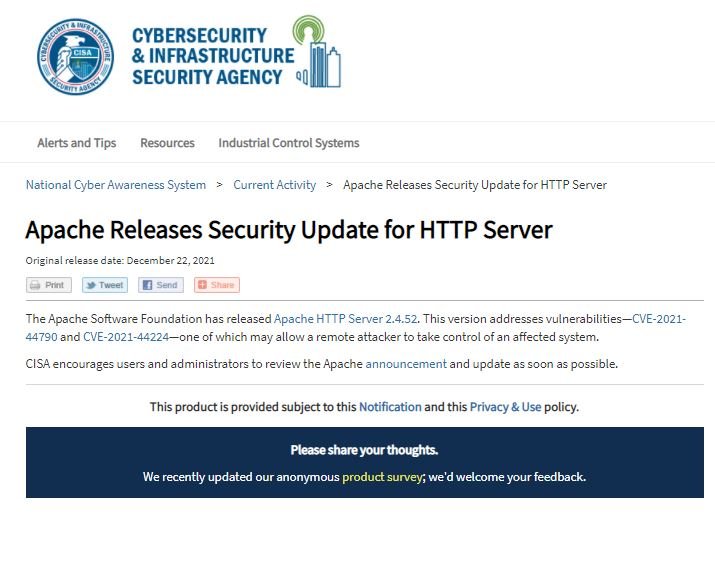
The developers of the Apache Software Foundation announced the release of a new version of Apache HTTP Server, hoping to fully address a newly detected critical vulnerability that would allow remote code execution in affected deployments.
In this regard, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) also issued an alert urgently requesting Apache HTTP Server users updating to v2.4.52 as soon as possible.
This update contains patches for CVE-2021-44790 and CVE-2021-44224, two flaws that would allow threat actors to take full control of an affected deployment. On the most severe of these flaws, Apache mentions: “A carefully designed request body can cause a buffer overflow in the multipart parser mod_lua (r: parsebody() called from Lua scripts).” So far there are no known cases of active exploitation of CVE-2021-44790.
Moreover, Apache describes CVE-2021-44224 as “a moderate-risk NULL pointer dereference that could lead to a server-side request forgery (SSRF) attack.” Because of this, a specially crafted URI sent to httpd configured as a forward proxy can cause a crash or, for configurations that mix forward and reverse proxy declarations, can allow requests to be directed to a declared UNIX domain socket endpoint.
This year has been very active in detecting security flaws in Apache HTTP Server; just a few weeks ago, CISA warned of a bug identified as CVE-2021-40438 and whose exploitation would allow malicious hackers to deploy server-side request forgery attacks. This flaw has already been exploited in the wild, so it remains a problem for Apache administrators.
While attempts to exploit this flaw are not an extended issue for all iterations of Apache HTTP Server, users of affected deployments are advised to stay on top of the latest update patches released by the foundation.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
THOUSANDS OF HACK-PROOF SECURE CELL PHONES CONFISCATED FROM SCOTLAND PRISONS
In its latest report, the Scottish Prison service revealed that a total of 1889 cell phones were confiscated due to misuse within local jails. These devices were delivered to thousands of prisoners in early 2020 as part of the coronavirus isolation measures, since the prisons could not receive visitors and contact with the outside was practically cancelled.
In announcing this move, former Justice Secretary Humza Yousaf mentioned that £2.7 million was authorized for the purchase of 7,500 allegedly hacking-proof phones. However, some prisoners discovered an effective method to release the restricted functions of these devices a few hours after they were handed over. At the moment it is unknown what method the prisoners used to hack these devices.
A source in Scotland’s prison service says hundreds of prisoners used this hacked equipment to operate illicit activities, including drug sales and extortion, in complicity with individuals outside the prisons. It was also reported that some gangs inside the prisons managed to steal the devices that were given to other inmates, as the program did not include prisoners considered dangerous.
To make the problem more serious, prison officials say it’s impossible to detect with the naked eye which devices have been tampered with by hackers, so prisons must invest considerable resources to find those phones capable of making unauthorized calls abroad, so the problem can’t be addressed in a matter of a few days.
For now, it has been decided that access to these phones will be revoked for inmates who misuse the devices, in addition to stricter measures to prevent the smuggling of new devices into prisons. These permits may be revoked for one month, two months or permanently.
Despite these measures, some congressmen have requested that the use of these devices be eliminated completely, as they believe that they only cause more problems than they solve and there is no way that the prison administration can guarantee their correct use.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
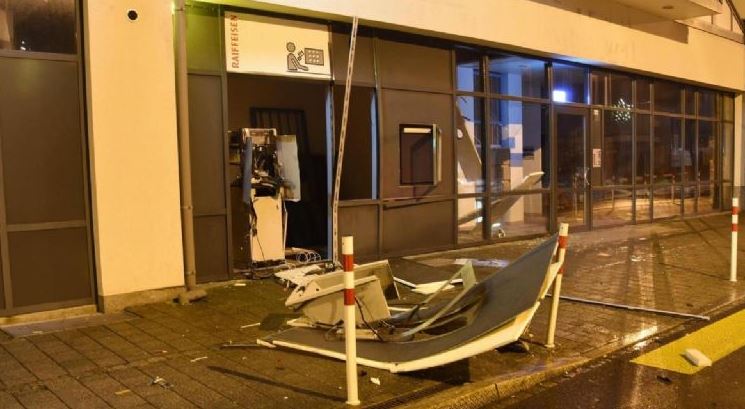
NEW KIND OF BOMB ATTACKS TO CASH OUT ATMS DISCOVERED IN SWITZERLAND
This has been a complex year for multiple banks in Switzerland, as criminal groups have experimented with all sorts of methods to keep cashing out ATMs across the country, in a practice popularly known as jackpotting. Although the main jackpotting methods include the use of malware and complex hacking tools, the latest wave of attacks seems to have left discretion behind.
