Month: April 2022
BORED APE YACHT CLUB NFTS HEIST. HOW COME THIS KEEPS HAPPENING OVER AND OVER AGAIN?
A group of cybercriminals managed to steal non-fungible token (NFT) worth about $3 million USD from the popular Bored Ape Yacht Club collection. Threat actors reportedly took control of the NFT collection Instagram account and posted a link to a fraudulent website from which the aforementioned assets could be stolen.
The attackers caught the attention of unsuspecting NFT collectors by offering a supposedly free token; these users followed the link posted on Instagram and connected their MetaMask cryptocurrency wallets to an address controlled by the hackers. Instead of receiving the aforementioned token, affected users found their wallets wiped out in minutes.
Shortly after, the project’s official Twitter account confirmed the attack: “Looks like BAYC’s Instagram was hacked; please don’t click any links or link your wallet to another site,” the message read.
Yuga Labs, creators of the Bored Ape Yacht Club, also confirmed that the attackers stole four Bored Apes, six Mutant Apes, and three Bored Ape Kennel Club NFT tokens, as well as other NFTs from various collections, mining assets totaling approximately $3 million USD.
The team behind the NFT collection claims to be actively working to establish contact with affected users, adding that the compromised account had multi-factor authentication and other security mechanisms enabled, so it is still unclear how the attack occurred. The investigation is still ongoing and updates are expected soon.
This is the second attack to hit BAYC in less than a month; In late March, the NFT project confirmed that its official Discord server had been compromised, putting hundreds of investors at critical risk of phishing. Shortly before the Discord server attack and in the context of the ApeCoin cryptocurrency launch, a hacking group stole more than $1.5 million USD through quick loan fraud.
These attacks are highly worrying for NFT developers, investors and enthusiasts, who have seen cybercrime as the main threat to the growth of these projects and their investment potential.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
A BASIC GUIDE TO BUILDING RELIABLE AND ETHICAL AI
Today’s artificial intelligence (AI) may still be far from the stuff of science fiction, but its impact on industries and society is profound and getting more prevalent. With its subset, machine learning, AI helps create safer workplaces, easier access to information, and reliable health diagnoses. Artificial intelligence is also used in virtual assistants, self-driving cars, facial recognition, and recommendation systems in social media, entertainment platforms, and e-commerce. (1)

The potential of AI is limitless, but as this technology advances, the risks also increase. With the technology’s growing influence, the need for rules that govern AI’s decision paths to guide its behavior is becoming apparent. Artificial intelligence relies on data; that’s why processes like data labeling are crucial to efforts in building an ethical AI.
Ethics and artificial intelligence
One of the problematic issues with unrestrained AI is data privacy violations, like what Facebook did when it gave Cambridge Analytica access to the AI-collected personal data of more than 50 million users. There’s also the case of a giant investment bank that allegedly used a gender-discriminating AI algorithm.(2)
Due to instances like these, the discussion regarding AI ethics is no longer the purview of academics and science fiction writers. Tech giants like Microsoft, Facebook, Google, and others are building teams to address ethical issues that result in the wholesale collection of data. Clearly, businesses and industries are responsible for ensuring that AI development is ethical and unbiased.
Basic guide for an ethical AI
For developers, the question of the ‘right’ outcome inevitably arises. Would the outcome be right for certain sectors at a certain period but disastrous for others? Would the system be trustworthy? Discussing these issues is critical for any AI ethics team. The opinions and ethics of the AI’s creators would be passed on to the algorithm.
The AI would no longer be neutral—it would embody the creators’ resolve and biases. Still, there are guides to ensure that the AI has a moral compass, guides that the creators can follow to ensure that the AI’s output is ethical.
Below is a basic guide to building reliable and ethical artificial intelligence:
- Customize AI ethical framework to suit your industry
Adapting a pre-existing framework is easy, but it might not suit your industry. Different companies use technologies differently. An organization serious about building an ethical AI should unequivocally express its ethical standards, including naming all its stakeholders and how the standards will be maintained. A governance structure that oversees the AI’s changing circumstances should also be included.
Moreover, risk mitigation should be baked into the framework. With this method in place, the ethical standards that the different stakeholders—product developers, data collectors, managers, and owners—should comply with are easily determined.
There should also be a straightforward process of elevating ethical concerns to an ethics committee or senior management. The framework should be flexible enough to focus not only on implementing regulations but also on including plans to handle atypical situations.
- Avoid biased datasets
Feeding unbiased datasets can be difficult when it comes to AI. That’s why organizations should include bias mitigation as early as possible. Bias can sneak in unnoticed during AI development, which can impede plans for an ethical AI. A vital stage during ethical AI development is data annotation, as the selected data and its annotator can affect the types of biases that may be injected into it. For example, data annotated wholly by white American males will not be the same compared with annotated data from a team composed primarily of Asian females.
In such cases, diversity can be a big help in avoiding a biased dataset. A large part of preventing bias is recognizing where it comes from, which is usually from data and its annotators.
It’s also vital for any company building an ethical AI to have a method of checking not only for biased algorithms, but also for potential privacy violations and other unethical outputs. (3)
- Conform with global AI ethical guidelines
Artificial intelligence has the potential to raise the global gross domestic product (GDP) by 14% by the year 2030. This game-changing impact makes it imperative for businesses to take advantage of AI. International organizations, such as UNESCO, developed a framework for member-states to adopt and ensure that disruptive technologies such as AI benefit the greatest number of people. (4)
With the expected increase in AI use and the continuous technological upgrades, these organizations also upgrade their framework constantly to keep up. The European Union, for example, revised AI use guidelines for its member-states in a bid to ensure that AI builds are trustworthy and human-centric. (5)
- Security
Another vital concern for building ethical AI is data privacy and security. This concern becomes apparent when an organization has no governance or data strategy set up at the project’s onset. Privacy, however, isn’t the sole concern when it comes to data.
Take companies that deal in financial services. Often, they collect confidential data that needs added security measures. The ideal data partner would have various security options to meet the clients’ requirements and a robust security system to protect the clients’ data and prevent data breaches. Moreover, the data partner should comply with the data regulations specific to the industry and the area.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how businesses are conducted. This technology is poised to affect the world economy massively in the years to come, and with increased AI use, risks are multiplied.
To ensure that AI remains trustworthy and free from biases, a guide for ensuring an ethical AI should be laid out, like the one mentioned in this article. Artificial intelligence can potentially affect the course of history, so guides and regulations to ensure that the technology can benefit the whole society and not just a few sectors are critical.
References
- “AI Applications: Top 14 Artificial Intelligence Applications in 2022”, Source: https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/artificial-intelligence-tutorial/artificial-intelligence-applications
- “Cambridge Analytica and Facebook: The Scandal and the Fallout So Far”, Source: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/04/04/us/politics/cambridge-analytica-scandal-fallout.html
- “Bad, Biased, And Unethical Uses of AI”, Source: https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2019/8/4-unethical-uses-ai
- “Sizing The Prize PwC’s Global Artificial Study: Exploiting The AI Revolution”, Source: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/data-and-analytics/publications/artificial-intelligence-study.html
- “Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI”, Source: https://ec.europa.eu/futurium/en/ai-alliance-consultation.1.html
2 CRITICAL VULNERABILITIES IN THE LINUX OPERATING SYSTEM ALLOW BACKDOORS TO BE INSTALLED WITH ROOT PRIVILEGES
A Microsoft security report details the finding of a set of vulnerabilities that would allow threat actors to escalate privileges on Linux systems in order to inject ransomware, backdoors, and other severe threats. The flaws were identified as Nimbuspwn and their exploitation would trigger access to root privileges on compromised systems.