Swiss authorities report an unusual increase in reports of bomb attacks on ATMs, each representing profits of at least 100,000 Euros in each incident. So far, Switzerland has recorded a total of 24 bomb attacks against the ATMs of different banks.
Over the past seven days, two attacks on ATMs were detected at Lucerne Central Station, which had to shut down its services for about four hours, with a second explosion on the outskirts of Zurich. The operators of these attacks usually act at night, using what appears to be dynamite to blow up the ATM’s inner box.

Among the plans to keep these attacks at bay is the installation of modern security systems that enable an armored steel door when the ATM’s electronic systems detect unusual activity around the device. France has successfully implemented these systems, so Switzerland is already considering their use.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
LASTPASS CUSTOMERS’ MASTER PASSWORDS BREACHED. CHANGE YOUR MASTER PASSWORD BEFORE HACKERS DO
As of this morning, multiple users of the LastPass password management tool began reporting that their master passwords were compromised after receiving a warning about login attempts in unknown locations. These email notifications also mention that access attempts may have been blocked.
Reports of compromised master passwords have been piling up for hours across social platforms like Facebook, Twitter and Reddit.
Senior Director Nikolett Bacso-Albaum said LastPass is investigating recent reports of possible malicious activity, determining that this is related to a common bot campaign. Apparently, threat actors are using users’ email addresses to try to access their online accounts arbitrarily using the well-known credential stuffing attack.
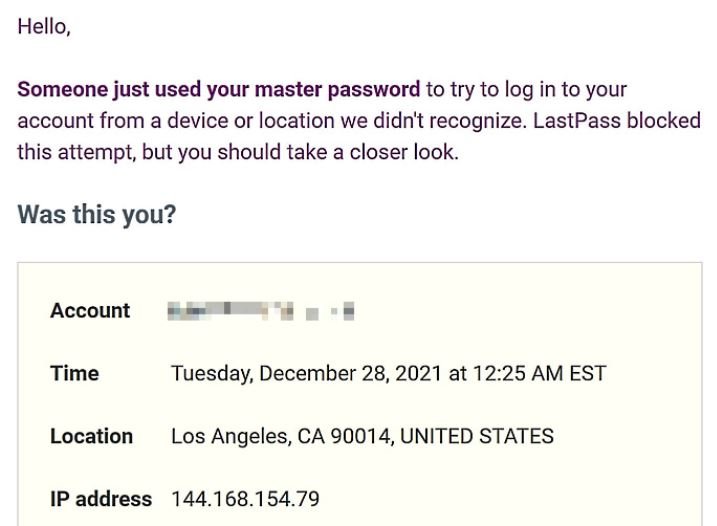
Even though these access attempts have been unsuccessful, users claim that their master passwords are unique to LastPass and should not have been found in separate cybersecurity incidents. The company does not yet seem to have an answer to this question.
LastPass did not add any details about how cybercriminals obtained these records, although researcher Bob Diachenko recently reported the detection of thousands of the platform’s credentials during the analysis of another leak. At the moment the picture seems complicated, as affected customers can’t even disable their LastPass accounts; when a user tries to do this, an unknown error message appears.
Given this situation, users of the platform are advised to keep abreast of any new updates on the incident.
This isn’t the first time LastPass users have suffered a similar incident. Two years ago, the company announced the fix of a critical vulnerability in the password manager Chrome extension that could have allowed malicious hackers to steal credentials last used to log into a website. Although the bug was addressed shortly, it left a very bad precedent for the company.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
RESEARCHER PUBLISHES CODE ON GITHUB TO DOWNLOAD VIDEOS FROM NETFLIX, AMAZON PRIME AND GITHUB AT NO COST
Despite the existence of tools for the protection of digital content, piracy always seems to be one step ahead of security teams on streaming platforms, which are simply not able to stop the leakage of their content outside their own platforms.
Platforms such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+ and others use tools such as Widevine DRM, a technology developed by Google for the protection of digital content. Widevine DRM includes three levels of security, with L1 being the most secure of all. Despite their advanced development and recognized capabilities, these kinds of tools can be compromised using various methods.
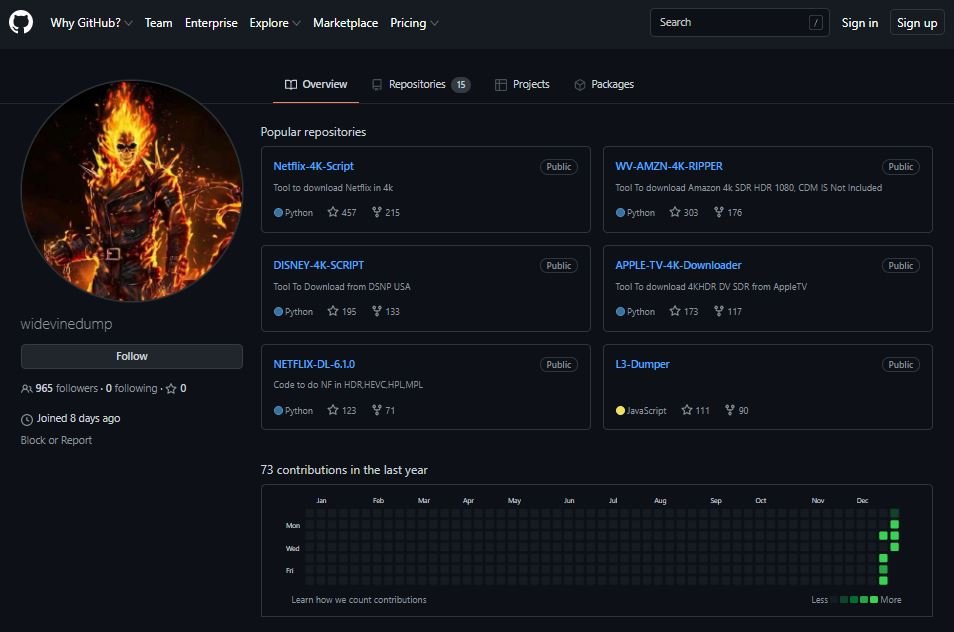
One such method for downloading content was recently revealed on GitHub, where a user identified as “Widevinedump” posted various repositories with tools that allow any user to download HD videos from major streaming platforms.