Nimbuspwn refers to the CVE-2022-29799 and CVE-2022-29800 flaws, which reside in networkd-dispatcher, a component that sends connection state changes on Linux machines. The flaws were discovered during an analysis of messages on the system bus, which led to a review of the code flow for networkd-dispatcher.

Microsoft researcher Jonathan Bar Or mentions that this set of flaws involves issues such as path traversal errors, symbolic link race conditions, and time-of-check-time-to-use (TOCTOU) race conditions. Additionally, during analysis it was observed that the network-dispatcher daemon was running with root privileges at system boot time.
Microsoft discovered that the daemon used a method called “_run_hooks_for_state” to discover and run scripts based on the state of the detected network.
The logic of this method includes returning executable scripts owned by the root user and the root group in the “_run_hooks_for_state” directory. The method executes each script in the above location using subprocess.Popen, while providing custom environment variables.
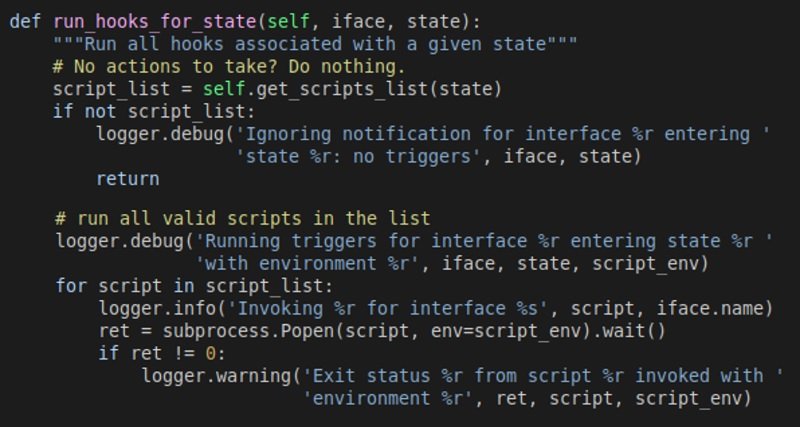
The execution of “_run_hooks_for_state” is what leads to the appearance of these security problems, as reported by Microsoft. Exploitation of Nimbuspwn would allow a threat actor with reduced privileges on the affected Linux system to escalate their privileges to the root level by sending arbitrary signals.
A description of the steps for a successful exploitation is shown in the following diagram, divided into three attack steps:
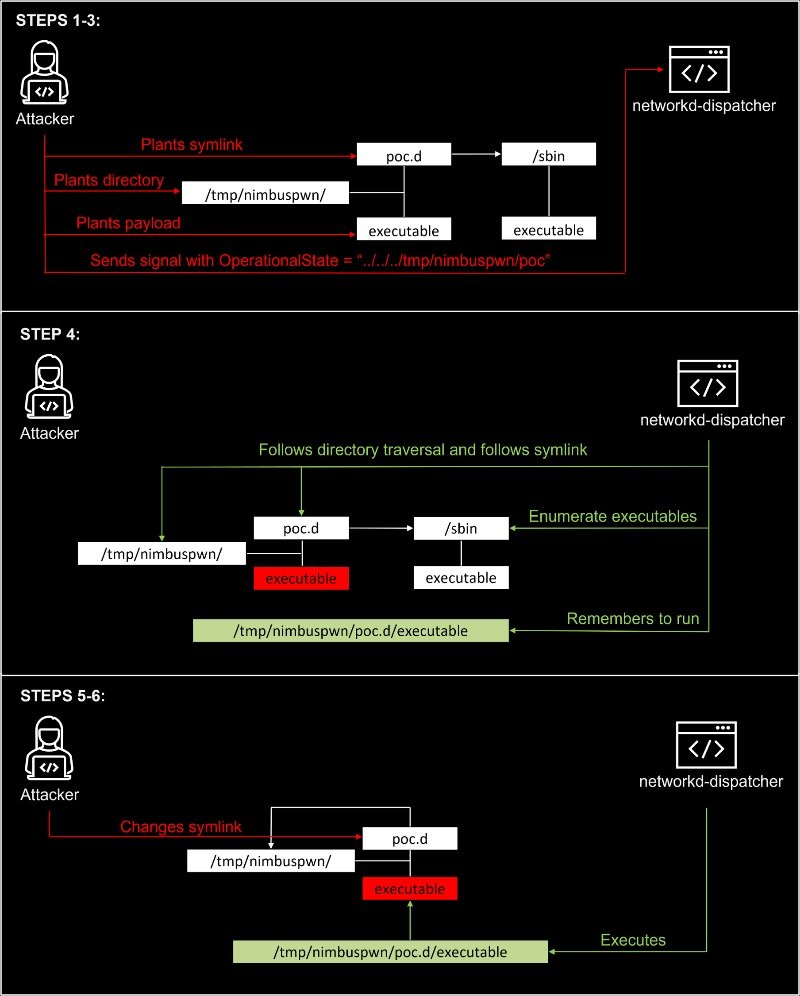
Microsoft specifies that successful exploitation requires planting various files on the affected system.
The report concludes by mentioning that there are many environments where the attack is feasible, including Linux Mint because the systemd-networkd service which normally has the bus name “org.freedesktop.Network1” is not started on boot by default. .
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
4 NEW VULNERABILITIES IN SONICWALL SONICOS AFFECT FIREWALLS AND OTHER SECURITY PRODUCTS: PATCH IMMEDIATELY
A recent cybersecurity report revealed the patching of at least four vulnerabilities in SonicOS, the operating system with which multiple solutions developed by the technology firm SonicWall work. According to this report, the successful exploitation of these flaws would have allowed threat actors to deploy multiple cyberattacks.
Below are brief descriptions of the reported flaws, as well as their tracking keys and scores assigned under the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
CVE-2022-22275: Improper processing of incoming HTTP/S traffic from WAN to DMZ would allow remote threat actors to evade security policy until tcp handshake is complete, triggering a denial of service (DoS) attack.
This is a flaw of medium severity and received a CVSS score of 5.1/10.
CVE-2022-22276: The configured SNMP service remains accessible to external users even if SNMP is disabled on the firewall interfaces, so malicious hackers can connect to the SNMP service, accessing information that would otherwise remain restricted.
The flaw received a CVSS score of 4.6/10.
CVE-2022-22277: SNMP-Reply includes SSID Password in clear text, which would allow remote attackers with the ability to intercept network traffic to gain access to sensitive data.
This is a low-severity bug and received a CVSS score of 3.8/10.
CVE-2022-22278: This flaw exists because the Content Filtering Service (CFS) in SonicOS returns a huge “HTTP 403 forbidden” message to the source address when users try to access resources prohibited by the CFS function.
Remote threat actors can send multiple requests to the system that trigger the 403 error and consume all available bandwidth, leading to a DoS condition. The flaw received a CVSS score of 4.6/10.
According to the report, the flaws reside in all SonicOS versions between 6.5 and 7.0.1.0-5030-1391.
While this vulnerability could be exploited by unauthenticated remote threat actors, no active exploitation attempts or the existence of an attack variant related to the attack have been detected so far. Still, users of affected deployments are encouraged to apply the available patches.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CHARGING STATIONS FOR ELECTRIC CARS IN THE UK ARE HACKED TO SHOW PORNOGRAPHY
Hundreds of electric vehicle drivers on the Isle of Wight, England, were taken by surprise when screens at a local charging station began displaying pornographic content as a result of what appears to be a cyberattack against GeniePoint, the company that manages the affected charging point.
According to a local report, screens at the charging point were supposed to display content from GeniePoint’s official website, although after pranksters made their own, these monitors began displaying adult websites, exposing users to all kinds of sexually explicit content.
The council immediately issued an apology to all users affected by the incident: “The council wishes to apologize to anyone who has found the web content inappropriate and for any inconvenience of the decommissioned charging points.”
Committed charging points are located at Quay Road, Ryde, Cross Street, Cowes and Moa Place. In addition, when trying to access the company’s website, visitors were also redirected to a pornographic site. This incident not only prevented electric car owners from charging their vehicles, but paralyzed the legitimate tasks of websites.
It was also reported that compromised charging points worked intermittently, constantly disconnecting from electric cars: “Charging points may be out of service for a short period of time before restarting remotely, so this could be the problem of it not working. Taking note of the malfunction and the incident, the council decided to replace the charging points with new ones, which could take a couple of months,” the report said.
With the proliferation of electric vehicles and the technology-laden ecosystem they foster, it is critical that government organizations, private companies, cybersecurity firms, and independent researchers take action to mitigate these attacks.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
NOW YOU CAN ASK GOOGLE TO REMOVE YOUR PHONE NUMBER, EMAIL ADDRESS, PHYSICAL ADDRESS AND OTHER PERSONAL CONTACT DATA FROM SEARCH RESULTS. LEARN HOW TO DO IT
After multiple scandals of inappropriate handling of personal information, reinforcing users’ privacy has become one of the primary goals of large technology companies. Such is the case of Google, which has just announced the implementation of new policies that will allow users to request the removal of certain personal content from Google Search results.
While it was already possible to make these requests in cases of doxing or leaking of bank details, the update will allow users to request the removal of other content that appears in search results, including personal contact information. Google will also allow the removal of additional information that may pose a risk of identity theft, such as access credentials to online platforms.
According to the report, the following records may be considered personal contact information:
- Government identification numbers, including social security numbers, tax identification keys and the like depending on the country in question
- Bank account numbers and credit cards
- Images of handwritten signatures
- Images of identity documents
- Medical records
- Physical addresses, phone numbers and email addresses
On the processes that are implemented when receiving one of these requests, Google ensures that they evaluate all the content of websites that may incur in the exposure of confidential data, trying not to limit the availability of other useful data for users. The company also looks at whether content users want to remove is part of public or government records; if so, the request is inadmissible.
Although this is undoubtedly good news, users should remember that removing this content from the results in Google Search, this will not remove the content from the Internet. To do this, it is necessary to communicate directly with the administrators of the website in question.
Google continues to implement changes to its policies in order to improve the privacy experience of its users. In recent days it was revealed the application of a new measure to allow users under the age of 18 to request the removal of any image of theirs from image search results. The parents and guardians of minors may also carry out this procedure.
Full information about these requests and other security and privacy measures implemented by Google is available on the company’s official communication channels.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
ZERO-DAY VULNERABILITIES IN NETATALK AFFECT NAS PRODUCTS FROM SYNOLOGY, QNAP AND WESTERN DIGITAL. PROTECT YOUR STORAGE SOLUTIONS BEFORE THEY’RE ENCRYPTED WITH RANSOMWARE
Several manufacturers of network-attached storage (NAS) solutions have alerted their customers to the detection of critical vulnerabilities in Netatalk. The exploitation of these flaws was demonstrated in one of the most recent versions of the Pwn2Own ethical hacking event, and they affect the devices of manufacturers such as Synology, QNAP and Western Digital.
The security alert mentions that at least six of the bugs reported in Pwn2Own reside in Netatalk, the open-source Apple Filing Protocol (AFP) file server. Many of the flaws could be exploited remotely by unauthenticated threat actors, which would completely compromise the affected devices.
In late March, security teams at Netatalk released patches to address seven vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2021-31439, CVE-2022-23121, CVE-2022-23122, CVE-2022-23123, CVE-2022-23124, CVE-2022-23125, and CVE-2022-0194.
The last Netatalk update was released in December 2018, so some manufacturers who resort to this solution assumed that the project was no longer being maintained. Such is the case with Western Digital, which released firmware updates to remove Netatalk; Western Digital products use Netatalk for access to network shares.
Netatalk began work on the fixes after the demonstration of the attack on Pwn2Own, so QNAP determined that some of its own NAS products could also be affected. This week, QNAP announced that updates for its QTS operating system would be available in the coming days; meanwhile, the company recommends customers disable AFP to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
On the other hand, Synology concluded that these errors could affect its DiskStation Manager and Synology Router Manager products. While an update is already available for DiskStation Manager, Router Manager solutions have not received security patches yet.
Although no active exploitation attempts have been detected so far, it is important to remember that NAS deployments are frequent targets of cybercriminal groups, especially ransomware operations and data theft, so it is critical that companies fix these flaws before it is too late.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CVE-2022-0543: VULNERABILITY IN REDIS WITH 10/10 CVSS SCORE. THOUSANDS OF LINUX SERVERS AFFECTED
A couple of months ago Ubuntu and Debian officials published security advisories related to CVE-2022-0543, a vulnerability derived from a bug in the Redis package in operating systems that received a score of 10/10 according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). According to security advisories, insufficient disinfection of the Lua environment, employed by Redis, could trigger the arbitrary execution of Lua and the evasion of The Redis sandbox environment, compromising thousands of Linux servers.
Last March, researcher Reginaldo Silva, who was credited with finding this vulnerability, published a proof-of-concept (PoC) code, followed by the report of a case of active exploitation just days later.
At this point, the cybersecurity community assumes that there are more public and private exploits, so threat actors will continue to actively try to exploit the flaw until a permanent fix is released.
WHO IS AFFECTED?
When the report was released, it was mentioned that the flaw only affected distributions that use Ubuntu or Debian Redis packages, in addition to the fact that exploitation requires a non-default configuration in Redis and exposure of this dangerous configuration on the Internet.
Although the massive exploitation of CVE-2022-0543 would appear to be a remote exploitation, the Rapid7 researchers decided to analyze the conditions that could facilitate a large-scale attack, in an attempt to calculate how many vulnerable implementations might be currently available. In addition, the exploitation requires a non-default configuration in Redis and exposure of this dangerous configuration on the Internet.