While the code is completely free and seemingly easy to use, it is necessary to mention that it might not be really safe, so its use is left to each person’s consideration.
The user posted a set of tools identified as DISNEY-4K-SCRIPT, Netflix-4K-Script, WV-AMZN-4K-RIPPER, HBO-MAX-BLIM-TV-Paramount-4k-Downloader, APPLE-TV-4K-Downloader and several other tools, ensuring that they all work and are maintained regularly.
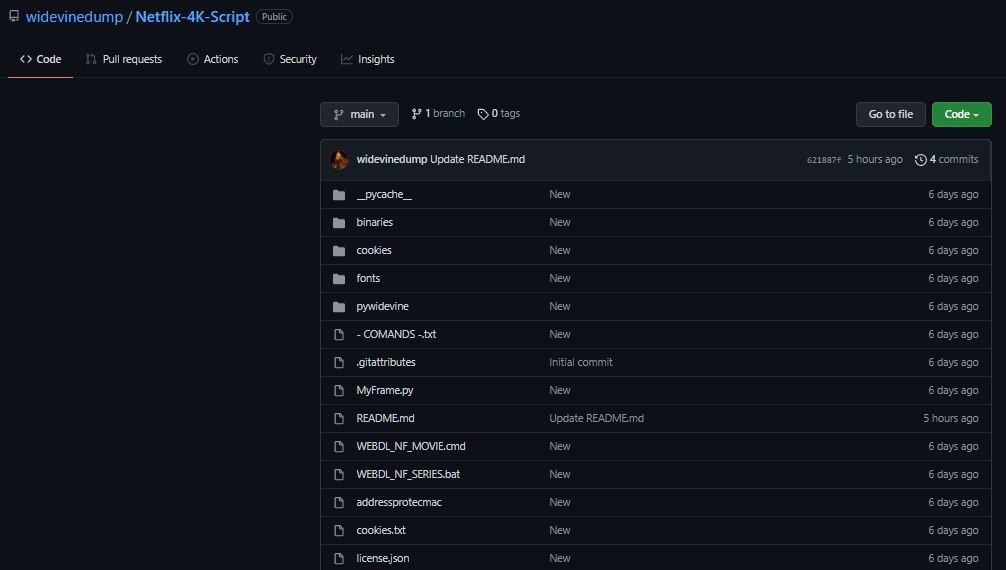
It all sounds too good and really easy, although there is always something behind these tools. Although this time it is not a virus, the trick is that widevinedump tools do not include the content decryption module, necessary to download content in 4K quality.
To access this module, users must pay a developer, which is possible by contacting Widevinedump, who even left their own email address for contact. Even though this toolkit is incomplete and may be insecure, it will surely prove useful to some users and developers.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
HACKERS ATTACK CRYPTOCURRENCY EXCHANGE PLATFORM: OVER 1.9 MILLION USERS AFFECTED
A hacking group self-called VNDCIO has been credited with a devastating cyberattack on the servers of Onus, a popular cryptocurrency exchange app based in Vietnam, generating losses for almost 2 million users on the platform. The information compromised during this incident is for sale on a well-known illegal forum on the dark web.
Faced with this situation, the company claims to be actively working to detect and correct the flaws that hackers addressed, in addition to implementing more functional methods to improve the security of its systems in general terms.
A day before the compromised information was exposed online, Onus reported to its users the detection of potentially malicious activity on their networks, although in the end it was not confirmed if any users would have been affected by the incident: As the days passed, the company confirmed the security breach: “By exploiting a security hole, a third party managed to gain unauthorized access to our systems, stealing hundreds of data from Onus,” said a statement from the firm.
The incident is believed to expose sensitive personal information of users, including full names, contact information, addresses, transaction history and even encrypted passwords. Experts say the leak could also involve copies of ID cards in the form of scans uploaded to Onus systems.
Hackers claim that most of the users whose data was exploited are Vietnamese. After posting images of user IDs in Vietnam, India and Indonesia, VNDCIO also published samples of what appear to be ID cards from the platform.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
55 VULNERABILITIES PATCHED IN DELL EMC UNITY. CHECK YOUR SERVERS FOR UPDATES
Cybersecurity specialists reported the finding of dozens of vulnerabilities affecting Dell EMC Unity. According to the report, successful exploitation of these 55 flaws could lead to severe cybersecurity risks scenarios, not to mention that there are a few publicly available exploits.
Below is a brief description of some of the reported flaws, in addition to their tracking keys and scores according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) scale.
CVE-2020-36229: A type confusion error in ldap_X509dn2bv when parsing X.509 DN in ad_keystring would allow remote threat actors sending specially crafted requests to crash it in a denial of service (DoS) condition.
This is a medium severity vulnerability and received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2020-17438: A boundary error while processing IP packets would allow malicious remote hackers to send specially crafted IP packets to the affected system, trigger an out-of-bounds write and thus executing arbitrary code.
This is a critical vulnerability with a CVSS score of 8.5/10.
CVE-2020-13987: A boundary condition in the uIP TCP/IP Stack component when calculating the checksums for IP packets in upper_layer_chksum in net/ipv4/uip.c would allow remote attackers sending specially crafted traffic to the system and trigger a DoS condition.
This vulnerability received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2020-13988: An integer overflow in the affected implementation would allow a remote threat actor to send a specially crafted IP packet and trigger a DoS condition.
This is a low severity flaw and received a CVSS score of 5.7/10.
CVE-2020-36221: An integer underflow within the serialNumberAndIssuerCheck() function in schema_init.c allows remote attackers to send specially crafted requests to the affected application, thus performing a DoS attack.
The flaw received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2020-36222: A reachable assertion in slapd in the saslAuthzTo validation allows remote hackers to send specially designed requests aiming to perform a DoS attack.
This is a medium severity vulnerability and received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2020-36223: A boundary error during the Values Return Filter control handling would allow remote hackers to send a specially crafted request to the slapd, performing a DoS condition.
The flaw received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2020-36224: The release of an invalid pointer when processing saslAuthzTo requests enables threat actors to send specially crafted requests and trigger DoS conditions.
The vulnerability received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2020-36225: A boundary error in the saslAuthzTo processing would allow remote attackers sending specially crafted requests to the slapd, triggering a DoS attack.
This is a medium severity vulnerability and received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2020-36226: The improper management of internal resources within the application leading to a memch->bv_len miscalculation during saslAuthzTo processing would allow remote attackers sending specially crafted requests to the slapd and perform a DoS attack.
According to the report, the reported flaws reside in the following products and versions:
- Dell EMC Unity XT Operating Environment (OE): before 5.1.2.0.5.007
- Dell EMC UnityVSA Operating Environment (OE): before 5.1.2.0.5.007
- Dell EMC Unity Operating Environment (OE): before 5.1.2.0.5.007
A full list of detected vulnerabilities is available at Dell official support platforms.
Most of these flaws could be remotely exploited by non-authenticated threat actors and there are at least three publicly available exploits, so users of affected implementations should install the official security patches as soon as possible.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
7 VULNERABILITIES PATCHED IN WIRESHARK. UPDATE IMMEDIATELY
Cybersecurity specialists report the detection of various vulnerabilities in Wireshark, the popular protocol analyzer used to perform analysis and troubleshoot communications networks, in addition to performing data and protocol analysis. According to the report, successful exploitation of these flaws would allow threat actors to deploy denial of service (DoS) attacks.
Below are brief descriptions of the reported flaws, as well as their respective identification keys and scores according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
CVE-2021-4186: Insufficient validation of user-provided inputs in the Gryphon dissector would allow remote threat actors to pass specially crafted traffic over the network and perform a DoS attack on the target system.
This is a medium severity vulnerability and received a CVSS score of 5.7/10.
CVE-2021-4185: An infinite loop in the RTMPT disector would allow remote malicious hackers to send specially crafted traffic over the network, consuming all available system resources and causing a DoS condition.
The flaw received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2021-4184: An infinite loop in BitTorrent’s DHT dissector would allow remote attackers to send specially crafted traffic over the network, consuming system resources and generating a DoS condition.
This is a flaw of medium severity and received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
CVE-2021-4183: Insufficient validation of user-provided entries in the pcapng file analyzer would allow threat actors to trick victims into opening a malformed packet trace file, deploying a DoS condition.
This is a flaw of medium severity and received a CVSS score of 5.7/10.
CVE-2021-4182: An infinite loop in the RFC 7468 file analyzer would allow remote threat actors to send their victims a specially crafted packet tracking file, thus consuming all the resources of the affected CPU.
The flaw received a CVSS score of 5.7/10.
CVE-2021-4181: Insufficient validation of user-provided inputs in the Sysdig event dissector would allow remote hackers to send specially crafted traffic over the target network, deploying a DoS attack.
This is a medium severity vulnerability and received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
No CVE key: An infinite loop in the Kafka protocol dissector would allow remote attackers to send specially crafted traffic over the network, consuming the resources of the affected system and resulting in a DoS attack.
The flaw received a CVSS score of 6.5/10.
According to the report, all detected flaws reside in the following Wireshark versions: 3.4.0, 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.4.3, 3.4.4, 3.4.5, 3.4.6, 3.4.7, 3.4.8, 3.4.9, 3.4.10 and 3.6.0.
Although flaws can be exploited remotely by unauthenticated threat actors, no active exploitation attempts have been detected so far. Still, users of affected deployments are encouraged to upgrade as soon as possible.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
BRECHA DE DATOS AFECTA A IMPORTANTE FIRMA DE LOGÍSTICA; MILLONES DE REGISTROS AFECTADOS
Los investigadores de Website Planet reportan el hallazgo de una brecha de datos afectando a D.W. Morgan, una firma multinacional de logística con sede en E.U. Según el reporte, la filtración se debe a un bucket de Amazon Web Services (AWS) completamente expuesto en línea, accesible sin medida de seguridad alguna.
La implementación comprometida contenía más de 2.5 millones de archivos, equivalentes a unos 100 GB de información de los clientes corporativos de D.W. Morgan. Ente los clientes de la firma se incluyen algunas de las compañías más valiosas de E.U.
El bucket de AWS expuesto incluía cinco carpetas almacenando cinco clasificaciones de archivos en específico, según pudieron detectar los investigadores:
- Planes y acuerdos de transporte
- Fotos de procesos
- Archivos adjuntos
- Firmas
- Documentos no identificados
A continuación daremos un breve repaso por las características de cada carpeta expuesta durante este incidente.
PLANES DE ACUERDOS Y DE TRANSPORTE
Esta primera carpeta incluye datos sobre los planes y acuerdos de transporte de la compañía; esta información incluye el curso de acción acordado para los conductores de reparto, personal de almacén y de seguridad. Entre los registros expuestos se encuentran:
- Detalles de los procesos
- Ubicaciones de las instalaciones
- Nombres completos
- Direcciones email empresariales de los clientes

FOTOS DE PROCESOS
Esta carpeta almacenaba al menos 800,000 imágenes ilustrativas sobre diversas partes del proceso de envíos en la compañía. Estas imágenes probablemente fueron capturadas por empleados para registrar envíos y documentos.
ARCHIVOS ADJUNTOS
Incluye toda clase de facturas, etiquetas de envío y listas de empaque que probablemente provengan de los sistemas email de la compañía. En total, había más de 10,000 de estos archivos en esta carpeta específica.