After a month of testing, experts discovered approximately 33,000 Redis servers connected to the Internet allowing unauthenticated access. Although the vulnerability also affects hosts that require authentication, the analysis focused on implementations that facilitate remote access.
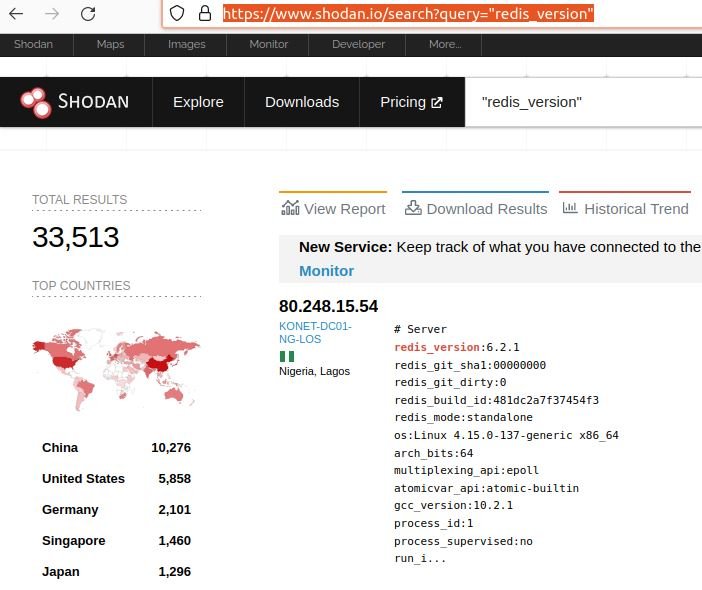
Based on this finding, it was simpler for the researchers to determine how many of these servers could be exposed to the exploitation of this flaw, for which they used the well-known Shodan search engine.
Next, experts began to filter potential affected implementations by applying criteria such as analyzed distribution and Redis version.
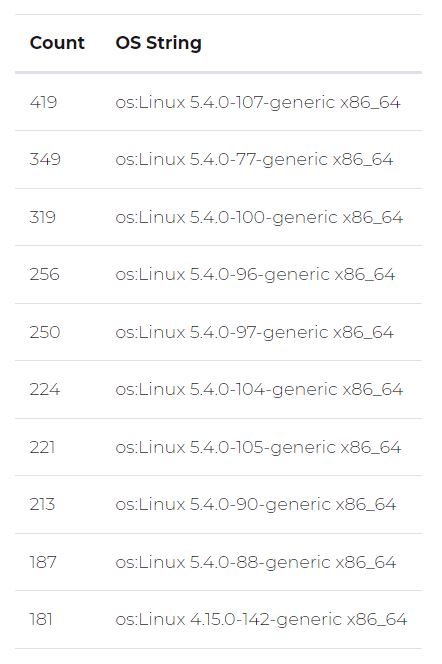
At the end of this process, up to 2,000 potentially vulnerable Redis servers were identified. Although it is not possible to know how many of these hosts installed Redis using affected packages, how many have received updates, or how many are honeypots, the risk should be taken seriously.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
CERT-IN MAKES MANDATORY FOR INDIAN COMPANIES TO REPORT HACKING/CYBER SECURITY INCIDENTS TO GOVERNMENT WITHIN SIX HOURS AFTER DETECTING THEM
A new guideline issued by the India’s Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) became a polemic issue for multiple government IT agencies. The Indian agency has determined that technology organizations should implement measures for the reporting of 20 different types of cyber security incidents within six hours after their detection.
On its reasons for making this determination, the agency mentions that its teams identified “certain gaps that hinder the analysis of security incidents”; in addition to this new deadline, CERT-In will encourage the submission of incident reports by analog mediums such as telephone or fax, in addition to e-mail.
The new mechanisms will apply to service providers, intermediaries, data center operators, enterprises and government organizations that manage IT infrastructure.
As mentioned above, the report lists 20 types of security incidents, including information breaches and ransomware infections. Although it is obvious that the situation merits a report in these cases, on other occasions CERT-In provides very little concrete definitions, as is the case of those defined as “Attacks or suspicious activities that affect systems/servers/software/applications in the cloud”.
In addition to ambiguous definitions, CERT-In has received criticism about how short the report window is. Other legislative frameworks such as EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) establish a deadline of 72 hours for the reporting of security incidents after their detection, while for the U.S. Government 24 hours are more than enough to submit these reports.
This is not the only update to the security incident reporting process in India. According to the new guidelines, organizations under this regulation must also keep a detailed record of all their information systems during the 180 days after the report, also having the obligation to deliver this data to CERT-In when requested.
Finally, additional requirements were established for organizations operating with cryptocurrency. Providers of services related to virtual assets will have to verify the identity of their customers and safeguard this data for at least five years, in what appears to be an aggressive measure against money laundering through cryptocurrency.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
GRUPO DE RANSOMWARE STORMUS AFIRMA HABER HACKEADO COCA-COLA Y ROBADO MILES DE ARCHIVOS CONFIDENCIALES
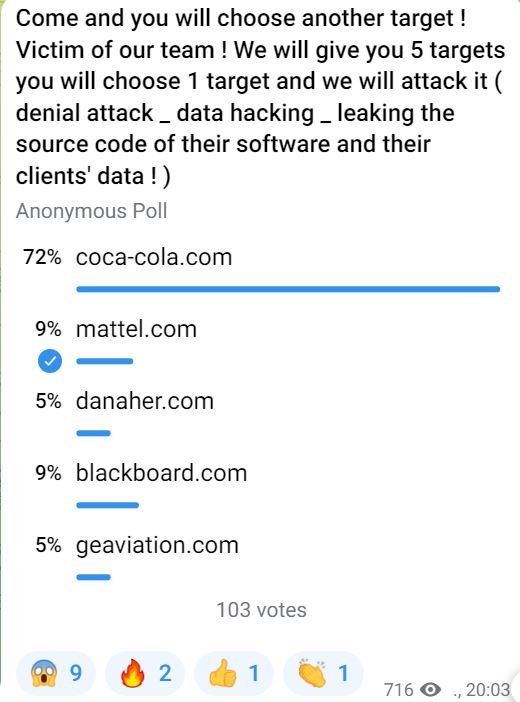
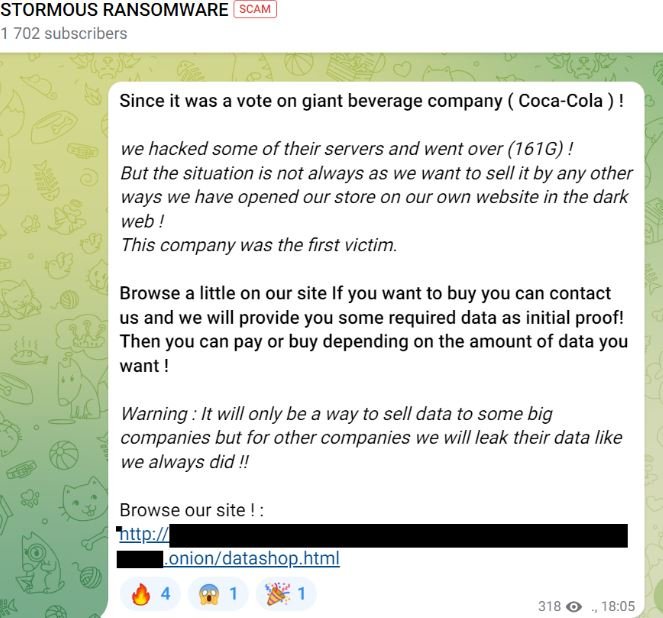
El grupo de ransomware Stormous publicó una actualización en su plataforma ilegal en línea asegurando que lograron hackear los sistemas de Coca-Cola Company, extrayendo más de 161 GB de información del grupo internacional de bebidas.