FIRMAS
Aunque se desconocen muchos detalles sobre las firmas encontradas en el bucket, es probable que se relacionen con los múltiples procesos de entregas en la compañía. La carpeta almacena más de 4.5 millones de archivos.
DOCUMENTOS NO IDENTIFICADOS
Más de 100,000 archivos que no parecen tener relación alguna entre sí, aunque incluyen información de identificación personal y detalles de clientes corporativos.

Los investigadores notificaron de inmediato a la compañía, que se apresuró a revocar el acceso inseguro a la información comprometida. No obstante, se desconoce por cuánto tiempo pudo permanecer expuesta esta información.
Del mismo modo que en cualquier otro incidente similar, los empleados y clientes corporativos afectados podrían verse expuestos a ataques de phishing, fraude de identidad y complejas campañas de ingeniería social, por lo que es fundamental que la compañía implemente los mecanismos de prevención necesarios para abordar el incidente.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VULNERABILIDAD SEVERA DE EJECUCIÓN REMOTA DE CÓDIGO EN APACHE HTTP SERVER
Los desarrolladores de Apache Software Foundation anunciaron el lanzamiento de una nueva versión de Apache HTTP Server, con lo que esperan abordar completamente una vulnerabilidad crítica recientemente detectada que permitiría la ejecución remota de código en implementaciones afectadas.
Al respecto, la Agencia de Ciberseguridad y Seguridad de Infraestructura de E.U. (CISA) también emitió una alerta solicitando urgentemente a los usuarios de Apache HTTP Server actualizar a v2.4.52 lo antes posible.
Esta actualización contiene parches para CVE-2021-44790 y CVE-2021-44224, dos fallas que permitirían a los actores de amenazas tomar control total de una implementación afectada. Sobre la más severa de estas fallas, Apache menciona: “Un cuerpo de solicitud cuidadosamente diseñado puede causar un desbordamiento del búfer en el analizador multiparte mod_lua (r: parsebody () llamado desde scripts Lua)”. Hasta el momento no se conocen casos de explotación activa de CVE-2021-44790.

Por otra parte, Apache describe a CVE-2021-44224 como “una desreferencia NULL de riesgo moderado que podría conducir a un ataque de falsificación de solicitudes del lado del servidor (SSRF)”. Debido a esto, un URI especialmente diseñado y enviado a httpd configurado como un proxy de reenvío puede causar un bloqueo o, para configuraciones que mezclan declaraciones de proxy reenvío e inverso, puede permitir que las solicitudes se dirijan a un extremo de socket de dominio Unix declarado.
Este año ha sido muy activo en cuanto a la detección de fallas de seguridad en Apache HTTP Server; apenas hace unas semanas, CISA alertó sobre un error identificado como CVE-2021-40438 y cuya explotación permitiría a los hackers maliciosos desplegar ataques de falsificación de solicitudes del lado del servidor. Esta falla ya ha sido explotada en escenarios reales, por lo que sigue siendo un problema para los administradores de Apache.
Si bien los intentos de explotación de esta falla no son un problema extendido para todas las iteraciones de Apache HTTP Server, se recomienda a los usuarios de implementaciones afectadas mantenerse al tanto de los últimos parches de actualización lanzados por la fundación.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
AUTORIDADES CONFISCAN MILES DE TELÉFONOS A PRUEBA DE HACKING EN CÁRCELES DE ESCOCIA
En su más reciente reporte, el servicio de prisiones de Escocia reveló que se confiscaron un total de 1889 teléfonos celulares debido al mal uso dentro de las cárceles locales. Estos dispositivos fueron entregados a miles de prisioneros a inicios de 2020 como parte de las medidas de aislamiento por coronavirus, ya que las cárceles no podían recibir visitantes y el contacto con el exterior era prácticamente nulo.
Al anunciar esta medida, el ex secretario de Justicia Humza Yousaf mencionó que se autorizó un gasto de 2.7 millones de libras esterlinas para la compra de 7,500 teléfonos supuestamente a prueba de hacking. No obstante, algunos prisioneros descubrieron un método efectivo para liberar las funciones restringidas de estos dispositivos unas cuantas horas después de que les fueron entregados. Por el momento se desconoce qué método usaron los prisioneros para hackear estos dispositivos.
Una fuente del servicio de prisiones de Escocia asegura que cientos de prisioneros usaron estos equipos hackeados para operar actividades ilícitas, incluyendo la venta de droga y extorsión, en complicidad con individuos al exterior de las cárceles. También se informó que algunas pandillas dentro de las prisiones lograron robar los dispositivos que fueron otorgados a otros reos, ya que el programa no incluía a prisioneros considerados peligrosos.
Para hacer más grave el problema, los funcionarios de prisiones dicen que es imposible detectar a simple vista qué dispositivos han sido manipulados por hackers, por lo que las prisiones deben invertir recursos considerables para encontrar aquellos teléfonos capaces de realizar llamadas no autorizadas al exterior, así que el problema no puede ser abordado en cuestión de unos pocos días.
Por lo pronto, se ha decidido que se revocará el acceso a estos teléfonos para los reos que hagan mal uso de los dispositivos, además de que se implementarán medidas más estrictas para prevenir el contrabando de nuevos dispositivos al interior de las cárceles. Estos permisos podrán ser revocados por un mes, dos meses o de forma permanente.
A pesar de estas medidas, algunos congresistas han solicitado que el uso de estos dispositivos se elimine por completo, ya que creen que solo causan más problemas de los que resuelven y no hay forma de que la administración de las prisiones pueda garantizar su uso correcto.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
NUEVOS ATAQUES BOMBA CONTRA CAJEROS AUTOMÁTICOS DETECTADOS EN SUIZA
Este ha sido un año complejo para múltiples bancos en Suiza, ya que los grupos criminales han experimentado toda clase de métodos para seguir vaciando cajeros automáticos a lo largo de todo el país, en una práctica popularmente conocida como jackpotting. Aunque los principales métodos de jackpotting incluyen el uso de malware y complejas herramientas de hacking, la más reciente oleada de ataques parece haber dejado atrás la discreción.
Autoridades suizas reportan un incremento inusitado en los reportes de ataques bomba contra cajeros automáticos, cada uno representando ganancias de al menos 100,000 euros en cada incidente. Hasta este momento, Suiza ha registrado un total de 24 ataques bomba contra los cajeros de diferentes bancos.
Durante los últimos siete días se detectaron dos ataques contra cajeros automáticos en la estación central de Lucerna, que tuvo que pausar sus servicios durante unas cuatro horas, con una segunda explosión en las afueras de Zúrich. Los operadores de estos ataques suelen actuar de noche, empleando lo que parece ser dinamita para hacer estallar la caja interior del cajero automático.

Entre los planes para mantener a raya estos ataques destaca la instalación de modernos sistemas de seguridad que habilitan una puerta de acero blindada cuando los sistemas electrónicos del cajero automático detectan actividad inusual alrededor del dispositivo. Francia ha implementado con éxito estos sistemas, por lo que Suiza ya considera su uso.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
HACKERS USAN EL MODO SEGURO DE WINDOWS PARA INSTALAR RANSOMWARE EN LOS SISTEMAS AFECTADOS
Un reporte de la firma de ciberseguridad Sophos señala la detección de un grupo de hacking que está tratando de evadir los controles de seguridad en los sistemas atacados mediante el uso combinado del Modo Seguro del sistema Windows y la herramienta de administración remota AnyDesk.
Como ya sabrá, el Modo Seguro de Windows es un método de soporte informático para la resolución de problemas que requiere de la inhabilitación de la mayoría de las herramientas de seguridad en el sistema en cuestión, mientras que AnyDesk brinda a los usuarios acceso remoto continuo a un sistema.
Los investigadores de Sophos descubrieron que los actores de amenazas detrás de esta campaña buscan infectar los sistemas vulnerables con la variante de ransomware AvosLocker, instalando la herramienta AnyDesk para habilitar de forma arbitraria el Modo Seguro y desactivar los mecanismos de seguridad en el sistema objetivo.
De este modo, se crea un escenario en el que los actores de amenazas tienen control remoto total sobre cada máquina que han configurado con AnyDesk, mientras que los sistemas afectados no son capaces de alertar al administrador legítimo sobre las acciones maliciosas. Los expertos de Sophos aseguran que esta es la primera ocasión en que encuentran a un grupo de hacking usando esta táctica.
Sobre AvosLocker, los expertos mencionan que esta es una plataforma de ransomware como servicio (RaaS) detectada por primera vez a mediados de 2021 y capaz de infectar tanto sistemas Windows como distribuciones Linux. Desde su detección, AvosLocker ha incrementado considerablemente su popularidad, con ataques confirmados en Estados Unidos, América Latina, Oriente Medio y algunas regiones de Asia.
El reporte agrega que la secuencia principal comienza con los atacantes usando PDQ Deploy para la ejecución de un script identificado como “love.bat” o “lock.bat” en los sistemas afectados. Posteriormente, los hackers lanzan una serie de comandos que preparan el sistema objetivo para la instalación del ransomware, reiniciando el sistema en Modo Seguro. La ejecución de comandos toma alrededor de cinco segundos e incluye la inhabilitación de los servicios de actualización de Windows y Windows Defender.
El uso de AnyDesk garantiza acceso de comando y control continuo a los actores de amenazas, además de que permite la creación de una nueva cuenta con detalles de inicio de sesión automático para conectarse al controlador de dominio afectado de forma remota, completando así el ataque.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
HACKEAN CONTRASEÑAS MAESTRAS DE CLIENTES DE LASTPASS; CAMBIE SU CONTRASEÑA MAESTRA DE INMEDIATO
Desde esta mañana, múltiples usuarios de la herramienta de gestión de contraseñas LastPass comenzaron a reportar que sus contraseñas maestras fueron comprometidas luego de recibir una advertencia sobre intentos de inicio de sesión en ubicaciones desconocidas. Estas notificaciones email también mencionan que los intentos de acceso pudieron ser bloqueados.
Los reportes sobre contraseñas maestras comprometidas llevan horas acumulándose a través de plataformas sociales como Facebook, Twitter y Reddit.
Al respecto, la directora senior Nikolett Bacso-Albaum mencionó que LastPass está investigando informes recientes sobre posible actividad maliciosa, determinando que esto está relacionado con una campaña de bots comunes. Al parecer, los actores de amenazas están usando las direcciones email de los usuarios para tratar de acceder a sus cuentas en línea de forma arbitraria empleando el conocido ataque de relleno de credenciales.

A pesar de que estos intentos de acceso han sido infructuosos, los usuarios afirman que sus contraseñas maestras son exclusivas de LastPass y no deberían haber sido encontradas en incidentes de ciberseguridad separados. La compañía no parece tener aún una respuesta para esta interrogante
LastPass no agregó detalle alguno sobre cómo los cibercriminales obtuvieron estos registros, aunque el investigador Bob Diachenko recientemente reportó la detección de miles de credenciales de la plataforma durante el análisis de otra filtración. Por el momento el panorama parece complicado, ya que los clientes afectados ni siquiera pueden deshabilitar sus cuentas de LastPass; cuando un usuario trata de hacer esto, aparece un mensaje de error desconocido.
Ante esta situación, se recomienda a los usuarios de la plataforma mantenerse al tanto de cualquier nueva actualización sobre el incidente.