Este incidente viene después de que el canal de Telegram controlado por Stormus lanzara una encuesta para que sus miembros eligieran la próxima compañía afectada, siendo Coca-Cola la elegida de entre otras empresa como Mattel o Danaher: “Hackeamos algunos de sus servidores y tenemos más de 161 GB… Hemos abierto nuestra tienda en nuestro propio sitio en dark web. Esta empresa fue la primera víctima. Navegue un poco en nuestro sitio”, se lee en el mensaje de los hackers.
Stormus también señala que la información comprometida de la compañía está a la venta, por lo que cualquier interesado en acceder a estos datos puede contactarlos y solicitar una prueba inicial para hacer negocios.
Después del ataque, los hackers de ransomware contactaron a los equipos de TI en Coca-Cola para exigir un rescate de más de 1.644 Bitcoin, unos $65,000 USD. Por el momento se desconoce si el gigante de las bebidas azucaradas está dispuesto a negociar con los cibercriminales o si siquiera han respondido a sus exigencias.

Sobre Stormus, especialistas en ciberseguridad mencionan que este grupo se hizo notar durante el inicio de la invasión rusa en Ucrania, cuando junto con la operación de ransomware Conti manifestó su apoyo al gobierno de Rusia. Como quizás ya sepa, múltiples grupos de ransomware operan desde territorio ruso, donde gozan de impunidad y, muy posiblemente, cuentan con el respaldo de grupos cercanos al Kremlin, lo que convierte al ransomware en una de las amenazas de ciberseguridad con mayores recursos tecnológicos y de infraestructura, garantizando su desarrollo y actividad constante.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
2 VULNERABILIDADES CRÍTICAS EN EL SISTEMA OPERATIVO LINUX PERMITEN INSTALAR BACKDOORS CON PRIVILEGIOS ROOT
Un reporte de seguridad de Microsoft detalla el hallazgo de un conjunto de vulnerabilidades que permitiría a los actores de amenazas escalar privilegios en sistemas Linux con el fin de inyectar ransomware, backdoors y otras amenazas severas. Las fallas fueron identificadas como Nimbuspwn y su explotación desencadenaría en el acceso a privilegios root en los sistemas comprometidos.
Nimbuspwn se refiere a las fallas CVE-2022-29799 y CVE-2022-29800, que residen en networkd-dispatcher, un componente que envía cambios de estado de conexión en máquinas Linux. Las fallas fueron descubiertas durante un análisis de los mensajes en el bus del sistema, lo que derivó en una revisión del flujo de código para networkd-dispatcher.

El investigador de Microsoft Jonathan Bar Or menciona que este conjunto de fallas involucra problemas como errores path traversal, condiciones de carrera de enlace simbólico y condiciones de carrera time-of-check-time-to-use (TOCTOU). Además, durante el análisis se observó que el daemon network-dispatcher se ejecutaba con privilegios root en el momento del arranque del sistema.
Microsoft descubrió que el daemon usaba un método llamado “_run_hooks_for_state” para descubrir y ejecutar scripts según el estado de la red detectada.
La lógica de este método incluye la devolución de scripts ejecutables propiedad del usuario root y el grupo root en el directorio “_run_hooks_for_state”. El método ejecuta cada script en la ubicación anterior mediante subprocess.Popen, a la vez que proporciona variables de entorno personalizadas.

La ejecución de “_run_hooks_for_state” es lo que lleva a la aparición de estos problemas de seguridad, según reporta Microsoft. La explotación de Nimbuspwn permitiría a un actor de amenazas con privilegios reducidos en el sistema Linux afectado escalar sus privilegios a nivel root mediante el envío de señales arbitrarias.
Una descripción de los pasos para una explotación exitosa se muestra en el siguiente diagrama, dividido en tres pasos de ataque:

Microsoft especifica que la explotación exitosa requiere plantar varios archivos en el sistema afectado.
El reporte concluye mencionando que hay muchos entornos en los que el ataque es factible, incluyendo Linux Mint debido a que el servicio systemd-networkd que normalmente posee el nombre de bus “org.freedesktop.Network1” no se inicia en el arranque de forma predeterminada.
Clayton Craft, el mantenedor de networkd-dispatcher, ya ha anunciado el lanzamiento de los parches necesarios, por lo que se ha solicitado a los usuarios de Linux abordar las fallas a la brevedad.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
4 NUEVAS VULNERABILIDADES EN SONICWALL SONICOS AFECTAN A LOS FIREWALLS Y PRODUCTOS DE SEGURIDAD: PARCHE INMEDIATAMENTE
Se ha confirmado la corrección de al menos cuatro vulnerabilidades en SonicOS, el sistema operativo con el que funcionan múltiples soluciones desarrolladas por la firma tecnológica SonicWall. Según este reporte, la explotación exitosa de estas fallas habría permitido a los actores de amenazas desplegar múltiples ciberataques.
A continuación se presentan breves descripciones de las fallas reportadas, además de sus claves de identificación y puntuaciones asignadas según el Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
CVE-2022-22275: El procesamiento incorrecto del tráfico entrante HTTP/S desde WAN a DMZ permitiría a los actores de amenazas remotos evadir la política de seguridad hasta que se complete el protocolo de enlace TCP, desencadenando un ataque de denegación de servicio (DoS).
Esta es una falla de severidad media y recibió un puntaje CVSS de 5.1/10.
CVE-2022-22276: El servicio SNMP configurado permanece accesible para usuarios externos incluso si el SNMP está deshabilitado en las interfaces del firewall, por lo que los hackers maliciosos pueden conectarse al servicio SNMP, accediendo a información que de otro modo permanecería restringida.
La falla recibió un puntaje CVSS de 4.6/10.
CVE-2022-22277: SNMP-Reply incluye SSID Password en texto no cifrado, lo que permitiría a los atacantes remotos con capacidad para interceptar el tráfico de la red obtener acceso a datos confidenciales.
Este es un error de baja severidad y recibió un puntaje CVSS de 3.8/10.
CVE-2022-22278: Esta falla existe debido a que Content Filtering Service (CFS) en SonicOS devuelve un enorme mensaje “HTTP 403 forbidden” a la dirección de origen cuando los usuarios intentan acceder a recursos prohibidos por la función CFS.
Los actores de amenazas remotos pueden enviar múltiples solicitudes al sistema que desencadenan el error 403 y consumen todo el ancho de banda disponible, llevando a una condición DoS. La falla recibió un puntaje CVSS de 4.6/10.
Según el reporte, las fallas residen en todas las versiones de SonicOS entre 6.5 y 7.0.1.0-5030-1391.