Esta no es la primera ocasión en que los usuarios de LastPass sufren un incidente similar. Hace dos años, la compañía anunció la corrección de una vulnerabilidad en la extensión de Chrome del administrador de contraseñas que podría haber permitido a los hackers maliciosos robar las credenciales utilizadas por última vez para iniciar sesión en un sitio web. Aunque el error fue abordado en breve, dejó un precedente muy malo para la compañía.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
INVESTIGADOR PUBLICA EN GITHUB CÓDIGO PARA DESCARGAR VIDEOS DE NETFLIX, AMAZON PRIME Y DISNEY+ SIN COSTO
A pesar de la existencia de herramientas para la protección del contenido digital, la piratería siempre parece estar un paso delante de los equipos de seguridad en plataformas de streaming, que simplemente no son capaces de detener la filtración de su contenido fuera de sus propias plataformas.
Plataformas como Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+ y otras usan herramientas como Widevine DRM, una tecnología desarrollada por Google para la protección del contenido digital. Widevine DRM incluye tres niveles de seguridad, siendo L1 el más seguro de todos. A pesar de su avanzado desarrollo y reconocidas capacidades, esta clase de herramientas pueden ser comprometidas empleando diversos métodos.

Uno de estos métodos para la descarga de contenido fue revelado recientemente en GitHub, donde un usuario identificado como “Widevinedump” publicó diversos repositorios con herramientas que permiten a cualquier usuario descargar videos en alta definición desde las principales plataformas de streaming.
Si bien el código es completamente gratuito y aparentemente fácil de usar, es necesario mencionar que podría no ser realmente seguro, por lo que su uso queda a consideración de cada persona.
El usuario publicó un conjunto de herramientas identificadas como DISNEY-4K-SCRIPT, Netflix-4K-Script, WV-AMZN-4K-RIPPER, HBO-MAX-BLIM-TV-Paramount-4k-Downloader, APPLE-TV-4K-Downloader y varias otras herramientas, asegurando que todas funcionan y son mantenidas con regularidad.

Todo suena demasiado bien y realmente fácil, aunque siempre hay algo detrás de estas herramientas. Si bien en esta ocasión no se trata de un virus, el truco es que las herramientas de Widevinedump no incluyen el módulo de descifrado de contenido, necesario para descargar contenido en calidad 4K.
Para acceder a este módulo, los usuarios deben pagar a un desarrollador, lo que es posible contactando a Widevinedump, quien incluso dejó su propia dirección email para contacto. A pesar de que este conjunto de herramientas está incompleto y puede ser inseguro, seguramente podrá resultar útil para algunos usuarios y desarrolladores.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
EL CIFRADO EN DISPOSITIVOS DE ALMACENAMIENTO WESTERN DIGITAL Y SANDISK TIENE VULNERABILIDADES CRÍTICAS
Un reciente reporte indica que los dispositivos de almacenamiento fabricados por diversas firmas tecnológicas podrían verse afectados por un conjunto de vulnerabilidades en el software de cifrado que estas herramientas usan en común. Entre los fabricantes afectados por estas fallas destaca Western Digital, que recientemente había lanzado actualizaciones de seguridad para su producto SanDisk SecureAccess (ahora llamado SanDisk PrivateAccess), que permite cifrar archivos y carpetas almacenadas en unidades flash USB de SanDisk.
Acorde al investigador Sylvain Pelissier, los problemas derivan de dos vulnerabilidades de derivación de claves que podrían ser explotados para obtener las contraseñas de un usuario objetivo. Estas fallas residen en el software de cifrado DataVault, desarrollado por ENC Security.

Esta es una solución que proporciona lo que sus creadores llaman “protección de datos de grado militar”, compatible con toda clase de sistemas, incluyendo unidades USB, discos duros, almacenamiento conectado en red (NAS), CDS e implementaciones en la nube. DataVault es empleado por otros proveedores además de SanDisk, incluyendo a Sony y Lexar entre sus principales clientes.
En su investigación, Pelissier utilizó ingeniería inversa y varias otras técnicas de hacking, lo que llevó al hallazgo de algunas debilidades que podrían permitir ataques de fuerza bruta. Estos problemas de seguridad fueron identificados como CVE-2021-36750 y CVE-2021-36751.
Según el experto, la función de derivación de claves era PBKDF2 usando 1000 iteraciones de MD5 para derivar la clave de cifrado. El salt utilizado para derivar las claves es constante y está codificado en todas las soluciones y todos los proveedores, lo que hace que sea más fácil para un actor de amenazas adivinar la contraseña de usuario.
Según el experto, la función de derivación de claves era PBKDF2 usando 1000 iteraciones de MD5 para derivar la clave de cifrado. El salt utilizado para derivar las claves es constante y está codificado en todas las soluciones y todos los proveedores, lo que hace que sea más fácil para un actor de amenazas adivinar la contraseña de usuario. Pelissier agrega que incluso usando un salt generado aleatoriamente sería fácil recuperar una contraseña.
Al respecto, ENC Security emitió un comunicado en el que reconocen que DataVault usaba un hash criptográfico unidireccional con un salt predecible, lo que lo hacía vulnerable a ataques de diccionario y otras variantes de hacking, poniendo en riesgo los datos de los usuarios. Las debilidades fueron abordadas con el lanzamiento de DataVault v7.2, por lo que se recomienda actualizar a la brevedad.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
HACKERS DEL RANSOMWARE AVOSLOCKER ENTREGAN HERRAMIENTA DE DESCIFRADO AL GOBIERNO DE E.U.
Después de llamar la atención del gobierno de E.U. cifrando los sistemas de una oficina pública, los operadores del grupo de ransomware AvosLocker publicaron una herramienta de descifrado gratuita para que las víctimas de esta infección puedan recuperar sus archivos comprometidos sin tener que pagar a los hackers.
Según el reporte, a pesar de que los hackers lograron robar información confidencial y cifrar los sistemas afectados como en cualquier otro ataque, después de darse cuenta de que la víctima era una agencia gubernamental decidieron entregar la herramienta de descifrado sin exigir el pago del rescate.