Si bien esta vulnerabilidad podría ser explotada por actores de amenazas remotos no autenticados, hasta el momento no se han detectado intentos de explotación activa o la existencia de una variante de ataque relacionada con el ataque. Aún así, se recomienda a los usuarios de implementaciones afectadas aplicar los parches disponibles.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
GOOGLE, APPLE, META Y OTRAS COMPAÑÍAS TECNOLÓGICAS SON ENGAÑADAS POR HACKERS PARA ACCEDER A INFORMACIÓN CONFIDENCIAL DE MENORES; ACOSO SEXUAL Y EXTORSIÓN
Un informe de Bloomberg señala que múltiples compañías tecnológicas habrían sido engañadas para entregar información confidencial de sus clientes, lo que permitió desplegar campañas de extorsión y acoso contra menores de edad.
Los actores de amenazas enviaron solicitudes legales fraudulentas a compañías como Meta, Apple, Google, Snapchat, Discord y Twitter haciéndose pasar por agentes de la ley. Cabe mencionar que la legislación estadounidense permite a los agentes policiales solicitar información bajo control de las compañías tecnológicas con fines legales en casos urgentes o en los que se considere que estos datos podrían ser evidencia importante.
Los datos obtenidos se usaron para atacar a mujeres y menores de forma muy específica; en algunos casos, las víctimas fueron presionadas para crear y compartir material sexualmente explícito, recibiendo fuertes amenazas si se negaban a cooperar con los criminales.
No se agregaron más detalles sobre la forma en que los datos fueron utilizados, aunque las fuerzas del orden y las empresas de tecnología siguen tratando de evaluar el alcance de este problema, que ha incrementado considerablemente durante los más recientes meses.
Fuentes cercanas a las compañías afectadas aseguran que es complicado para el personal que recibe estas solicitudes separar las solicitudes legítimas de los potenciales engaños, ya que en realidad no parece haber diferencias entre los mensajes enviados por los agentes y los usados por los cibercriminales.
Al respecto, el antiguo director de seguridad de Facebook Alex Stamos mencionó: “Sé que estas solicitudes de datos se utilizan en emergencias reales que pueden poner vidas en riesgo, y es trágico que se abuse de este mecanismo para dañar la integridad de los usuarios”.
Stamos cree que las agencias del orden deben implementar mejores mecanismos de autenticación para evitar el compromiso de sus cuentas de correo, evitando así el principal vector para este tipo de ataques. Además, corresponde a las compañías tecnológicas implementar políticas de confirmación como un mecanismo para filtrar solicitudes potencialmente maliciosas.
Un portavoz de Google dijo que la compañía descubrió una solicitud de datos fraudulenta en algún momento de 2021, asegurando que se identificó al posible responsable y se notificó a las fuerzas del orden: “Trabajamos activamente con las fuerzas del orden y otros actores en la industria para detectar solicitudes de datos ilegales”.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
ESTACIONES DE CARGA PARA AUTOS ELÉCTRICOS EN REINO UNIDO SON HACKEADAS PARA MOSTRAR PORNOGRAFÍA
Cientos de conductores de vehículos eléctricos en la Isla de Wight, Inglaterra, fueron tomados por sorpresa cuando las pantallas de una estación de carga local comenzaron a mostrar contenido pornográfico a consecuencia de lo que parece ser un ciberataque contra GeniePoint, compañía que administra el punto de carga afectado.
Según un reporte, pantallas en el punto de carga debían mostrar contenido del sitio web oficial de GeniePoint, aunque después de que los bromistas hicieran de las suyas, estos monitores comenzaron a mostrar sitios web para adultos, con lo que los usuarios fueron expuestos a toda clase de contenido sexual explícito.
El consejo emitió inmediatamente una disculpa a todos los usuarios afectados por el incidente: “El consejo desea disculparse con cualquiera que haya encontrado el contenido web inapropiado y por cualquier inconveniente de los puntos de carga fuera de servicio”.
Los puntos de carga comprometidos se localizan en Quay Road, Ryde, Cross Street, Cowes y Moa Place. Además, al tratar de acceder al sitio web de la compañía, los visitantes también eran redirigidos a un sitio pornográfico. Este incidente no solo impidió a los propietarios de autos eléctricos cargar sus vehículos, sino que paralizó las tareas legítimas de los sitios web.
También se reportó que los puntos de carga comprometidos trabajaban de forma intermitente, desconectándose constantemente de los autos eléctricos: “Los puntos de carga pueden estar fuera de servicio por un corto período de tiempo antes de reiniciarse de forma remota, por lo que este podría ser el problema de que no funcione. Tomando nota del mal funcionamiento y el incidente, el consejo decidió reemplazar los puntos de carga por otros nuevos, lo que podría tomar un par de meses”, señala el reporte.
Con la proliferación de vehículos eléctricos y el ecosistema cargado de tecnología que fomentan, es fundamental que las organizaciones gubernamentales, empresas privadas, firmas de ciberseguridad e investigadores independientes tomen cartas en el asunto para mitigar estos ataques.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
YA PODEMOS PEDIR A GOOGLE QUE ELIMINE NUESTRO NÚMERO TELEFÓNICO, DOMICILIO, DIRECCIONES EMAIL Y OTROS DATOS DE CONTACTO PERSONAL DE LOS RESULTADOS DE BÚSQUEDA. APRENDA CÓMO HACERLO
Después de múltiples escándalos de manejo inapropiado de información personal, reforzar la privacidad de los usuarios se ha convertido en uno de los objetivos primordiales de las grandes empresas tecnológicas. Tal es el caso de Google, que acaba de anunciar la implementación de nuevas políticas que permitirán a los usuarios solicitar la eliminación de ciertos contenidos personales de los resultados en Búsqueda de Google.
Si bien ya era posible realizar estas solicitudes en casos de doxing o filtración de detalles bancarios, la actualización permitirá a los usuarios solicitar la eliminación de otros contenidos que aparecen en los resultados de búsqueda, incluyendo información de contacto personal. Google también permitirá la eliminación de información adicional que pueda representar un riesgo de robo de identidad, como credenciales de acceso a plataformas en línea.
Según el reporte, los siguientes registros podrán considerarse como información de contacto personal:
- Números de identificación gubernamentales, incluyendo números de seguridad social, claves de identificación fiscal y similares según el país en cuestión
- Números de cuentas bancarias y tarjetas de crédito
- Imágenes de firmas manuscritas
- Imágenes de documentos de identidad
- Registros médicos
- Direcciones físicas, números telefónicos y direcciones email
Sobre los procesos que se implementan al recibir una de estas solicitudes, Google asegura que se evalúa todo el contenido de los sitios web que pueden incurrir en la exposición de datos confidenciales, tratando de no limitar la disponibilidad de otros datos útiles para los usuarios. La compañía también analiza si el contenido que los usuarios desean eliminar forma parte de registros públicos o gubernamentales; de ser así, la solicitud es improcedente.
Aunque esta es sin dudas una buena noticia, los usuarios deben recordar que eliminar este contenido de los resultados en Búsqueda de Google, esto no removerá el contenido de Internet. Para ello, es necesario comunicarse directamente con los administradores del sitio web en cuestión.