Aunque los hackers cortaron de tajo con este ataque, parece que se negaron a entregar una lista de la información robada a la agencia afectada, además de mantener en secreto el método de hacking utilizado.
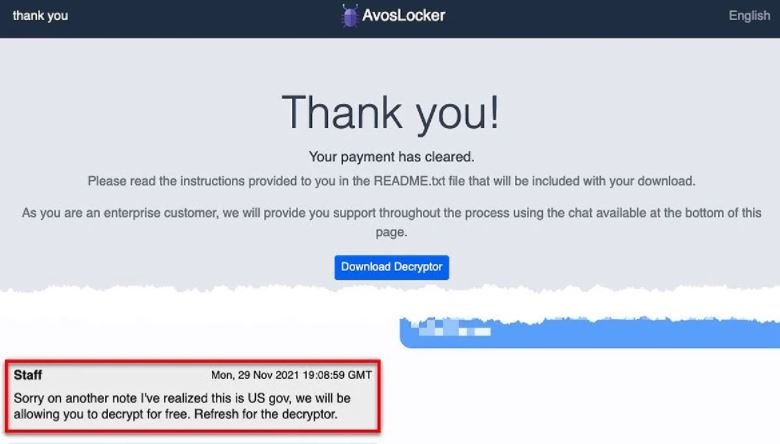
Esta tarde, un supuesto miembro de AvosLocker intercambió algunos mensajes con un investigador independiente; el presunto hacker asegura que aunque su grupo despliega ataques contra cualquier objetivo por igual, tratan de evitarse problemas con entidades gubernamentales y hospitales, pero no hay un control estricto sobre las actividades de sus afiliados: “A veces un afiliado puede bloquear una red sin verificar de quién se trata; es difícil que el gobierno entregue el dinero de los contribuyentes a un grupo de hacking”, agrega.
Como recordará, AvosLocker es una operación de ransomware como servicio (RaaS), lo que significa que los desarrolladores principales se dedican exclusivamente al mantenimiento del malware y de los sistemas informáticos relacionados con el ataque, mientras los grupos afiliados compran el acceso al virus y se encargan de desplegar los ataques para después dividir las ganancias obtenidas.
Desde hace meses las autoridades de E.U. comenzaron a ejercer mayor presión contra los grupos de ransomware, lo que ha llevado al cierre de peligrosas operaciones como DarkSide, BlackMatter y Avaddon. Aunque en muchos casos estos cierres son temporales o simples relanzamientos, los grupos de ransomware enfrentan cada vez más problemas con las agencias de la ley.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
7 VULNERABILIDADES ABORDADAS EN WIRESHARK. ACTUALICE DE INMEDIATO
Especialistas en ciberseguridad reportan la detección de diversas vulnerabilidades en Wireshark, el popular analizador de protocolos utilizado para realizar análisis y solucionar problemas en redes de comunicaciones, además de realizar análisis de datos y protocolos. Según el reporte, la explotación exitosa de estas fallas permitiría a los actores de amenazas desplegar ataques de denegación de servicio (DoS).
A continuación se presentan breves descripciones de las fallas reportadas, además de sus respectivas claves de identificación y puntajes acorde al Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
CVE-2021-4186: La validación insuficiente de las entradas proporcionadas por el usuario en el disector Gryphon permitiría a los actores de amenazas remotos pasar tráfico especialmente diseñado a través de la red y realizar un ataque DoS en el sistema objetivo.
Esta es una vulnerabilidad de severidad media y recibió un puntaje CVSS de 5.7/10.
CVE-2021-4185: Un bucle infinito en el disector RTMPT permitiría a los hackers maliciosos remotos enviar tráfico especialmente diseñado a través de la red, consumiendo todos los recursos del sistema disponibles y provocando una condición DoS.
La falla recibió un puntaje CVSS de 6.5/10.
CVE-2021-4184: Un bucle infinito en el disector DHT de BitTorrent permitiría a los atacantes remotos enviar tráfico especialmente diseñado a través de la red, consumiendo los recursos del sistema y generando una condición DoS.
Esta es una falla de severidad media y recibió un puntaje CVSS de 6.5/10.
CVE-2021-4183: La validación insuficiente de las entradas proporcionadas por los usuarios en el analizador de archivos pcapng permitiría a los actores de amenazas engañar a las víctimas para abrir un archivo de seguimiento de paquetes con formato incorrecto, desplegando una condición DoS.
Esta es una falla de severidad media y recibió un puntaje CVSS de 5.7/10.
CVE-2021-4182: Un bucle infinito en el analizador de archivos RFC 7468 permitiría a los actores de amenazas remotos enviar a sus víctimas un archivo de seguimiento de paquetes especialmente diseñado, consumiendo así todos los recursos del CPU afectado.
La falla recibió un puntaje CVSS de 5.7/10.
CVE-2021-4181: La validación insuficiente de entradas proporcionadas por el usuario en el disector de eventos Sysdig permitiría a los hackers remotos enviar tráfico especialmente diseñado a través de la red objetivo, desplegando un ataque DoS.
Esta es una vulnerabilidad de severidad media y recibió un puntaje CVSS de 6.5/10.
Sin clave CVE: Un bucle infinito en el disector del protocolo Kafka permitiría a los atacantes remotos enviar tráfico especialmente diseñado a través de la red, consumiendo los recursos del sistema afectado y resultando en un ataque DoS.
La falla recibió un puntaje CVSS de 6.5/10.
Según el reporte, todas las fallas detectadas residen en las siguientes versiones de Wireshark: 3.4.0, 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.4.3, 3.4.4, 3.4.5, 3.4.6, 3.4.7, 3.4.8, 3.4.9, 3.4.10 y 3.6.0.
Aunque las fallas pueden ser explotadas de forma remota por actores de amenazas no autenticados, hasta el momento no se han detectado intentos de explotación activa. Aún así, se recomienda a los usuarios de implementaciones afectadas actualizar a la brevedad.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