Google sigue implementando cambios en sus políticas a fin de mejorar la experiencia en privacidad de sus usuarios. En días recientes se reveló la aplicación de una nueva medida para permitir a los usuarios menores de 18 años solicitar la eliminación de cualquier imagen suya de los resultados de búsqueda de imágenes. Los padres y tutores de los menores también podrán llevar a cabo este trámite.
La información completa sobre estas solicitudes y otras medidas de seguridad y privacidad implementadas por Google está disponible en los canales de comunicación oficiales de la compañía.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
CÓMO CAYÓ LA BANDA DE ESTAFADORES Y HACKERS COLOMBIANOS QUE ROBÓ EL DINERO DE MILLONES DE PERSONAS
Después de una compleja operación, la Policía Nacional de Colombia logró desmantelar una red cibercriminal responsable del hackeo sufrido por múltiples instituciones gubernamentales. Según el reporte, la operación estaba a cargo de un individuo identificado como Fabio Molina, quien ya ha sido arrestado.
Al respecto, el director de la Policía Nacional José Luis Vargas menciona: “Esta es una de las operaciones más importantes para la seguridad cibernética de Colombia en los últimos años. Con el material probatorio recolectado durante estos años se decidió que Molina es un peligro para la sociedad”.
Según Vargas, Molina y sus cómplices accedieron a información gubernamental registrada durante los últimos tres años mediante el uso de diversas herramientas de acceso remoto (RAT), infectando las computadoras afectadas y accediendo a contraseñas, emails, imágenes, escaneos, capturas de pantallas, archivos y bases de datos. Las autoridades encontraron más de 1,500 muestras de malware, lo que demuestra las capacidades de estos cibercriminales.

Las autoridades incautaron múltiples dispositivos, descubriendo que los hackers almacenaban más de 400,000 emails, incluyendo 116 mensajes enviados por Presidencia de la República. Molina y sus cómplices enfrentarán cargos por delincuencia organizada, uso de software malicioso, violación de datos personales y acceso no autorizado a sistemas informáticos protegidos.
Esta operación inició en 2019, cuando la Presidencia de la República presentó una denuncia relacionada con un correo electrónico malicioso desde una cuenta presuntamente controlada por la Fiscalía General de la Nación. Un empleado alertó a las autoridades y el Centro Cibernético de la Policía Nacional dio inicio a la investigación, que desentrañó una prolongada investigación y que finalmente ha dado sus frutos.
Las autoridades de Colombia siguen invirtiendo grandes recursos en el combate al cibercrimen. Durante 2021, la Policía Cibernética atendió más de 48,000 denuncias por posibles delitos cibernéticos, además de bloquear unos 150,000 intentos de ciberataques al año y más de 15,000 URLs vinculadas a posibles esquemas fraudulentos en línea.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VULNERABILIDAD DE ESCALADA DE PRIVILEGIOS Y EJECUCIÓN REMOTA DE CÓDIGO EN AZURE POSTGRESQL FLEXIBLE SERVER
Microsoft ha corregido una falla de seguridad en Azure PostgreSQL que podría haber sido explotada para la ejecución de código malicioso. El jueves, investigadores de Wiz publicaron un aviso sobre la vulnerabilidad, apodada como “ExtraReplica” y descrita como una “vulnerabilidad de base de datos entre cuentas” en la infraestructura de Azure.
Microsoft Azure es un servicio de nube híbrida y representa a cientos de miles de clientes empresariales. Según Wiz, se podría usar una “cadena” de vulnerabilidades para eludir el aislamiento de inquilinos de Azure, lo que evita que los clientes de los sistemas de software como servicio (SaaS) accedan a los recursos que pertenecen a otros inquilinos.
El vector de ataque central de ExtraReplica se basa en una falla que permitía a los atacantes acceder a las bases de datos de PostgreSQL sin autorización. Una vez que se ha seleccionado un servidor flexible PostgreSQL público objetivo, un atacante debe encontrar la región de Azure del objetivo “resolviendo el nombre de dominio de la base de datos y haciéndolo coincidir con uno de los rangos de IP públicos de Azure”, según el reporte.
Luego, se debe crear una base de datos controlada por el atacante en la misma región. La primera vulnerabilidad, que se encuentra en las modificaciones del motor PostgreSQL de Azure, se explotaría en la instancia controlada por el atacante, lo que llevaría a privilegios de “superusuario” escalados y la capacidad de ejecutar código.
El segundo error de la cadena, que reside en el proceso de autenticación del certificado, se activaría en la instancia de destino a través de la replicación para obtener acceso de lectura.
Si bien este ataque podría usarse en una subred, también se podría abusar de la fuente de Transparencia de Certificados para recuperar certificados SSL de dominio y extraer el identificador único de una base de datos, expandiendo así la superficie de ataque potencial más allá de una subred.
La vulnerabilidad fue revelada a Microsoft en enero, cuando sus equipos de seguridad analizaron la falla y pudieron replicarla. Wiz recibió un pago de $40,000 USD como recompensa por su informe. La falla fue corregida con éxito, por lo que ya no representa un peligro para los clientes de Microsoft; mejor aún, no se conocen casos de intento de explotación activa.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
EL NUEVO RANSOMWARE ONYX BORRA LOS ARCHIVOS EN LUGAR QUE CIFRARLOS; NO SERÁ FÁCIL RECUPERARSE DE ESTA INFECCIÓN
Especialistas en ciberseguridad han detectado una nueva operación de ransomware programada para la destrucción de archivos de más de 2 MB en lugar de cifrarlos, lo que impide que esta información sea recuperada aún si se paga el rescate. Esta nueva variante es conocida como Onyx y fue reportada por MalwareHunterTeam.
Al igual que otras operaciones de ransomware, los hackers de Onyx roban datos de las redes comprometidas antes de cifrar los dispositivos. Estos datos luego se utilizan en esquemas de “doble extorsión”, amenazando a las víctimas con publicar la información robada si no se realiza el pago del rescate.
Según la plataforma en dark web del ransomware Onyx, hasta el momento hay seis víctimas confirmadas.
Como se menciona anteriormente, la principal característica de este ransomware es la capacidad de eliminar archivos en lugar de cifrarlos. Las capturas de pantalla publicadas a continuación muestran que Onyx analiza el sistema en busca de archivos de menos de 2MB para su eliminación, aunque también puede eliminar permanentemente archivos de mayor tamaño:
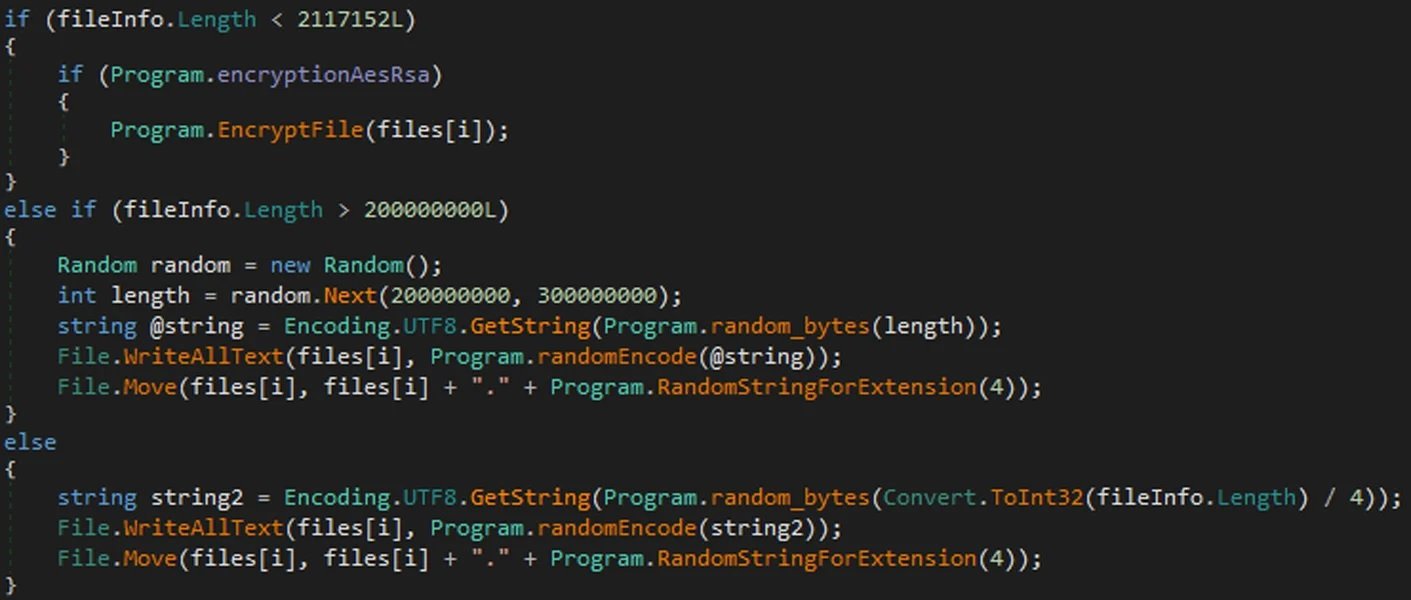
Como se trata de datos creados aleatoriamente y no cifrados, no hay forma de descifrar archivos de más de 2 MB de tamaño. Incluso si la víctima paga, el descifrador puede recuperar solo los archivos cifrados más pequeños.
Al respecto, el investigador forense Jiří Vinopal menciona que esta nueva variante está basada en el ransomware Chaos, que incluye la misma rutina de encriptación dañina y es un comportamiento completamente anticipado y programado por los hackers.
Debido a que este proceso es intencional y no un error, se recomienda a las víctimas de Onyx no pagar el rescate bajo ninguna circunstancia.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
VULNERABILIDADES DÍA CERO EN NETATALK AFECTAN PRODUCTOS NAS DE SYNOLOGY, QNAP Y WESTERN DIGITAL. PROTEJA SUS SOLUCIONES DE ALMACENAMIENTO ANTES DE QUE SEAN INFECTADAS CON RANSOMWARE
Diversos fabricantes de soluciones de almacenamiento conectado a la red (NAS) han alertado a sus clientes sobre la detección de vulnerabilidades críticas en Netatalk. La explotación de estas fallas fue demostrada en una de las más recientes versiones del evento de hacking ético Pwn2Own, y afectan a los dispositivos de fabricantes como Synology, QNAP y Western Digital.
La alerta de seguridad menciona que al menos seis de las fallas reportadas en Pwn2Own residen en Netatalk, el servidor de archivos de código abierto Apple Filing Protocol (AFP). Muchas de las fallas podrían ser explotadas de forma remota por actores de amenazas no autenticados, lo que comprometería por completo los dispositivos afectados.
A finales de marzo, los equipos de seguridad en Netatalk lanzaron parches para abordar siete vulnerabilidades, identificadas como CVE-2021-31439, CVE-2022-23121, CVE-2022-23122, CVE-2022-23123, CVE-2022-23124, CVE-2022-23125 y CVE-2022-0194.

La última actualización de Netatalk fue lanzada en diciembre de 2018, por lo que algunos fabricantes que recurren a esta solución asumieron que el proyecto ya no recibía mantenimiento. Tal es el caso de Western Digital, que lanzó actualizaciones de firmware para eliminar Netatalk; los productos Western Digital usan Netatalk para el acceso a recursos compartidos de red.
Netatalk comenzó a trabajar en las correcciones después de la demostración del ataque en Pwn2Own, por lo que QNAP determinó que algunos de sus propios productos NAS también podrían verse afectados. Esta semana, QNAP anuncio que las actualizaciones para su sistema operativo QTS estarían disponibles en los próximos días; mientras tanto, la compañía recomienda a los clientes deshabilitar AFP para mitigar el riesgo de explotación.
Por otra parte, Synology concluyó que estos errores podrían afectar a sus productos DiskStation Manager y Synology Router Manager. Mientras que ya hay una actualización disponible para DiskStation Manager, las soluciones Router Manager siguen sin recibir parches de seguridad.
Aunque hasta el momento no se han detectado intentos de explotación activa, es importante recordar que las implementaciones NAS son objetivo frecuente de los grupos cibercriminales, especialmente de operaciones de ransomware y robo de datos, por lo que es fundamental que las compañías corrijan estas fallas antes de que sea tarde.
Para conocer más sobre riesgos de seguridad informática, malware, vulnerabilidades y tecnologías de la información, no dude en ingresar al sitio web del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS).
GITHUB WAS HACKED. SOURCE CODE IS FILTERED FROM DIFFERENT REPOSITORIES
In its latest security report, GitHub confirmed that a group of threat actors are using OAuth tokens from legitimate users to download information from private repositories. The campaign was detected a week ago and dozens of compromised repositories have already been seen, which were using OAuth applications maintained by Heroku and Travis-CI.
Mike Hanley, GitHub’s chief security officer, confirmed the incident by mentioning that even the platform uses some of the affected apps: “Our analysis suggests that threat actors could be mining the contents of the downloaded private repository, to which the stolen OAuth token had access, in search of secrets that could be used to move to another infrastructure.”
The list of affected applications includes:
- Heroku Dashboard (ID: 145909)
- Heroku Dashboard (ID: 628778)
- Heroku Dashboard – Preview (ID: 313468)
- Heroku Dashboard – Classic (ID: 363831)
- Travis CI (ID: 9216)
GitHub’s security teams identified unauthorized access to their npm production infrastructure on April 12, when threat actors used a compromised AWS API key. This key could have been obtained by downloading some private npm repositories using the compromised tokens.
The tokens used for the attack were revoked when the platform identified the compromise. Hanley confirmed that the impact of the incident includes unauthorized access to private GitHub.com repositories, in addition to potential access to npm packages on its AWS S3 storage.
Even though threat actors could have stolen information from the compromised repositories, the platform has concluded that none of the packages were modified for malicious purposes: “npm uses an infrastructure independent of GitHub,” Hanley’s message ended.
Security teams on the platform are already working to notify affected users, in addition to maintaining an active investigation into the intrusion. To speed up the investigation, GitHub recommends users review their organizations’ audit logs, in addition to the security logs for each account to identify potential signs of attack.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
